Location, location, location
advertisement

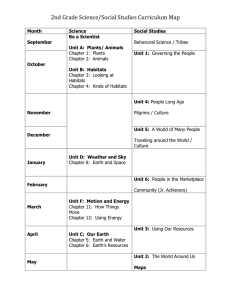
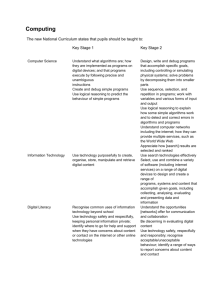
Theme - LOCATION, LOCATION, LOCATION Science History Geography Art DT Computing Year 1 Seasonal Changes observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies. Local study significant historical events, people and places in their own locality. Textiles to use a range of materials creatively to design and make products Year 2 Living things and their habitats explore and compare the differences between things that are living, dead, and things that have never been alive. identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including micro-habitats describe how animals obtain their food from plants and other animals, using the idea of a simple food chain, and identify and name different sources of food. Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, light, water, nutrients from soil, and room to grow) and how they vary from plant to plant investigate the way in which water is transported within plants explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. All living things recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways explore and use classification keys to help group, identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment. All living things (Plants) describe the differences in the life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird describe the life process of reproduction in some plants and animals Maps use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language (e.g. near and far; left and right) to describe the location of features and routes on a map use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key. UK name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage Structures build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable Algorithms understand what algorithms are; how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions Maps use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world UK name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time Textiles to improve their mastery of art and design techniques Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 All living things describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including micro-organisms, plants and animals give reasons for classifying plants and animals based on specific characteristics. Local Study a local history study (For example: one of the British areas of study listed above tracing how several aspects national history are reflected in the locality (this can go beyond 1066) history or a site dating from a period beyond 1066 that is significant in the locality.) create and debug simple programs use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs Structures apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures Algorithms Use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output