Slide 1
advertisement

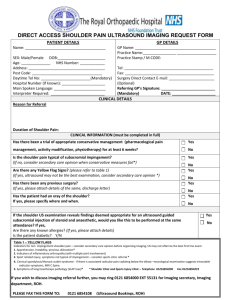
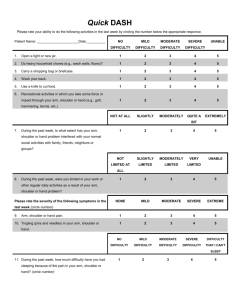
GP LECTURE SERIES 2013 THE SHOULDER Assessment, treatment and functional considerations Basic rotator cuff anatomy and function Dynamic stability of the glenohumeral joint The RC tendons blend together to become the joints capsule Allows for increased mobility but compromises stability Shallow glenoid fossa supported by a cartilaginous labrum cover RC’s aim to maintain the HOH in optimal contact with the glenoid fossa throughout range 3D assessment • Upper and lower fibres of trapezius work together to E/IR the scapula • Serratus anterior keeps the medial border of the scapula in close contact with the thorax • If 1 or more of these forces become under/over active abnormal shoulder, neck or back mechanics could result Thoracic spine and shoulder function Compensatory thoracic spine E, rot and LF to allows for more arm elevation Hypomobile/stiff spinal and rib joints mean more movement needs to take place at the GHJ Increase kyphosis protracts the scapula causing an imbalance throughout the shoulder girdle Poor sitting posture & ergonomics Looking at the bigger picture The shoulder and thoracic spine can also be affected by structures way down the kinetic chain Core strength and posture are very important and need to be addressed Often diagnosing a shoulder condition is simply the symptom of a much bigger cause Hawkins Kennedy Test Test for impingement and bursal bunching Position for testing: Arm abducted to 90 degrees the examiner administers a downward pressure on the forearm into internal rotation whilst stabilising the humerus. Full/Empty can test Test for supraspinatus/infraspinatu s tear/tendonitis Position for testing: Patient in standing or sitting abducts arms to 90 degrees. - Supraspinatus; empty can - Infraspinatus; full can Apprehension Test Test for anterior instability or recent shoulder dislocation/subluxation Position for testing: patient lies in supine with shoulder abducted at 90 degrees and in maximal external rotation. The humerus is supported and overpressure into external rotation administered. The anterior capsule should be supported and then overpressure released to confirm instability Crank-pivot test • Designed to identify a labral tear or SLAP lesion. • Position for testing: Patient in supine, arm in external rotation, examiner compresses the humeral head into the glenoid fossa and pivots the arm back and forth. Frozen shoulder Related to a loss of range throughout all degrees of freedom in the shoulder – need to look at all AM’s External rotation most affected followed by abduction and then flexion Particular attention should be taken to look at the scapula - sometimes range may seem equal both sides, but this is only being achieved by excessive compensatory scapulothoracic joint movement rather than normal glenohumeral joint function Physiotherapy and Shoulder Disorders Analysis of the results and effectiveness of exercise across all available clinical trials demonstrates that Physiotherapy exercises for mixed shoulder disorders & rotator cuff diseases are effective at; - Reducing pain - Improving muscle strength - Increasing function - Improving general well-being Unsurprisingly the longer the patients performed the prescribed exercises the greater the reduction in their pain (Green, Buchbinder & Hetrick 2013) Shoulder Impingement Manual therapy applied by experienced physical therapists, combined with a supervised exercise programme was found to be better than exercise alone for patients with shoulder impingement syndrome in; - Increasing strength - Decreasing pain - Improving function (Bang & Deyle, 2000) Frozen Shoulder No evidence that Physiotherapy, Pharmaceutical intervention or corticosteriod injections change the outcome of idiopathic frozen shoulder (Brukner & Khan 2006) However, early range of motion exercises and education on the pathway of frozen shoulder are effecting in restoring range, relieving pain and improving function (Brukner & Khan, 2006) It is also important to correct secondary complications that may arise from having a stiff and painful GHJt