Fall09_Kim_Sam_Austi..
advertisement

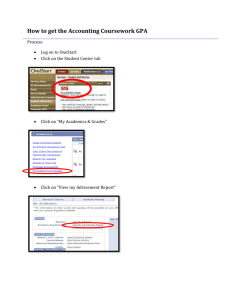
Kim Allen, Sam O’Flaherty, and Austin Schantz Design Front View NOTE: All dimensions are in inches 3D Conceptual Design Side View Top View Force Calculations Force Calculations Continued Known values Fp=250 lbs W=575 lbs FS=3 FS=3 Calculated Values Fw=127.63 lbs FB=447.37 lbs Force Calculations Continued Max Deflection=.1 inch From this Max strain εmax-B=.025 εmax-w=.004545 If FB=447.37 lbs Then σB=FB/A=1.553 psi EB= σB/ εmax-B=61.32 psi=.000422787 GPa If Fw=127.63 lbs Then σw=Fw/A=7.977 psi Ew= σw/ εmax=1755.12 psi=.0121GPa Composite Design Theoretical Values Initial Values E1 (GPa) E2 (GPa) G (GPa) ν S-Glass Fiber/Epoxy 52.6 17.1 5.25 0.28 Closed Cell Foam Core .689476 .689476 .27579 0.3 Calculated Values E1 (GPa) E2 (GPa) G (GPa) ν In-Plane Load 3.66 1.65 0.56 0.29 Bending Load 9.09 3.37 1.08 0.28 Note that the Emax =.0121 GPa. This composite lay-up should hold Test Section Small section with same material layup as project Planned Use: Find the maximum compressive and torsion load the layup could withstand Actual Use: Identify the difficulties in manufacturing and bagging a 3-D project Manufacturing Foam Core Construction Hot Wire Drilling the hole for the axle Sanding Foam Core Laying Up the Foam with Glass Fiber Composite The Big Wheel Bagged and ready for vacuum curing Beginning the Lay-up Attaching Front yoke and Preliminary Testing Drilling Holes for Bolts Making sure it holds our weight Adjusting Yolk Making Sure it Moves Smoothly Making Sure it moves and can hold extra weight Final Product Testing Testing Plan Ride around a parking lot Basic turns Riding up a small ramp Test completed 3 times Results Tests completed successfully Withstood pull-up and torsion forces Conclusion Successes Weight rated for an adult rider Withstood forces Project completed!!!!! Failures Pedals slip within the hub limiting acceleration Metal components added significant weight Test section not suitable for analysis QUESTIONS?