EOCT Study guide project
advertisement

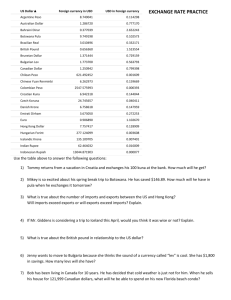
EOCT Study Guide Project Hunter Corbett Fundamental Economic Concepts Scarcity Scarcity: A fundamental economic problem facing all societies that result from a combination of scarce resources and people’s virtually unlimited wants Trade Offs and Opportunity Costs Trade Offs: Alternatives that must be given up when one is chosen rather than another Opportunity Cost: Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another Production Possibilities Graph This shows the possible combinations of goods or services produced. The further away from the start point the more effectively the resources are being used. The closer to the start, it shows that the good or service production is not doing well. This graph also shows what can be gained or lost at certain points. Economic Systems Traditional Basic Questions answered by: Custom and Habit Advantages: Stable and predictable economy, Everyone knows their role Disadvantages: Lower standard of living, Don’t accept new ideas Examples: Rainforest Tribes Aborigines, Mbuti Command Basic Questions answered by: Government or Central Agency Advantages: Change direction quickly, Many public services offered for a low cost Disadvantages: Consumer wants and needs are not met, No incentive to work hard Examples: North Korea, Soviet Union Economic Systems Market Basic Questions answered by: Consumers and Producers Advantages: Adjust to change quickly, Individual freedom Disadvantages: Only reward those who are productive, Public goods lacking Examples: USA, France, UK, Canada, Japan Mixed Basic Questions answered by: Consumers, Producers and Government Advantages: Lack of government interference, Large variety of goods and services Disadvantages: Guard against market failures, Lacking public goods Examples: UK, Japan, Germany, Canada, France Traditional Market Command Mixe d Economic and Social Goals 1. Economic Freedom - people being able to make their own economic decisions 2. Economic Efficiency - make economic decisions so that the benefits gained are greater than the cost, it involves careful use of resources to decrease the amount of resources that are wasted 3. Economic Equity - people should be paid the same for the same kind of work, no false advertising, “Lemon Laws” limited days to return product, include warranties Economic and Social Goals 4. Economic Security - protection from adverse economic events= layoff/ illnesses, social security supports the ill, disabled, elderly, unemployed 5. Full Employment - provide as many jobs as possible if you want to work you should be able to find a job 5% or less unemployment rate 6. Price Stability - prices shouldn’t increase too much so that people can have more goods and services or freedom from inflation 7. Economic Growth - allows consumers to have more goods and services to chose from as population grows Circular Flow Diagram Revenue Consumer Spending Product Market Goods and Services Goods and Services Households Labor and Resources Wages Businesses Resources Factor Market Pay for Resources Microeconomics Demand Demand: Represents all the different amounts of goods and services people will buy at different prices Slope - On a demand curve, the slope is downward Law of Demand According to the Law of Demand, when price goes up quantity demanded goes down When price goes down quantity demanded goes up Relation to Price - There is an inverse relationship between price and demand Demand Curve and Schedule Demand Curve: Graph showing the quantity demanded at each and every possible price Price Quantity Demanded $3.00 1 $2.50 1 Demand Schedule: Listing $1.50 2 showing the quantity demanded at all possible prices $1.00 2 $0.50 3 Factors that Affect Shifting Moving along the demand curve: changes in quantity Consumer Income: more income = consumers buy more and shift right less income = buy less and shift left Number of Consumers: population increases = more demand and shift right population decrease = less demand and shift left Substitutes: goods that can be used in place of other goods, product price increase = demand for substitute increase and shift right demand for product decrease = shift left Change in Expectations: the way people think/feel about future market demand for new product = shift left Complements: products that are used with each other, if demand for product decreases, then demand for complement product decreases and shifts left Consumer Taste: what is in style and popular, increase in popularity = demand increase and shift right decrease in popularity = demand decrease and shift left Examples of Factors Increase money Growing population Butter and Margarine New technology Hot dogs and hot dog buns New fashion Supply Supply: The amount of a product, output, that producers are willing to bring to the market at each price Slope - The slope of a supply curve is positive Law of Supply According to the Law of Supply, when price goes up the quantity supplied goes up When the price goes down down supply goes Relation to price - There is a direct relationship between price and supply Supply Curve and Schedule Supply Curve: a graph of the information in a supply schedule Price Quantity Supplied $1 0 $2 10 $3 20 $4 30 Supply Schedule: a listing of various quantities of a particular product supplied at all possible prices Factors that Affect Shifting Number of Suppliers: number of people providing a good or service, increase in suppliers = increase in supply and shift right decrease in suppliers = decrease in supply and shift left Technology: items in process used to make products, new technology = increase in supply and old technology or breakdown = decrease in supply Government Regulations: mandates from government that businesses must follow, more regulations = increase in cost and decrease in production and shift left, less regulations = decrease in cost and increase in production and shift right Cost of Inputs: land, labor, capital goods used to make products, cost of inputs increase = decrease in production and shift left, cost of inputs decrease = increase in production and shift right Productivity: making of goods and services to connect employee morale, increase in productivity = increase in supply and shift right, increase in productivity = supply increase and shift left More Factors that Affect Shifting Expectations: beliefs about future prices, belief prices will increase = decrease in supply and shift left, belief prices will decrease = increase in supply and shift right Subsidies and Taxes: payment to encourage economic activities, increase subsidies = increase in supply and shift right decrease in subsidies = decrease