Geologic Time Scale Lecture
advertisement

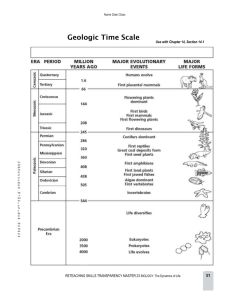
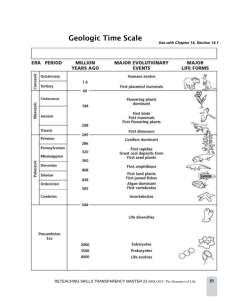
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth’s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until the present. At the end of each era a mass extinction occurred, many kinds of organisms died out, although there were other extinctions going on during each period of geologic time. Using the fossil record, paleontologists have created an idea of the different types of common organisms in each geologic period. Eras are subdivided into periods...periods are subdivided into epochs. Era Period Epoch E + P = EP Various models, diagrams, and pictures can be used to illustrate the vastness of time involved in and to show the diversity of life evident across geologic time. Mesozoic Era CretaceousFlowering Plants, Major extinction of Dinosaurs Jurassic- Early birds & Mammals, abundant dinosaurs Triassic- Lots of Conifers, 1st Dinos, 1st Mammals Paleozoic PermianMass Extinction of marine animals like trilobites Devonian – Early trees SilurianEarly land plants OrdovicianEarly Fish Precambrian ProterozicSingle→Multicellular Organisms. Archean– Oldest fossils, bacteria & sinlge celled organisms 88% of the History of Earth 4.6 Billion Years Ago – 450 Million Years Ago (Color in 27 wedges) Earth's first era of time. 5 major events occurred during this era: (1) the formation of the Sun and light (2) the creation of the Earth (3) the creation of the atmosphere through volcanic out-gassing (4) the creation of the oceans (5) the creation of life Began with simple life forms such as bacteria and simple algae. There was a rise of simple organisms such as jellyfish and sea worms by the end of the era. Few fossils because the life forms were soft-bodied and had no hard skeleton. Geological Events: Earth Began Biological Events: Bacteria Appear Soft-Bodied Multi-Cellular Organisms Appear Ancient Life 544 Million Years Ago – 244 Million Years Ago (Color in 3 wedges) Animal Life: Began with the early invertebrates, such as trilobites and brachiopods. Continued to develop early vertebrate fish, arachnids and insects. Later came the first amphibians and near the era’s end the reptiles became dominant. Plant Life: Early land plants included simple mosses, ferns, and then cone-bearing plants. By the end of the era, seed plants were common. The mass extinction that ended the era caused most marine invertebrates as well as amphibians to disappear. Geological Events: Biological Events: Shallow seas cover • Great explosion of invertebrates in the sea (Trilobites appear) • Land plants appear • Insects and spiders appear • Age of fish begins • First reptiles appear • Trilobites become extinct much of the land Coral reefs develop Pangaea forms Appalachian Mountains form Middle Life 245 Million Years Ago – 65 Million Years Ago (Color in 1 ½ wedges) Reptiles were the dominant animals of this era, including the various dinosaurs. Small mammals and birds also appeared. Toward the end of the era, flowering plants appeared and the kinds of mammals increased. The mass extinction that ended the era caused the dinosaurs to become extinct. Geological Events: Hot, dry conditions dominate Pangaea Pangaea splits Widespread volcanic activity Biological Events: Dinosaurs appear Largest dinosaurs thrive Dinosaurs become extinct Mammals, birds and flowering plants appear Recent Life 65 million years ago - Today (Color in a ½ wedge) New mammals appeared while others became extinct. Mammals had to evolve to adapt to different environments. The diversity of life forms increased. Flowering plants became most common. Humans are also part of the most recent period of this era. Many mountain ranges formed ex. Alps in Europe, Himalayas in India & Rocky Mountains in the USA Geological Events: Rocky Mountains and Himalayas form Continental glaciers cover Antarctica Ice age ends Biological Events: First grasses appear Mammals, flowering plants, and insects dominate the land Humans appear