Stages of Labor
advertisement
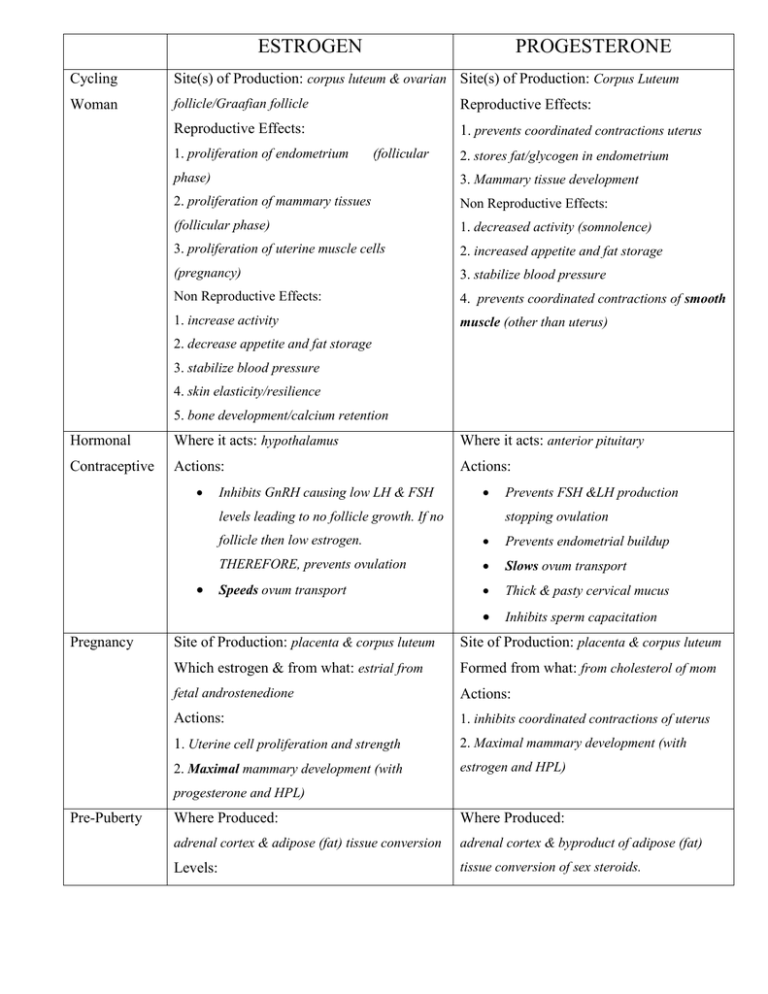
ESTROGEN PROGESTERONE Cycling Site(s) of Production: corpus luteum & ovarian Site(s) of Production: Corpus Luteum Woman follicle/Graafian follicle Reproductive Effects: Reproductive Effects: 1. prevents coordinated contractions uterus 1. proliferation of endometrium (follicular 2. stores fat/glycogen in endometrium phase) 3. Mammary tissue development 2. proliferation of mammary tissues Non Reproductive Effects: (follicular phase) 1. decreased activity (somnolence) 3. proliferation of uterine muscle cells 2. increased appetite and fat storage (pregnancy) 3. stabilize blood pressure Non Reproductive Effects: 4. prevents coordinated contractions of smooth 1. increase activity muscle (other than uterus) 2. decrease appetite and fat storage 3. stabilize blood pressure 4. skin elasticity/resilience 5. bone development/calcium retention Hormonal Where it acts: hypothalamus Where it acts: anterior pituitary Contraceptive Actions: Actions: Inhibits GnRH causing low LH & FSH levels leading to no follicle growth. If no Pregnancy Prevents FSH &LH production stopping ovulation follicle then low estrogen. Prevents endometrial buildup THEREFORE, prevents ovulation Slows ovum transport Speeds ovum transport Thick & pasty cervical mucus Inhibits sperm capacitation Site of Production: placenta & corpus luteum Site of Production: placenta & corpus luteum Which estrogen & from what: estrial from Formed from what: from cholesterol of mom fetal androstenedione Actions: Actions: 1. inhibits coordinated contractions of uterus 1. Uterine cell proliferation and strength 2. Maximal mammary development (with 2. Maximal mammary development (with estrogen and HPL) progesterone and HPL) Pre-Puberty Where Produced: Where Produced: adrenal cortex & adipose (fat) tissue conversion adrenal cortex & byproduct of adipose (fat) Levels: tissue conversion of sex steroids. lower amplitudes but still cycling Levels: lower amplitudes but still cycling Menopause Where/How Produced: (ovaries may continue Where/How Produced: (ovaries may continue to produce some) to produce some) Adrenal cortex produces androstenedione that Adipose tissue conversion of sex steroid makes adipose tissue converts to estrone progesterone as by product Levels: Levels: Low, non-cycling Low, non-cycling FYI Endocrinology of Menopause Relationships between hormones stay the same, so: Very low estrogen stimulates GnRH GnRH stimulates FSH and LH Not much estrogen produced in response to LH and inhibin very low. GnRH increases, then FSH and LH increase GnRH, FSH and LH levels high postmenopause (opposite of prepuberty). Hormones Produced During Pregnancy HCG HPL ESTRIAL PROGESTERONE Human Chorionic Human Placental (fetal viability) (placental viability) Gonadotropin Lactogen Where/How Fertilized Placenta Placenta, from Placenta, from Placenta & Produced? ovum & fetal moms cholesterol Corpus placenta androstenedione Actions RELAXIN Luteum (chemically (similar to 1. Mammary 1. Prevent 1. Soften similar to LH) prolactin) Gland develop. coordinated ligaments 1. Signals CL 1. Makes 2. Uterine cell contractions of allowing to stay alive alveoli proliferation uterus mvmt in and produce functional and strength 2. Mammary develp. joints progesterone 2. Increases 3. Drops for labor 2. Highest in # of alveoli to allow coordinated 3rd trimester contractions for labor & Delivery Stages of Labor I. Stage 1 a. Phase 1: Latent, longest phase (many hours but variable) i. Cervical dilation 3-5 cm ii. Mild discomfort, contractions further apart b. Phase 2: Active (cervical os is expanding) i. Cervical dilation 4-7 cm ii. Increased discomfort, contractions more often and stronger c. Phase 3: Transition (cervical effacement complete) i. Cervical dilation 8-10 cm ii. Most discomfort, contractions very strong and close together II. Stage 2 a. From full effacement/dilation until delivery b. “Pushing” c. Shorter than Stage 1 (30-120 mins) III. Stage 3 a. Passing of placenta after birth of baby b. Easiest phase, squishy sack instead of baby!