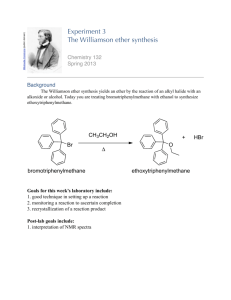
c) Give chemical formulas for the following polyatomic ions: [2]
advertisement
![c) Give chemical formulas for the following polyatomic ions: [2]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010095060_1-7266f37817152cd723b8025a3ccf36ba-768x994.png)
Section A; Multiple choice: 30 points (1 each): Answer each of the following multiple choice questions on the computer card provided by shading (be sure this is dark enough) the letter (A, B, C, or D) that corresponds to the best response in each case. A1) Which of the following acid-base combinations would be buffers? a) b) c) d) H2SO4, HSO4HF, CNH2CO3, HCO3HClO3, ClO3- (Need a weak acid/conjugate base combination) A2) Blood has an osmolarity of 0.30 M. Which of the following solutions/liquids would be isotonic with blood? a) b) c) d) 0.15 M NaCl (osmolarity = molarity * i; here, i = 2) 0.30 M NaCl 0.20 M C6H12O6 Water A3) According to VSEPR theory, when there are three electron groups present around a central atom, the angle between any of those groups is a) 180o b) 120o c) 109.5o d) 60o A4) According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, the average kinetic energy of all particles in a system depends on the a) b) c) d) number of gas molecules in the container molar mass of the gas number of collisions per unit time absolute temperature of the gas A5) Which of the following is a weak acid? a) b) c) d) HCN H2SO4 HCl HClO3 (All others listed are strong) A6) The lowest energy subshell in any electron shell is the ___ subshell a) b) c) d) S p d f (s<p<d<f) A7) For the following reaction, [N2O4] = [O2] = 1.5 M; [N2] = 4 M at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant would have a value of N2O4(g) N2(g) + 2O2(g) a) b) c) d) 9 4 0.17 6 A8) What is the degree of uncertainty in measurement that can be provided by the following ruler? a) b) c) d) 0.1 mm 1 mm 1 cm 10 cm (1/10th of the smallest graduation) A9) The bond having the highest dipole moment in the list below is a) b) c) d) C-F N-O H-C S-O (biggest different in electronegativities) A10) How many electrons could be held in the orbitals that are contained in the second energy shell? a) b) c) d) 2 3 6 8 (2 in 2s orbital; 6 more in the 2p orbitals) A11) In the series of structures shown below, which one is an acid? (c: others don’t have a polar H-X bond) .. .. .. .. .. .. .. a b .. . . .. c .. .. .. .. . . .. d A12) If 1g of KClO4 is dissolved in 1 L of water, the resulting mixture will be a) b) c) d) acidic basic conductive called a suspension (cation isn’t acidic; anion isn’t basic; not a suspension if it dissolves) A13) An unlabeled bottle contains an aqueous solution of a sodium salt whose anion is either S2-, NO3-, C2H3O2-, or SO42- . When a solution containing Ba2+(aq) is added, a yellow solid is produced. The (salt) must be a) b) c) d) Na2S NaC2H3O2 NaNO3 Na2SO4 (check solubility rules at back of exam) A14) In an acid-base titration, HCl is used to titrate 10.0 mL of 2.5 M Ca(OH)2. It takes 20.0 mL of the acid to reach the end point. What is the concentration of HCl in this experiment? a) b) c) d) 5.0 M 1.3 M 2.5 M 10 M A15) Which one of the following quantities are not affected by temperature? a) b) c) d) Density reaction rate %(m/v) %(m/m) (temperature affects volume – see: thermal expansion) (absolute temperature affects reaction rate) (temperature affects volume) (mass is not affected by temperature) A16) Which species is isoelectronic with O? a) b) c) d) Mg2+ NSe2Ne A17) Which of these molecules/ions is flat? a) b) c) d) CH4 NO3NH4+ NH3 (tetrahedral) (trigonal planar) (tetrahedral) (trigonal pyramid) A18) Earlier this year, I carried out a demonstration that involved pouring liquid nitrogen onto a balloon. The scientific law that pertained to the experiment is a) b) c) d) Charles’s Law (volume is proportional to abs. temperature at constant P, n) Boyle’s Law Dalton’s Law Murphy’s Law A19) Which of the following is not a colligative/colloidal property of solutions? a) b) c) d) vapor pressure boiling point elevation hydrogen bonding osmotic pressure A20) Which of the following is amphiprotic? a) b) c) d) H3O+ H2O HCl NH3 (see class notes) A21) Which of the following processes is an exothermic change of state? a) b) c) d) sublimation freezing evaporation melting (heat is a reactant) (heat is a product) (heat is a reactant) (heat is a reactant) A22) The activation