Shoulder &Upper arm Physical Examination Babak Vahdatpour MD
advertisement

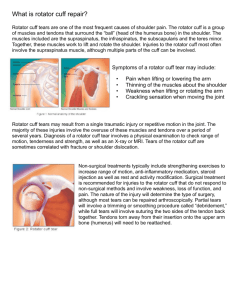
In the name of GOD Sheikhlotfolah mosque Shoulder &Upper arm Physical Examination Babak Vahdatpour MD Assistant professor Department of Physical Medicine & Rehab. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences DDx. of Shoulder Pain or reduced R.O.M • • • • • • • • • Rotator Cuff Dis. Adhesive Capsulitis Calcific Tendonitis Dynamic Functional Instability A.C Degenerative Joint Dis. Glenohumeral Degenerative Joint Dis. Arthropathy(crystalline & Rheumatoid) Cervical Radiculopathy Tumors(shoulder girdle & lung apex) Physical Examination • • • • • • inspection palpation range of motion strength provocative shoulder test neck & elbow Inspection • • • • • • • • both shoulders exposed inspection of both shoulders swelling asymmetry muscle atrophy scars ecchymosis venous distension Inspection • squaring of the shoulder → anterior dislocation Swollen subacromial bursa in R.A Rupture of the left pectoralis major tendon. Inspection Fractured left clavicle. Swollen sternoclavicular joint due to a fracture of the medial end of the left clavicle • scapular "winging" → shoulder instability serratus anterior dysfunction trapezius dysfunction • Rupture of the long head of the biceps tendon (arrow). Inspection • atrophy of the supraspinatus or infraspinatus → rotator cuff tear suprascapular nerve entrapment neuropathy Palpation • tenderness • deformity 1.subacromial space → rotator cuff tendinitis impingement syndrome calcific tendinitis rotator cuff tear 2.bicipital groove → bicipital tendinitis bicipital tendon subluxation, tear 3.acromioclavicular joint 4.anterior glenohumeral joint → glenohumoral arthritis osteonecrosis glenoid labrum tear adhesive capsulitis 5.sternoclavicular joint 6.posterior edge of acromion → rotator cuff tendinitis calcific tendinitis rotator cuff tear 7.suprascapular notch → suprascapular nerve entrapment 8.Quadrilateral space → axillary nerve entrapment Range of Motion testing • compared with the unaffected side • active & passive : loss of active motion alone → weakness of muscle than joint ds : LOM with both active & passive Ex → arthropathies adhesive capsulitis Range of Motion testing • Flextion & Extension • Abduction & Adduction (scapulohumeral rhythm) • Internal rotation & External rotation • Scapular Retraction & Protraction Apley scratch test Painful arc of abduction. Passive shoulder abduction Shrugging of the scapula to increase abduction (right shoulder) Measurement of rotation in 90° abduction. A, Neutral position. B, External rotation. C, Internal rotation. Muscle testing • • • • • Scapular stabilizers Rotator cuff Humeral Adductor/Internal Rotators Humeral Abductors Elbow Flexors & Extensors Scapular stabilizers – Serratus ant. – Rhomboids – Trapezius Evaluating the Rotator cuff • supraspinatus infraspinatus teres minor subscapularis • pain • weakness Supraspinatus • "empty can" test (Jobe test) FIGURE 3. Supraspinatus examination ("empty can" test). The patient attempts to elevate the arms against resistance while the elbows are extended, the arms are abducted and the thumbs are pointing downward. Infraspinatus and Teres minor FIGURE 4. Infraspinatus/teres minor examination. The patient attempts to externally rotate the arms against resistance while the arms are at the sides and the elbows are flexed to 90 degrees Subscapularis & other int. rotators Humeral Adductor/Internal Rotators • Pecturalis Major • Latissimus Dorsi Humeral Abductors • Deltoid • Supraspinatous Elbow Flexors & Extensors • • • • Biceps Brachialis Brachioradialis Triceps Provocative test Neer's test(sign) • subacromial impingement • impingement test : injection FIGURE 5. Neer's test for impingement of the rotator cuff tendons under the coracoacromial arch. The arm is fully pronated and placed in forced flexion. Hawkin's test • subacromial impingement • rotator cuff tendonitis FIGURE 6. Hawkins' test for subacromial impingement or rotator cuff tendonitis. The arm is forward elevated to 90 degrees, then forcibly internally rotated. Drop-arm test • rotator cuff tear • supraspinatus dysfunction O`Brien test A.C joint or labrum injury Cross-chest test • acromioclavicular joint dysfunction FIGURE 7. Cross-arm test for acromioclavicular joint disorder. The patient elevates the affected arm to 90 degrees, then actively adducts it. Ant. Apprehension • ant. instability FIGURE 8. Apprehension test for anterior instability. The patient's arm is abducted to 90 degrees while the examiner externally rotates the arm and applies anterior pressure to the humerus. Relocation & Release test Jerk test & post. Apprehension test • Post. instability Sulcus sign • inferior glenohumeral instability FIGURE 10. Sulcus test for glenohumeral instability. Downward traction is applied to the humerus, and the examiner watches for a depression lateral or inferior to the acromion. Speed's maneuver • proximal tendon of the long head of the biceps Yergason test • biceps tendon FIGURE 9. Yergason test for biceps tendon instability or tendonitis. The patient's elbow is flexed to 90 degrees, and the examiner resists the patient's active attempts to supinate the arm and flex the elbow. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome • Adson`s test Thoracic Outlet Syndrome • Roos` test 33 pole Isfahan