File - Kielburger Social Studies
advertisement

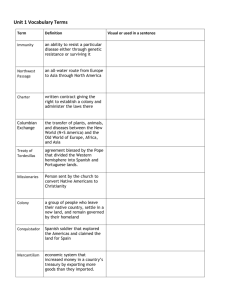
Chapter 3: Exploration and Colonization 3.1 - An Era of Exploration • We came with our ships to Cape Comfort, where we saw five [Virginia Indians] running on the shore. . . . [After] rowing ashore, the captain called to them a sign of friendship, but they were at first very [fearful] until they saw the captain lay his hand on his heart. Upon that they laid down their bows and arrows and came very boldly to us, making signs to come ashore to their town, which [they call] Kecoughtan. Happy Vikings (not Columbus) Day! • Real evidence has been hard to find linking the original “founder” of the Americas • In the year 1001, Vikings led by Leif Ericson reached northern tip of N. America – Vinland (present-day Newfoundland) Columbus Reaches the Americas • King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain financed the Italian captain’s voyage • Travel west across the Atlantic to hit the East Indies – Valuable trade market Columbus Reaches the Americas • August 1492, set sail with the Santa Maria, Nina, and the Pinta • Reached land on October 12, thought to be the East Indies • Actually landed on islands in the Caribbean Sea, found signs of gold – Named the West Indies Columbus Reaches the Americas • Brought back to Europe things unfamiliar to Europeans (tobacco) • Believed the Tainos (Indians) could be converted to Christianity and become slaves • Eventually made three more voyages • Founded in 1493, the colony of Hispaniola (Haiti and Dominican Republic) • Colony – group of people who settle in a distant land but are still ruled by the government of their native land The Impact • Europeans believed Native Americans were inferior to their society • Used Tainos to work in mines, houses, and ranches • New age of exploration to the Americas Ferdinand Magellan • First to cross the Pacific Ocean – Journey began in 1519 • Eventually killed himself in a battle with locals off the Philippine Islands • One ship returned to Spain in 1522, and the first to circumnavigate (sail around the world) The Columbian Exchange • The exchange of goods and ideas between hemispheres To the Americas… • Horses, bananas, oranges, bluegrass, daisies, smallpox, influenza • Diseases killed almost 90% of people in the Caribbean Islands and Mexico To Europe… • Corn, potatoes, beans, peanuts, peppers, use snowshoes, trapping techniques, political structures 3.2 – Spain Builds an Empire • Conquistadors – Spanish conquerors in the Americas • Permission to make settlements • Hernando Cortes, most notorious conquistador Conquest of the Aztecs • Moctezuma – emperor of the Aztecs • In 1519, the Spanish were warmly welcomed, but were driven out when Moctezuma was made prisoner in his own city • Spanish, with the help of Aztec rivals, killed the emperor and destroyed the capital Conquest of the Incas • Francisco Pizarro sailed down Pacific coast of S. America in 1532 • Captured and executed the Incan emperor Atahualpa – Empire soon collapsed in the control of Pizarro Why did the Spanish win? • Superior military equipment • Spanish had horses; mounted soldiers • Disease Spanish Explorers • Juan Ponce de Leon – looked for legendary fountain of youth • Hernando De Soto – explored Florida and the Mississippi River New Spain • Set up the Laws of the Indies to govern the Spanish colonies • Pueblos – towns where the Spanish lived • Presidios – forts where the soldiers lived • Missions – religious settlements run by Catholic priests – Convert natives to Christianity New Spain • Social classes – Peninsulares, Creoles, Mestizos, and Natives • Blend of cultures between Natives and Spanish • Encomiendas – land grants that included the right to demand labor or taxes from Native Americans Rise of the Slave Trade • Natives could not withstand workload demanded of them • Bartolome de Las Casas suggested bringing Africans to the Americas for the labor • Idea spread and gave rise to the slave trade 2.3 – Colonizing North America • Desire to find a northwest passage in North America – Waterway through or around North America • Henry Hudson – first to explore present day New York Protestant Reformation • Martin Luther, German monk, believed people could be saved only by faith in God • Protested against the church, and supporters became known as Protestants • Europe split: Roman Catholics and Protestants New France • Samuel de Champlain founded Port Royal in 1605 • The French were coureurs de bois, meaning they lived and worked in the woods • Did not attempt to conquer Native Americans French Explorers • Father Jacques Marquette and Louis Joliet explored the Mississippi River • Robert de La Salle explored the Gulf of Mexico and founded Louisiana • Brought African slaves to French colonies New Netherland (Present Day New York) • Peter Minuit bought Manhattan from Native Americans, called the island New Amsterdam • Rivaled with the French in the fur trade – Wanted an alliance with Native Americans • Alliance – an agreement between nations to aid and protect one another – Allied with the Iroquois The Impact • European conflicts encouraged warfare between tribes • Natives took advantage of European technology • Conversion to Christianity • Moved Native Americans west, into the territory of tribes – Conflicts would last for decades 2.4 – Building the Jamestown Colony • England was jealous of Spain gaining riches from their colonies • Sir Walter Raleigh gained permission from Queen Elizabeth to begin a settlement in North America • Landed in Roanoke Roanoke Mystery • After a year, food shortage challenged the colonists so they went home • John White returned with a new group of settlers, but White soon left for England • Returning three years later, White found no traces of the settlers Jamestown • King James I gave the Virginia Company a charter to settle lands in present day Virginia • Named the settlement Jamestown in 1607 • Swampy lands, government disagreements, and sickness created trouble for the settlers Struggling Jamestown • Captain John Smith organized labor for the settlers • Established an agreement with Chief Powhatan to be supplied with corn • The corn supply from the Native Americans created tension Temporary Peace? • Tensions settled when John Rolfe married Pocahontas • Still, Jamestown settlers suffered daily with starvation • By 1612, Jamestown settlers began growing tobacco • Tobacco was very profitable and allowed the colony to prosper Government in Virginia • Strict laws and regulations took freedoms from the settlers • Reform was needed and the Virginia Company set up a House of Burgesses – Burgesses – representatives to the government • The H.O.B. would discuss and decide on laws for the colony Government in Virginia • Voters elected representatives to make these laws – Representative government • Only free, white males were allowed to vote on representatives Women and Africans in Virginia • Women were outnumbered by men, but ironically survived hardships better than men • Women had to make everything from scratch • Africans came to Virginia for farming skills • Africans were eventually sold and used as slave laborers and could not vote or own property 3.5 – Seeking Religious Freedom • Pilgrim – anyone who makes a long journey for religious freedom • Europeans that sought religious freedom founded the Plymouth Colony Why the Pilgrims Left • Religious wars between Protestants and Roman Catholics • English law demanded an established church (the chosen religion) – Anglican Church • Persecution – mistreatment or punishment of people because of their beliefs Plans for a New Life • Separatists of the Church of England won a charter in 1620 to establish a colony in North America • The crew sailed on the Mayflower and landed in Cape Cod (Massachusetts) The Mayflower Compact • Forty-one male passengers signed the Mayflower Compact • It promised that the Pilgrims and “strangers” would unify into a civil government • Make laws that insured the “general Good of the Colony” Hardship of the Plymouth Settlers • Lack of food sources and harsh winter • Settlers were stricken with disease and starvation • Makeshift houses made from the earth • William Bradford’s leadership helped sustain the colony Help from Native Americans • English speaking Native Americans Samoset and Squanto helped the Pilgrims plant crops • Strong harvests led to the tradition of Thanksgiving in the United States