energy for the reaction R P is indicated by the energy difference labeled ___ in the diagram shown to the right. a) b) this one c) d) A23) Two liquids (ethanol and dimethyl ether) are studied to determine their boiling points. Ethanol is a polar substance and dimethyl ether is non-polar. They also have the same number of C, H, and O atoms in their formulas. It would be expected that a) b) c) d) Ethanol would have a higher vapor pressure than dimethyl ether Dimethyl ether would have a lower boiling point than ethanol Dimethyl ether would have a higher vapor pressure than ethanol (b & c mean the same thing) Ethanol would be more volatile than dimethyl ether A24) In which of the following substances would London forces be the strongest? a) b) c) d) Ar Kr Xe Rn (London forces increase with molar mass) A25) When the temperature of 5.0 L a gas is changed from 10 oC to 20 oC, the volume of the gas becomes a) b) c) d) 2.5 L 10 L 0.19 L 5.2 L (volume change is proportional to absolute temp. change) A26) A solution that is added to red blood cell (r.b.c.) fluid is found to cause the red blood cells to swell, and eventually, burst. The solution that was added a) b) c) d) has a lower osmotic pressure than r.b.c. fluid caused crenation of the red blood cells is isotonic with r.b.c. fluid is hypertonic A27) Lead belongs to which elemental grouping? a) b) c) d) metals non-metals noble gases metalloids A28) Which of the following molecules is not linear? a) b) c) d) CO2 HF CS2 SF2 (a double bond between C and each O: two electron groups linear) (anything with two atoms must have linear molecular geometry) (very much like CO2) (Lewis structure similar to H2O: bent) A29) How many milliequivalents are present in 10 mL of 2.0 M K2SO4? a) b) c) d) 60 20 80 10 A30) Which of the following solutions would be expected to have the highest osmotic pressure? a) b) c) d) 2 M K3PO4 4 M NaCl 3 M C6H12O6 3 M Na2CO3 (osmolarity = 2M x 4 = 8M) (osmolarity = 4M x 2 = 8M) (osmolarity = 3M x 1 = 3M) (osmolarity = 3M x 3 = 9M) Section B; Problems: 70 points (7 questions @ 10 points each): Answer each of the following questions in the space provided. B1) “TUMS” is a drugstore remedy for acid indigestion and primarily contains the base, CaCO3. a) Write an equation for the reaction of “TUMS” with gastric juice (aqueous HCl). [2] 2HCl + CaCO3 CaCl2 + 2H2CO3 b) What is the H3O+ concentration in a solution that has a pH = 1.38? [3] [H3O+] = 10-pH = 10-(1.38) = 0.042M c) What is the OH- concentration in this same solution? [3] [𝐻3 𝑂+ ][𝑂𝐻 − ] = 1𝑥10−14 1𝑥10−14 = [𝑂𝐻 − ] = 2.39883 … 𝑥10−13 0.041686938 … [𝑂𝐻 − ] = 2𝑥10−13 𝑀 d) Two acids (HA and HX) have acid ionization constants of Ka = 10-5 and Ka = 10-8, respectively. Which is the stronger acid? [2] Answer = HA Notes: larger Ka means stronger acid. B2a) Drunk driving and its consequences are major social, economic, and medical problems. In Nova Scotia, a person with a blood alcohol concentration of 0.080 % (v/v) is considered legally impaired. What volume (mL) of pure alcohol does this concentration represent, assuming a person’s total blood volume is 5.0 L? [4] 𝑣 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 %( ) = ( ) 𝑥100% 𝑣 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 0.08% = ( ) 𝑥100% 5000𝑚𝐿 0.08% 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 =( ) 100% 5000𝑚𝐿 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 8𝑥10−4 = ( ) 5000𝑚𝐿 4𝑚𝐿 = 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 b) A saline solution is 0.90 %(m/v) NaCl. What is the molarity of this solution? [3] 𝑚 𝑔 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 %( ) = ( ) 𝑥100% 𝑣 𝑚𝐿 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 100 mL of this solution would have 0.90g of solute (NaCl, 58.44 g/mol): 0.90𝑔 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 1000𝑚𝐿 ( )( )( ) = 0.15𝑀 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 100𝑚𝐿 𝑠𝑜𝑙′𝑛 58.44𝑔 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 1𝐿 c) How many milliequivalents would 250 mL of this solution provide? [3] B3a) A helium-filled balloon has a volume of 10.0 L at 27oC and a pressure of 663 mm Hg. What volume, in liters, will the balloon occupy at an altitude where the pressure is 96 mm Hg and where the temperature is -30.0oC? [4] 𝑃1 𝑉1 𝑃2 𝑉2 = 𝑇1 𝑇2 𝑃1 𝑉1 𝑇2 = 𝑉2 𝑇1 𝑃2 (663𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔)(10.0𝐿)(243𝐾) = 𝑉2 = 55.94 … 𝐿 = 56𝐿 (300𝐾)(96𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔) b) At 20oC, in a 5.00L container, a mixture of He, Ne, and Ar gases has a pressure of 12.00 atm. What is the partial pressure of the Ne, given that the ratio by moles of He:Ne:Ar is 3:2:1. [2] Dalton’s Law: for a mixture of gases, the total pressure of the gases in the mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. If a gas mixture is 2 parts Ne in a total of 6 parts (3+2+1), this is the same things as saying the mixture is 2/6 (or 1/3) Neon. So the partial pressure of Ne in the mixture is 1/3 of 12 or 4.00 atm. In fact, the pressures of the gases in the 3:2:1 He:Ne:Ar mixture are 6.00 atm, 4.00 atm, and 2.00 atm. c) How many moles of Ar are contained in the flask? [4] 𝑃𝑉 = 𝑛𝑅𝑇 𝑃𝑉 (2.00𝑎𝑡𝑚)(5.00𝐿) =𝑛= = 0.416𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐴𝑟 𝐿. 𝑎𝑡𝑚 𝑅𝑇 (293𝐾) (0.0821 ) 𝑚𝑜𝑙 . 𝐾 Notes: Just use the partial pressure of Ar here (not the total pressure). Again, need to convert Celsius to Kelvin before using the equation. B4a) What is the pH of a solution consisting of 40.02 g of HF and 41.99 g of NaF in a 1.00 L volume? (pKa for HF = 3.17) [4] b) Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when NaOH is added to this solution. [2] The NaOH (a base) reacts with the buffer’s acid component (HF): NaOH + HF NaF + H2O c) Give examples (formulas) of a strong electrolyte and a non-electrolyte, and names for each. [4] Strong electrolyte ________________________ Name: __________________________ Weak electrolyte ________________________ Name: __________________________ B5) The atoms in acetic acid are connected as shown in the structure below. a) Complete the structure to transform it to a proper Lewis structure. [3] b) Indicate the molecular geometry around each of the indicated “central” atoms in the molecule. [6] c) Is the acetic acid molecule, as a whole, polar or non-polar? [1] (polar – the O-H bond and C=O bond have electronegativity differences of > 0.4) Notes: add up the total number of electrons in the formula HC2H3O2: 24 total electrons. Each bond costs 2e-, so there are 10 (24 – 14) electrons that can be used to complete octets for the structure above (there are 7 bonds already drawn in the structure shown above). If you complete the octets on the oxygens (cost = 10e-), that leaves a structure where the carbon still does not have an octet: The bottom O must share a pair of electrons with C to make a double bond, to get this structure: B6a) List four factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction: [4] i) ii) iii) iv) concentration of the reactant temperature presence of a catalyst surface area of the reactants b) For the reaction shown below, indicate the reducing agent: [1] 3H2S(g) + 2HNO3(aq) 3S(s) + 2NO(g) + 4H2O(l) Reducing agent: H2S; oxidizing agent: HNO3. c) What is the oxidation number for N in HNO3? [1] Answer = __+5___ d) In the equilibrium shown below, indicate the effect (e.g. “shift-to-right”) of each change that is made to the reaction contents: [4] NiO(s) + CO(g) Ni(s) + CO2(g) i) ii) iii) iv) Add CO(g) to mixture: Increase the temperature of the reaction: Decrease the volume of the container: Add N2(g) to the mixture: (endothermic) _shift to right_______ _shift to right_______ _ no effect _________ _ no effect _________ B7a) A mixture of hydrazine and hydrogen peroxide is used as fuel for rocket engines. The two substances react according to the equation below: N2H4 + 2H2O2 N2 + 4H2O What mass of N2H4 is needed to produce 1.51 x 1024 molecules of N2? [6] The molar mass of N2H4 is 32.06g/mol, so using dimensional analysis: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑁2 𝐻4 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁2 𝐻4 32.06𝑔 𝑁2 𝐻4 1.51𝑥1024 𝑁2 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑒𝑠 ( )( )( ) = 80.4𝑔𝑁2 𝐻4 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑁2 6.02𝑥1023 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁2 𝐻4 b) Write out the full electron configuration (no noble gas shortcut this time) for arsenic. [2] As: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3 Note: The chemical symbol for arsenic is not Ar. (This is argon.) c) Give chemical formulas for the following polyatomic ions: [2] hydronium: _H3O+_ nitrate: _NO3-_ HOORAY!! BONUS QUESTION!!!! [1] Who is the handsome devil pictured to the right? (Hint: it’s not Justin Bieber) Answer: _Avogadro_