Medicines and drugs - chemistryatdulwich
advertisement

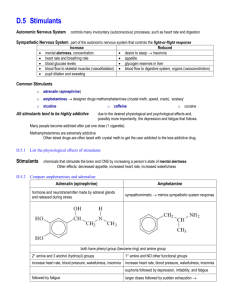
Medicines and drugs Stimulants stimulants •nicotine, caffeine, amphetamines •the intention of these drugs is to have similar effects to adrenaline which is a natural stimulant. •amphetamines have similar structures to adrenaline. stimulants • affect central nervous system; act on neurotransmitters which are chemicals that acts as messengers and stimulate pathways • increase activity of the brain • largely opposite to depressants physiological effects short term increased heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate dilation of pupils constriction of arteries sweating increased alertness and concentration decreased appetite stimulating effects. long term increased risk of heart disease increased blood pressure coronary thrombosis stomach ulcers. tolerance: increasing amounts cause damage/death/overdose/letha l dose amphetamines • group of drugs which mimic the effect of adrenaline • classified as symphatomimetic drug as it stimulates the symphatetic nervous system • adrenaline or epinephrine = hormone released in times of stress e.g. pain, cold, fear, … • response to increased adrenaline: • • • • increased heart beat/blood pressure Increased blood flow to brain and muscles Increased air flow to lungs Increased mental alertness compare • Common: both amphetamines and epinephrine have a phenyl-ethyl-amine chain which is benzene ring linked to an amine group by a carbon chain • Different: functional groups • amphetamines: • primary amine • epinephrine: • 3 hydroxyl groups • secondary amine nicotine • A nicotine molecule contains the following functional groups: a tertiary amine, aromatic benzene ring structures with nitrogen atoms in them, and double bonds (alkene functional group). physiological effects nicotine short term effects increased heart rate increased blood pressure reduced urine output increased concentration long term effects increased risk of cancer or stroke heart disease / thrombosis stomach ulcers emphysema bronchitis shortage of breath coughing bad breath yellowing of teeth or fingers adverse effect on pregnancy addiction to tobacco reduction in capacity of blood to carry oxygen; withdrawal symptoms / weight gain (on quitting); caffeine • Caffeine is a psychoactive stimulant. When consumed in large amounts it can cause anxiety, irritability and sleeplessness. It is a weak diuretic i.e. causes the body to lose more water than it takes in • Its structure is similar to nicotine. structure of caffeine • aromatic rings containing both carbon and nitrogen – like nicotine • tertiary amine group • two amide groups (- N – C = O) caffeine consumption in small amounts • increased mental alertness • greater ability to concentrate •diuretic; dehydration large amounts •can cause anxiety, irritability, nausea •dependence