wrist-3
advertisement

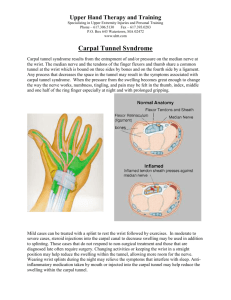
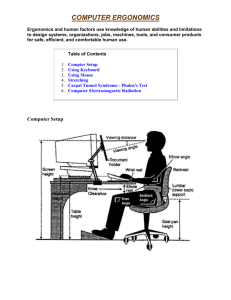
Kinesiology PED 2440 The Wrist Exercises and Injuries Exercises Wrist curls Squeezing tennis balls www.bodybuilding.com Scaphoid Fractures Scaphoid fractures account for about 60 percent of all wrist (carpal) fractures. They usually occur in men between ages 20 and 40 years, and are less common in children or in older adults. The break usually occurs during a fall on the outstretched wrist. It’s a common injury in sports and motor vehicle accidents. • • The angle at which the wrist hits the ground determines the injury. If the wrist is extended at a 90-degree angle or greater, the scaphoid bone will break; if the angle is less than 90 degrees, the lower arm bone (radius) will break. Scaphoid Fractures Signs and symptoms Pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist. Motion (gripping) may be painful. May be some swelling on back and thumb side of wrist. Pain may subside, then return as a deep, dull aching. Marked tenderness to pressure on the "anatomical snuffbox," a triangularshaped area on the side of the hand between two tendons that lead to the thumb. Scaphoid Fractures The scaphoid is more susceptible to injury than any of the other carpal bones because of its unique position bridging the proximal and distal rows of the carpal bones. This frequency is due to a tenuous blood supply, with only one dorsoradial artery to the proximal pole, which results in a nearly 100% incidence of avascular necrosis in proximal fractures and a 30% incidence in distal fractures. Any tenderness in the anatomic snuffbox over the dorsal scaphoid (figure 1b) should prompt treatment as for a fracture. Scaphoid Fractures Arthritis of the Wrist • Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive condition that destroys the smooth articular cartilage covering the ends of bones. The bare bones rub against each other, resulting in pain, stiffness and weakness. OA can develop due to normal "wear-and-tear" on the wrist or as a result of a traumatic injury to the forearm, wrist or ligaments. • Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disease that affects the joint linings and destroys bones, tissues, and joints. Rheumatoid arthritis often starts in smaller joints, like those found in the hand and wrist, and is symmetrical, meaning that it usually affects the same joint on both sides of the body. Arthritis of the Wrist • Signs and symptoms OA of the wrist joint manifests with swelling, pain, limited motion and weakness. These symptoms are usually limited to the wrist joint itself. RA of the wrist joint usually manifests will swelling, tenderness, limited motion and decreased grip strength. In addition, hand function may be impaired and there may be pain in the knuckle joints (metacarpophalangeal or MP joints). Joint swelling may also put pressure on the nerves that travel through the wrist. This can cause a lesion to develop (compression neuropathy) or lead to carpal tunnel syndrome. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Osseofibirous canal -osseo = bones -fibro = ligament One nerve Nine tendons 1. Carpal Bones 3. Median Nerve 2. Transverse Carpal Ligament 4. Nine Flexor Tendons - 4 flexor digitorum superficialis - 4 flexor digitorum profundus - 1 flexor pollicis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 1. Scaphoid 2. Lunate 3. Triquetrum 4. Pisiform 5. Trapezium 6. Trapezoid 7. Capitate 8. Hamate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome “Medial wall” – Pisiform and Hamate “Lateral wall” – Scaphoid and Trapezium “Floor” – Lunate, Triquetrum, Trapeziod and Capitate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Transverse Carpal Ligament Trapezium Hamate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms Pain and numbness in 13 fingers and half of the 4th or ring finger Symptoms do not include palm or little finger Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pathology “a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve with the carpal tunnel” Causes Genetics Lifestyle (diabetes, gout, arthritis, pregnancy, and alcoholism are risk factors) Repetitive motion. Keyboard, rock climbing, tennis, Trauma Pressure inside the tunnel can double with CTS Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pressure on median nerve Overuse of flexor muscles Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Modification in activities Table height, wrist angle, elbow angle 10-15 minute breaks Exercises and warm-up wrist flexor muscles Flex fingers tightly then extend and abduct fingers for 5 seconds With arms extended, flex and extend wrist several times followed by circumduction of the wrist Removable wrist brace Anti-inflammatory medicines NSAID Cortisone Surgery – carpal tunnel release Scare tissue Questions?