Wave Interference - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
advertisement

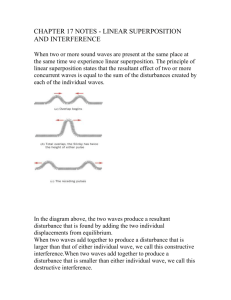
Wave Interference Chapter 8.3 Interference • What happens when 2 waves pass through the same region of space at the same time Types of Interference • Constructive Interference – When 2 crests arrive at the same time (or 2 troughs) – The 2 crests move the wave upwards to make a larger wave (temporary) • Destructive Interference – When 1 crest and 1 trough arrive at the same time and cancel each other out if they are identical in size (temporarily). – Partially destructive waves may not cancel each other but dampen the wave temporarily. Constructive Interference Destructive Interference Constructive Destructive Partially Destructive Interference Interference Interference Interference • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xqo6sEt 1cUE Quick Quiz • 1. Several positions along the medium are labeled with a letter. Categorize each labeled position along the medium as being a position where either constructive or destructive interference occurs. Answers • Constructive Interference: G, J, M and N • Destructive Interference: H, I, K, L, and O How is this similar to crashes??? How is it different??? • Momentum • Energy Principle of Superposition • In the region where the waves overlap, the result and displacement is the algebraic sum of their separate displacements. – NOTE: A crest is positive and a trough is negative! – NOTE: Waves do not change shape or size when they meet. They can pass through each other. However, when they overlap, a different shaped wave emerges temporarily! Example of Superposition • If one wave has an amplitude of +3cm and the other wave has an amplitude of -6cm, the resultant displacement is … • -3cm. Example 2 of Superposition • If one wave has an amplitude of +3cm and the other wave has an amplitude of +6cm, the resultant displacement is … • +9cm. • See page 355 for diagrams! Superposition of Waves Superposition of Waves Superposition of Waves Questions for You • Page 362 – 1, 2, 3 (use graph paper for this one!) • Worksheet Answers • 1. Constructive interference – amplitude at superposition is 4 cm (2 + 2). • 2. Destructive interference - cancel out (+2 + -2 = 0). • 3. Principle of Superposition – states that the displacement is the sum of the separate displacements Standing Waves • When two pulses with equal but opposite amplitudes meet. • The waves have the same shape, amplitude and wavelength but opposite directions. Node • You can find points in the medium that are completely undisturbed at all times (destructive interference). • A point where disturbances caused by two or more waves result in no displacement. • **MATH 11: On the SA! • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Standing_wave.g if Antinode • You can find one point that undergoes the greatest displacement. • Point of maximum displacement of two superimposed waves (constructive interference) • Occur at crests and troughs. • Occur halfway between nodes. • There are nodes at the end of a rope and antinodes in the middle. • The resulting wave appears to be standing still. This is a standing wave. • http://www.physicsclassroom.com/mmedia /waves/harm4.cfm Page 357 Page 357 How do we get a standing wave? • Have one vibrating source. • The second wave is actually the reflected wave from the incident wave • Example: Violin strings • Waves move toward the fixed ends of the violin. When they reach the ends, the waves reflect back. There is interference. Standing waves form if nodes occur at the ends of the string/violin. This occurs if the strings are vibrating at the resonance frequency. Animation • http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/w aves/u10l4c.cfm Questions for You • Page 362 • 4, 5 Answers • 4. You would see nodes evenly spaced and antinodes (as crests and troughs at the same time) evenly spaced between the nodes. It is called a standing wave because the nodes are not moving. • 5. The nodes are distributed at distances of half the wavelength (as are the antinodes). The antinodes are spaced evenly between these. Nodes are on the equilibrium or sinusoidal axis. Antinodes are found at troughs and crests. • Nodes are caused by destructive interference. Antinodes are caused by constructive interference. Wave Properties Worksheet • Part of a wave = questions 1 to 10 • Wave Boundaries and Interference = questions 11 to 15, 17 • We will cover 16 next day!


![Wave Interference []](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009269968_1-97379e48baef1370e4514f73f8b3c35d-300x300.png)