in supply and shift left, taxes are fees paid to the government, increase in taxes = decrease in supply and shift right and decrease in taxes = increase in supply and shift left Prices Price: The value of a product in money determined by supply and demand Price Ceilings and Floors Price Ceiling: highest legal price that can be charged Price Floor: lowest legal price that can be charged Price Shifts Supply constant and demand increase - shift right Demand constant and supply increase shift right Supply constant and demand decrease - shift left Demand constant and supply decrease - shift left Business Organization - Sole Proprietorship ❏ ❏ ❏ ❏ Number of Owners: one Management of Business: owner Receives Profits: owner Liability: unlimited liability - owner pays all debts ❏ Life of Business: limited life - business ends when owner dies ❏ Tax Payments: single Taxation - profit taxed individuals income Business Organization - Partnership ❏ ❏ ❏ ❏ Number of Owners: two or more Management of Business: owners Receives Profits: owners divide profits Liability: unlimited liability - owners share debts ❏ Life of Business: limited life - business ends when owner dies ❏ Tax Payments: single taxation - profits are treated like income for owners Business Organization - Corporation ❏ ❏ ❏ ❏ Number of Owners: any number Management of Business: board of directors Receives Profits: divided by shareholders Liability: limited liability - if business fails then only investment is lost ❏ Life of Business: unlimited life - continues after death of stockholder ❏ Tax Payments: double taxation - taxed on profits and shareholders taxed on dividends Market Structures Perfect Competition Many firms Identical Products Easy Entry into Market Price Taker setting power Extreme Competition Example: Agriculture Monopolistic Many firms Similar Products Easy Entry into Market Some Price setting power High Competition Example: Fast Food Market Structures Oligopoly Firms dominated by Few Similar Products Hard Entry into Market Limited Price setting power Some Competition Examples: Cars and Sodas Monopoly One firm No substituted Products Impossible Entry Price Maker power No Competition Examples: Natural, Geographic, Technological, Pricing of Market Structures Highest : Lowest Pricing Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic Perfect Competition Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product GDP: The best measure of US economic health and shows overall growth that consists of the total amount dollars of final goods and services produced within the US in a year Formula: c + i + g + (x-m) = GDP Excluded Products Intermediate Goods - make final products already in GDP Secondhand Sales - Sale of used goods Nonmarket Transaction - services not paid for Underground Economy - unreported or illegal activities Examples of Excluded Products Intermediate Goods Secondhand Sales Nonmarket Transactions Underground Economy Business Cycle Monetary Policy Monetary Policy: Policy used by the Federal Reserves to expand or shrink the money supply in order to affect cost and availability of credit Monetary Policy during Phases Expansion Phase Recession Phase Fed sells bonds/ Securities Uses Open Market Operations Reserve Regulations increase Interest Rates Increase Discount Rates Increase Shrinks Money Supply Uses Tight Money Policy Fed buys bonds/ Securities Uses Open Market Operator Reserve Requirements Decrease Interest Rates Decrease Discount Rates Decrease Expands Money Supply Uses Easy Money Policy Fiscal Policy Fiscal Policy: Policy used by the Government Revenue Collection, such as taxes, and expenditure spending to influence the economy Fiscal Policy during Phases Expansion Phase Taxes Increase Government Spending Decreases “Stepping on the Brake.” Recession Phase Taxes Decrease Government Spending Increases “Stepping on the Gas Pedal.” Unemployment Unemployment: People available for work who have made effort to find a job and worked for a profit Formula: Unemployment Rate = % of unemployed people divided by the total number of the civilian work force Types of Unemployment Frictional - workers that are between jobs Example: Working at Burger King then going to McDonald’s Structural - change in the economy reduces demand for workers and their skills or employees lack skills Example: Blacksmith Types of Unemployment Technological - results from technology improvements that make some jobs obsolete Example: Robots doing human job Cyclical - related to changes in business cycle Example: Layoffs do to cut in production Seasonal - changes in weather or demand for products International Economics Absolute and Comparative Advantage Absolute Advantage: Ability to make more of something than another nation can Comparative Advantage: Ability to make something at a lower opportunity cost than another nation can Trade Barriers Types Tariff - Tax on imports, known as a duty Quota - Limits placed on the amount of a good that can be imported Embargo - Government ordered ban on trade Free Trade VS Protectionists Free Trade Against trade barriers because: ● They work only if other countries don’t do the same ● have nearly halted trade in past Free Trade is good because: ● exposes the population to new products ● Makes specialization possible Free Trade VS Protectionists Protectionists ● Practice of limiting foreign trade ● National Security - trading makes nation dependent on imports ● Infant Industries - new industries develop ● Domestic Jobs - barriers can help protect american workers by making imports cost more than domestic goods ● Flow of Money - limiting imports helps keep dollars in the US ● Dumping - practice of exporting goods at a price that is below the exporting country’s price Trading Blocks EU (European Union) - trade zone of 27 european nations Nations: Belgium, Italy, Netherlands NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) - no trade barriers between Canada, USA and Mexico Nations: Canada, USA, Mexico ASEAN (Association of SouthEast Asian Nations) - trade association of 10 southeast nations Nations: Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia Exchange Rates Foreign Exchange Rates: Prices that currencies are bought and sold Fixed: The value of a country’s currency if set at an unchanging rate compared to another country Flexible: Supply and demand determine that value of one’s currency compared to another US Dollar compared to other Currencies 1 US dollar = .80 Euro 1 US dollar = 8.51 Argentine Peso 1 US dollar = 5.94 Danish Krone 1 US dollar = 1 Bermudan Dollar 1 US dollar = 7.99 Macanese Pataca 1 US dollar = 13.57 Mexican Peso 1 US dollar = 1.26 New Zealand Dollar EOCT Date: December 9 and 10, 2014