Perimeter and Area
advertisement

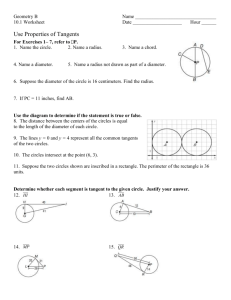
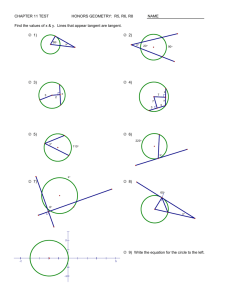
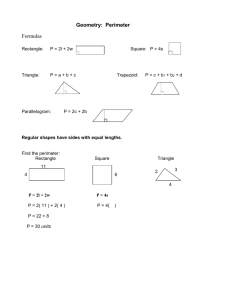
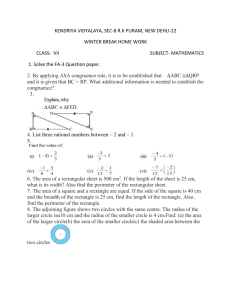
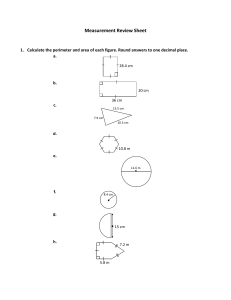
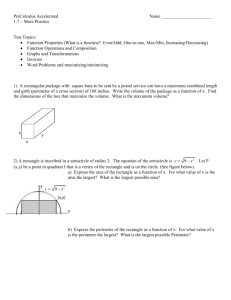
Perimeter and Area Please view this tutorial and answer the follow-up questions on loose leaf to turn in to your teacher. Definitions • Perimeter: The distance around the outside of a plane shape • Circumference: The distance around the outside of a circle • Area: The amount of space taken up by a plane shape Perimeter When you are finding the perimeter of a plane shape, you must add up the lengths of each side of the shape. 12 ft 16 ft 16 ft 12 ft Pick a starting point and then continue to work your way around the shape until all sides have been accounted for. Perimeter 12 ft I’ll choose the top left corner as my starting point. 16 ft 16 ft 12 ft 12 16 12 16 56 Perimeter 12 ft So the perimeter of this rectangle is 56 ft. 16 ft 16 ft 12 ft 12 16 12 16 56 Perimeter The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference. To find the circumference of a circle, you can use the following formulas: C 2 r or C d Let’s take a look at an example. Perimeter C 2 r 5 ft or C d Do we have the radius or the diameter? 5 is the radius so we can use the first formula. Perimeter C 2 r or C d Let’s use 3.14 for pi and 5 for the radius. 5 ft C 2(3.14)(5) C 31.4 ft Area The following is a list of formulas for basic plane shapes: 1 Triangle: A bh 2 Rectangle: A lw Square: A bh 1 A (b1 b2 )h 2 Parallelogram: Trapezoid: Circle: A r 2 As 2 Area First, let’s try to find the area of a triangle. 4 ft 6 ft 5 ft 1 A bh 2 We can always tell which values are the base and height because they will always meet at a right angle. Area First, let’s try to find the area of a triangle. 4 ft 6 ft 5 ft 1 A bh 2 In this case, 6 ft is the base of the triangle and 4 ft is the height. 1 A (6)(4) 2 2 A 12 ft Area Next up…a rectangle! 8 ft 10 ft 10 is the length and 8 is the width. Plug these values into the formula to find the area. A lw A (10)(8) A 80 ft 2 Area You can use the same formula to find the area of a square. 4 ft 4 ft A lw A (4)(4) A 16 ft 2 Area Or you can use the formula for a square. You’ll get the same answer for both. 4 ft 4 ft As 2 A4 2 A 16 ft 2 A lw A (4)(4) A 16 ft 2 Area Parallelograms are similar to rectangles, but you have to be careful to choose the correct values from the figure. You’ll need to find a base and height. 5m 11 m 7m Which values would you choose for the base and height? Area Since we know that base and height always meet at a right angle, we should choose 11 for our base and 5 for our height. A bh 5m 11 m 7m A (11)(5) A 55m 2 Area For a trapezoid, you’ll need to find two bases and a height. Look for two sides that are parallel and the length that connects them. 14 in Which two sides are parallel? 9 in 21 in Area The sides with lengths of 14 in. and 21 in. are parallel. They are connected by a height of 9 in. 14 in 9 in 21 in 1 A (b1 b2 )h 2 Plug these values into the formula to find the area of this trapezoid. Area The sides with lengths of 14 in and 21 in are parallel to each other. They are connected by a height of 9 in. 14 in 9 in 21 in 1 A (b1 b2 )h 2 1 A (21 14)(9) 2 A 157.5in 2 Area To find the area of a circle, you’ll need to find the radius of that circle. What is the value of the radius in this circle? 6 cm Since 6 is the diameter, we need to divide it by 2 to find the radius. Area To find the area of a circle, you’ll need to find the radius of that circle. So, the radius is 3. 6 cm Plug this value into the formula to find the area for this circle. Area To find the area of a circle, you’ll need to find the radius of that circle. HINT: Use 3.14 for π. A r 2 A 3.14(3 ) 2 6 cm A 28.26cm 2 Follow-Up Questions Answer the following questions on loose leaf and hand them in to your teacher. Follow-Up Questions 1) Find the perimeter of each figure. a) c) 17 m 13 cm 5 cm 23 m 12 cm b) 9 ft d) 8 in 4 ft 6 ft 4 ft 15 ft Follow-Up Questions 2) Find the area of each figure. a) c) 14 m 12 cm 15 cm 14 m 18 cm b) 11 in 9 ft d) 4 ft 6 ft 4 ft 15 ft