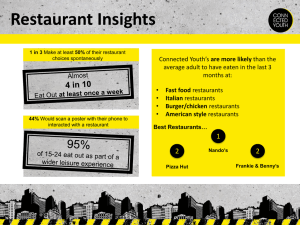
Types of Restaurants
advertisement

Chapter Two: Kinds and Characteristics of Restaurants and Their Owners • Various Kinds and Characteristics of Restaurants • Chain vs.. Independent Restaurant Operations • Lives and Contributions of Prominent Past and Present Restaurateurs TYPES OF RESTAURANTS Quick-Service Steak House Fine-Dining Ethnic Theme Chef-Owner Bakery-Cafe 2 QUICK-SERVICE McDonald’s and Burger King • First fast food restaurant in 1870s • Quick food production time is key • Goal is to serve maximum number of customers in minimum amount of time 3 QUICK-SERVICE CONT’D • Computers are used to anticipate sales volume • Precooked or partially cooked foods are ordered and then finished off to decrease production time • Time, temperature, and meat thickness are used to determine doneness 4 STEAK HOUSES Lone Star and Outback Steakhouse • Limited menu caters to a well-identified market • Service ranges from walk-up to high end • High food costs (as high as 50%) and low labor costs (as low as 12%) • Majority of customers are men 5 STEAK HOUSES CONT’D High-end operations: • may have sales of $5m or more per year • greater investment in building, fixtures and equipment • serve well-aged beef • high percentage of wine and hard liquor sales Low-end operations: • sales of $500,000 per year • beer and moderately priced wine 6 TYPES OF STEAK • Steaks vary from a few ounces to well over 1lb • Tenderloin is most tender, runs along backbone (most popular) • T-bone is cut from small end of loin • Porterhouse contains T-bone and piece of tenderloin • Wet aged: meat that’s wrapped in cryovac, sealed, and refrigerated for several days • Dry aged: controlled temperature, humidity, and air flow 7 FINE DINING Daniel and Charlie Trotter’s • Found in wealthy areas • Cuisine and service is expensive and leisurely • Usually proprietor- or partnerowned • Restaurants are small, usually less than 100 seats • Very low table turnover (can be <1) • Customers dine on special occasions and to impress business relations 8 ECONOMICS OF FINE DINING • • • • Expensive, average check runs $60 or more High rent Large PR budgets High labor costs due to the necessity of highly experience employees • Much of profits come from wine • Tables, linen, dishes, décor very costly 9 FINE DINING MENUS • Expensive, imported items – Foie Gras – Caviar – Truffles • Presentation very important • Focus on visual, auditory, and psychological experience • Extensive, expensive wine list 10 THEME Planet Hollywood and Hard Rock Cafe • Built around an idea emphasizing fun and fantasy • Glamorize sports, travel, eras in time • Celebrities are central to many theme restaurants (some are owners) 11 THEME LIFE CYCLE • Short life cycle compared to other types popular of restaurants • Do well outside major tourist attractions • Locals tire of the hype when food is often poor • Most of the profits come from merchandise, not food sales 12 THEME COSTS • Require large investments and budgets • Often fail because too much is spent on image and not enough on food and service • High capital and operational costs • Extreme décor can be very pricey • Often require excessive labor – Curators, consultants, animal handlers, etc. 13 THEME CATEGORIES • Hollywood and the movies • Sports and sporting events • Time- the good old days • Travel- trains, planes, and steamships • Ecology and the world around us 14 ETHNIC Olive Garden and Panda Express • Many types – Mexican, Italian, Moroccan, Chinese, Thai, etc, or combinations several • Often owned or operated by persons of ethnic background • Feature dishes native to the country • Can be argued that every ethnic restaurant is also a theme restaurant, with the national culture as the theme 15 CHEF-OWNER Spago and Emeril’s • Part of American tradition of family restaurants – Husband is operator/chef – Wife is hostess – Children serve, bus, etc. • Publicity is key in gaining attention • Wolfgang Puck best known – Owns Spago in Beverly Hills, with his wife as partner 16 ADVANTAGES TO CHEF OWNERSHIP • Having an experienced, highly motivated person in charge • Name often already known and synonymous with great food • Can be very profitable 17 DISADVANTAGES TO CHEF OWNERSHIP • Chefs often less knowledgeable about “the numbers” • Can often make more money working as a chef in a name restaurant • Possibility of marital or partner dispute 18 BAKERY-CAFE Panera Bread Company and La Madeleine • Different than a bakery in that they serve soups, salads, and sandwiches • Mainly quick-service establishments • Many bake off goods that are prepared elsewhere or do final proofing after receiving goods • Use central commissary systems • Variety of setting, products, and ambiance 19 The End 20