Year 11 Chemistry Prac Test 2011
advertisement

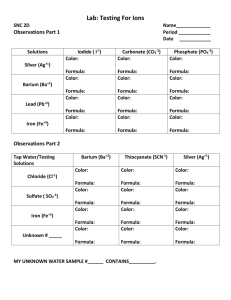
Name: ___________________ Year 11 Chemistry – 2011 Practical Assessment Task 1 Station 1: (20 marks) Equipment: A copy of the SI Chemical Data book The following question is on PROPERTIES OF THE ELEMENTS. The answers are to be found on pages 6 - 13 of the SI Data Book. Page 5 explains the symbols used. 1a) Name any 3 elements that are liquid at 1000C. 1b) (i) Draw up a table to include the Atomic Numbers and the melting points of the following elements: Graphite (carbon); Silicon; Germanium; Tin (white) and Lead. (ii) comment on one trend found in your data (iii) Name one general characteristic which these elements have in common and one in which they differ. 1c) Find Page 10. Show the symbol and name the element that has a ‘cubic’ structure. 1d) Name one metallic element which when solid, floats on water. Turn to Pages 14 - 15. You will find explanations for the symbols found in the PROPERTIES OF INORGANIC COMPOUNDS section. Use this information for Question 2 only. 2a) The solubility of a substance is the maximum amount of the substance (in grams) that would dissolve in 100g, of water. Calculate the maximum amount of Potassium chlorate that would dissolve in 25 g. of water. Show your working. 2b) Name a compound of Silicon that has a relative molecular mass between 100 and 110. 3) You are given a mixture of Magnesium sulfate and Barium sulfate and told to carry out a gravimetric analysis of this mixture. All you know about these two chemicals is that: (i) they are white crystalline substances (ii) Magnesium sulfate is soluble and Barium sulfate is not. (a) Identify the property you can use to separate the mixture. (b) Write down the steps you could follow to carry out the gravimetric analysis of this mixture. (c) Use the following data to calculate the % composition of each of the two chemicals making up the mixture. total mass of barium sulfate + magnesium sulfate solution + beaker mass of beaker mass of dried magnesium sulfate mass of dried barium sulfate = 169.79 g = 145.65 g = 7.39 g = 1.25 g Station 2: (10 marks) – Properties of Elements At this station you are provided with: two elements A and B; a liquid X; a test-tube rack with large test tubes; a small measuring cylinder and equipment to set up an electrical circuit. Experiment 1 Place 10 mL of liquid X in a large test tube Add a strip of element A to the liquid in the test tube Observe the reaction and write down two pieces of evidence to show that a chemical reaction has taken place. Experiment 2 Use the equipment provided to test sample A and B for electrical conductivity Examine both elements for lustre (how shiny they are) and for malleability (a) Put your results in table form. (b) A student decided that element B was aluminium. (i) Write the electron configuration of aluminium (ii) Write an equation to show the formation of an ion of aluminium (iii) State one use of aluminium and a property that makes it suitable for that use. (c) A sample of Aluminium contains 55% Aluminium-26 and 45% Aluminium-28. Calculate the atomic mass of Aluminium from this sample. Station 3: (10 marks) – ‘Bonding’ exercise At the teacher’s desk, there are 2 models: A and B 1) Which model, A or B represents an element? 2) Describe the bonding in each model. 3) Name one property for each of the substances represented. State how each property relates to its bonding. 4) Use the kits provided to make accurate models of CO2 and CH4. Show both these models to your teacher before you break them up again. (Key: Carbon = black Hydrogen = white Oxygen = red)