Patterns of Evolution: Convergent Evolution vs
advertisement

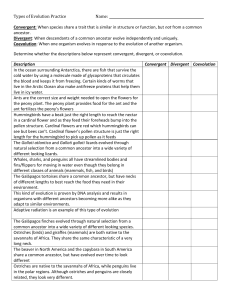
Patterns of Evolution: Convergent Evolution, Coevolution & Divergent Evolution Convergent Evolution Occurs when different organisms that live in similar environments become more alike in appearance and behaviour. The environment selects similar adaptations in unrelated species. Organisms develop analogous structures (same function, but different origins). Examples: - Bird wings/insect wings - Shark fins/dolphin fins More examples: Placental Mammals: top row Marsupial Mammals: bottom row Coevolution When two species evolve together. There is a mutual evolutionary influence between two species. The species have a symbiotic relationship (interaction between members of two populations). Example: - Birds and flowers Divergent Evolution The process by which an ancestral species gives rise to a number of new species that are adapted to different environmental conditions and are less alike. Often occurs when a species colonizes a new environment. Also known as adaptive radiation. Examples: - Darwin’s Finches. - Brown bears and polar bears Divergent Evolution