exponent targets - Mason County Schools
advertisement

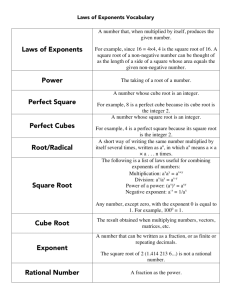
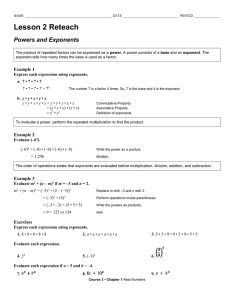
EXPONENTS UNIT 8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3-5 = 3-3 = 1/33 = 1/27. _____ 1. I can recognize that a negative exponent means to write the base and exponent as a denominator. This means I can change the negative exponent to a positive number and place it in the denominator position. For example, 32 × 3-5 = 3-3 = 1/33 = 1/27. _____ 2. I can explain the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3-5 = 3-3 = 1/33 = 1/27. _____ 3. I can apply the properties of integer exponents to produce equivalent numerical expressions. _____ 4. I can multiply exponents. _____ 5. I can divide exponents. _____ 6. I can raise an exponent by an exponent. _____ 7. I can apply the zero product rule for exponents. 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. _____ 4. I can use square root and cube root to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. _____ 5. I can know that the square root of 2 is irrational. _____ 6. I can evaluate perfect square roots and cube roots. Vocabulary: exponent, base, cube root, square root, irrational, rational, square, cube