+ JMJD NAME: PREPARING FOR THE HONORS CHEMISTRY
advertisement

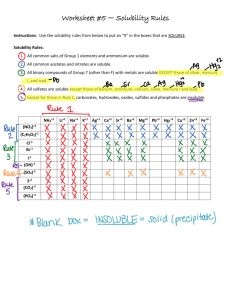
+ JMJD NAME: PREPARING FOR THE HONORS CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM MAY 2011 Format: Multiple choice (about 100) and free response. Test taking strategy: -Watch your time and your point values. Some of the multiple choice require careful calculations, so do them carefully. However, multiple choice are 2 pts each, so if one requires a lot of time to do, skip it and come back later after you have gone through the free response section where the questions tend to be worth more points. -Your test begins at 11 am, so eat protein before hand to keep your brain in good shape. -DO NOT stay up late the night before!!! Work out a study schedule carefully well in advance of your test. Reference materials: You will be provided with a periodic table, value for R, atm/mm Hg/torr conversions, a list of alkanes, reactivity series, solubility table Areas you will need to study thoroughly: 1. Organic Chemistry: -organic chem. test; bldg blocks of life quiz 1. How do you name organic compounds with functional groups? 2. How do you draw organic compounds with functional groups? 3. What are the characteristics and structures of the functional groups you have studied? 4. What are aromatic compounds, especially benzene, and how are compounds with them named? 5. What kind of C-C bonds are there in organic compounds? Tell about them. 6. What are the 4 building blocks of life? For each, draw/describe the structure, tell what elements are in them, give its characteristics, name and draw/describe the monomers that make them up 2. Reaction types -test 1. Name and give examples of the reaction types from chapter 8. Look in the chapter for those special types of synthesis and decomposition reactions and write them down 2. How do you use the activity series to predict reactions? What type? 3. How do you tell if a double displacement reaction will go? 4. Use the solubility table given with this handout and the activity series as needed to do p. 295 #50-51. 3. Mole, chemical composition -quiz 1. Rework any sample problems and practice in Chapter 7 that you feel uncomfortable with. Don’t worry about calculating avg atomic mass 2. Do at least 5 of these: pp. 252-254 # 50,54,57,58c, 59, 60,61,64a,65,67 4. Stoichiometry -partner test 1. Rework any sample problems and practice in sections 12.1 and 12.2 that you need to review. 2. Do at least 5 of these: pp. #26,28,30,33,36,39, 49 5. Caffiene lab -your lab 1. What is the structure of caffeine and what properties of it and substances in tea allow the caffeine to be separated? 2. Describe are the key steps to isolate and purify the caffeine in the traditional and green methods. Include the chemistry behind the steps. Use a flow chart if you like. 6. Gas Laws -test, quiz 1. Describe the general properties of an ideal gas according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory and contrast with real gases 2. What are the units of pressure? No, do NOT memorize how many torrs are in a pascal… 3. State Boyle’s, Charles’, Gay-Luassac/s, Avogadro’s laws by equations 4. State Bay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes and Dalton’s law of partial pressures 5. State and be able to use the Ideal Gas law 6. Rework any sample problems and practice that we did in Chapter 12 (all except problem F). 7. Do at least 5 of these: pp. 446-448 #40,46,51,56,63,64,65,66,68,69. 7. Intermolecular forces -test 1. Rework any sample problems on which you need practice. 2. Choose two problems in the back of the chapter to do. 3. No more details here. You know what to restudy. 8. Solutions -double quiz 1. Rework any sample problems on which you need practice. 2. Choose two problems in the back of the chapter to do. Do more if you need in order to feel confident here. 3. No more details here. You know what to restudy. 9. Equilibrium -little test 1. Rework any sample problems on which you need practice. 2. Choose two problems in the back of the chapter to do. Do more if you need in order to feel confident here. 3. No more details here. You know what to restudy. 10. Acids/bases -little test TBA 11. Nomenclature -Review your polyatomic groups. Know the baking soda, vinegar, sand, glass, nitric acid, acetic acid, sulfuric acid, sulfurous acid, nitrous acid. Be prepared to name / write the formula for any ionic or covalent compound. 12. Additional discussed in class: Detailed Table of Solubility Rules for Ionic Compounds any anion + alkali ions (Li+,Na+,K+,Rb+,Cs+,Fr+) = soluble sodium fluoride, NaF, is soluble any anion + hydrogen ion [H+(aq)] = soluble hydrogen chloride, HCl, is soluble any anion + amonium ion (NH4+) = soluble ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is soluble nitrate NO3- + any cation = soluble potassium nitrate, KNO3, is soluble acetate (CH3COO-) + any cation = soluble sodium acetate, CH3COONa, is soluble Chloride (Cl-), Bromide (Br-), Iodide (I-) + silver (Ag+), lead (Pb2+), mercury (Hg2+), copper (Cu+), thallium (Tl+) = low solubility (insoluble) silver chloride, AgCl, forms a white precipitate (a white solid) + any other cation = soluble potassium bromide, KBr, is soluble Sulphate (SO42-) + + Sulfide S2- Hydroxide OH- Phosphate, PO4 , Carbonate, CO32-, sulphite, SO323- calcium (Ca2+), strontium (Sr2+), barium low solubility = (Ba2+), silver (Ag+), lead (Pb2+), radium (Ra2+) (insoluble) any other cation barium sulphate, BaSO4, forms a white precipitate (a white solid) = soluble copper sulphate, CuSO4, is soluble alkali ions (Li+,Na+,K+,Rb+,Cs+,Fr+), alkali + earth metals (Be2+,Mg2+,Ca2+,Sr2+,Ba2+,Ra2+), = and H+(aq), NH4+ soluble magnesium sulfide, MgS, is soluble + any other cation = low solubility (insoluble) zinc sulfide, ZnS, is insoluble + alkali ions (Li+,Na+,K+,Rb+,Cs+,Fr+), H+(aq),NH4+,Sr2+,Ba2+,Ra2+,Tl+ = soluble strontium hydroxide, Sr(OH)2, is soluble + any other cation = low solubility (insoluble) silver hydroxide, AgOH, is insoluble (forms a precipitate) + alkali ions (Li+,Na+,K+,Rb+,Cs+,Fr+), H+(aq),NH4+ = soluble ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4, is soluble + any other cation = low solubility (insoluble) magnesium carbonate, MgCO3, is insoluble