Factor
advertisement
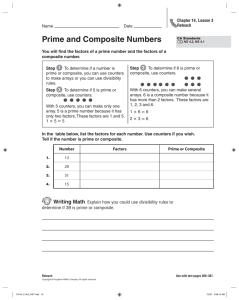
Factors, Primes & Composite Numbers O Product – An answer to a multiplication problem. 7 x 8 = 56 Product O Factor – a number that is multiplied by another to give a product. 7 x 8 = 56 Factors O Factor – a number that divides evenly into another. 56 ÷ 8 = 7 Factor ARRANGEMENT OF COUNTERS Take 6 counters and arrange them in different ways 5 1 Row × 6 Counters = 6 Counters 6 3 Rows × 2 Counters per row = 6 Counters 7 2 Rows × 3 counters per row = 6 counters 8 6 Rows × 1 counter = 6 counters 9 As we can see, 6 can be written as product of two numbers in many ways: 1×6=6 2×3=6 3×2=6 6×1=6 1, 2, 3 and 6 are factors of 6 10 What are the factors? 6 x 7 = 42 7 x 9 = 63 8 x 6 = 48 4 x 9 = 36 6&7 7&9 8&6 4&9 What are the factors? 42 ÷ 7 = 6 63 ÷ 9 = 7 48 ÷ 6 = 8 36 ÷ 9 = 4 7 9 6 9 Who has heard of a Factor Rainbow? A factor rainbow helps you find all of the factors of a number. It is called a rainbow because all of the factor pairs connect to make a rainbow! How do we do it!?!?!? Making a factor rainbow is easy as pie! Let’s try one: Find all of the factors for the number 12. We start by counting and seeing if a number can be multiplied to equal 12. 1 2 3 4 6 How many factor pairs are there for the number 12? 3 12 One more time... How many factor pairs are there for the number 18? 3 1 2 3 6 9 18 YOU TRY! Make factor rainbows for the following numbers and tell how many factor pairs each number has. 15 24 Prime Number – a number that has only two factors, itself and 1. 7 7 is prime because the only numbers that will divide into it evenly are 1 and 7. Examples of Prime Numbers 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17 Special Note: One is not a prime number. Composite number – a number that has more than two factors. 8 The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, 8 Examples of Composite Numbers 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12 Our Lonely 1 It is not prime because it does not have exactly two different factors. It is not composite because it does not have more than 2 factors. Special Note: One is not a prime nor a composite number.