8th Alg LF Jan 11
advertisement

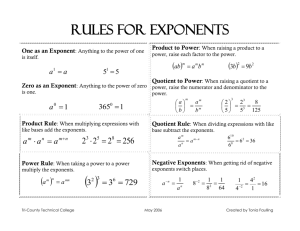
FRAME THE LESSON Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize Supporting TEKS: A.10 (A) add and subtract polynomials of degree one and degree two A.10 (B) multiply polynomials of degree one and degree two A.10(C) determine the quotient of a polynomial of degree one and polynomial of degree two when divided by a polynomial of degree one and polynomial of degree two when the degree of the divisor does not exceed the degree of the dividend A.10 (D) rewrite polynomial expressions of degree one and degree two in equivalent forms using the distributive property A.10 (F) decide if a binomial can be written as the difference of two squares and, if possible, use the structure of a difference of two squares to rewrite the binomial Readiness TEKS: A.10 (E) factor, if possible, trinomials with real factors in the form ax2 + bx + c, including perfect square trinomials of degree two A.11 (B) simplify numeric and algebraic expressions using the laws of exponents, including integral and rational exponents Process TEKS: A.1A, A.1B, A.1C, A.1D, A.1E, A.1F, A.1G TEACHER: Algebra I 8th Math CLASS: LESSON DATE: Jan 11-15, 2016 Unit 6: Laws of Exponents, Expressions and Factoring 3rd 6 Weeks Teaching Points & Activities: Unit Rates, Constant Rates of Change & Constant of Proportionality Engage: Monday Explore: Pearson 5.1 “Zero and Negative Exponents”, pg. 476-488. Explain: Use the 5 steps to teach the 5 E’s of the lesson process. Wednesday Thursday Friday Pearson 5.2, “Multiplying Powers with the Same Base”, pg. 489-501. Pearson 5.3, “More Multiplication Properties of Exponents”, pg. 502-513. Pearson 5.4, “Division Properties of Exponents”, pg. 514-525. Pearson 5.5, “Rational Exponents and Radicals”, pg. 526-536. Use the 5 steps in Pearson to teach the 5 E’s of the lesson process. Use the 5 steps in Pearson to teach the 5 E’s of the lesson process. Use the 5 steps in Pearson to teach the 5 E’s of the lesson process. Elaborate: Use the 5 steps in Pearson to teach the 5 E’s of the lesson process. The Student will simplify numeric and algebraic expressions using the laws of exponents, including integral and rational expressions. The student will combine like terms and multiply and divide using the laws of exponents. Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: Step 3 is the lesson check in each lesson. You can use these to differentiate learning and group students accordingly in order to maximize the learning experience. Step 5 is the Evaluate Assess and Intervene in each lesson. You may also opt to have students take the Lesson Quiz through PearsonTexas.com. The Quiz will be automatically scored, and appropriate remediation, practice, or enrichment will be assigned based on student performance. Week 18 Resources: Tuesday Assess Student learning & assign remediation. Pearson Algebra I Teacher Resource Download Center TI-84 Calculators Pearson Texas.com Virtual Nerd Tutorials Homework and Tutorials App. Online Assessment Evaluate: TX EOC Practice Stop & Check for Understanding—High Level Questions Critical Writing Prompt: Do the rules for multiplying negative integers apply to simplifying negative exponents? Explain. Have students complete the Writing Prompts in the Student Companion to evaluate their problem-solving model. ELPS: (4) (F), (3) (G), (3) (D) Objective/Key Understanding: M T W TH F How do you know that an algebraic expression with a negative exponent is in simplest form? Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: Interactive Exploration, pg. 478. Rigor & Relevance: (Real World How can a table of exponential expressions help you understand the properties of zeros and negative exponents? Vocabulary: Base Reciprocal Factor Index Radical expression exponent simplest form scientific notation nth root radicand zero property identity simplify radical square root negative exponent exponential expression simplified form principal square root Connection) Positive exponents are a notation for repeated multiplication. Students should understand that negative exponents are a notation for repeated division. Scientific notation was developed to make very large and very small numbers accessible. Use your calculator to see large of a number you can input using scientific notation and without using it.