عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint - An-Najah Staff - An
advertisement

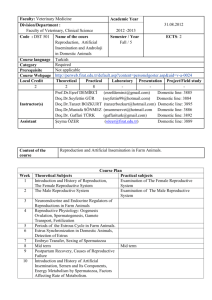
THERIOGENOLOGY 1 12484 Dr. Hatem Atalla D.V.M PhD An-Najah National University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine 2009 Course Description Theriogenology is a one semester (2 H Theory + 2 H Practice) course designed to provide the Veterinary Students with knowledge, training and understanding of reproduction processes in domestic animals from puberty and genesis to gestation, and Artificial insemination processes from semen collection to insemination. Course Objectives 1. Describe the reproductive anatomy and reproductive function in domestic animals. 2. Demonstrate proper artificial insemination techniques in cattle. 3. Discuss factors affecting efficiency of reproduction in animals. 4. Demonstrate proper semen handling and pregnancy diagnostic techniques. 5. Describe and discuss estrus synchronization and embryo transfer programs 6. Evaluate the collected semen by the macroscopic and microscopic semen examinations. 7. Inseminating cows and Applying hormones and sponges for estrus synchronization Assessment This course will be evaluated by 3 exams, in addition to the practical exam as short answer question and oral and practical examinations. First examination 15 points Second examination 15 points Practical examination 30 points Participation, quizzes, reports Final examination 40 points Total 100 points Text Books Main Text Book: Applied Animal Reproduction, Joe Bearden, John Fuquat, Second Edition 1984 Suggested Reading: Reproduction in Farm Animals, E.S.E. Hafez, 6th edition 1993 Reproduction in Cattle, A.R. Peters and P.J.H. Ball, 2nd edition 1994 Current Therapy in Theriogenology, Morrow, 1986 COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 1 The female reproductive organs, 9 Functions of female reproductive organs The male reproductive organs, 25 Functions of male reproductive organs Week 2 Natural Synchronization processes, 41 Primary Reproductive Hormones of the Pituitary Gland, 45 Control of the Pituitary Gland by the Hypothalamus, 46 Hormones of the Glonads, 48 Primary Reproductive Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex, 52 Week 3 Endocrine Function of the Uterine/Placental Unit, 53 Reproductive Role of Prostaglandins, 53 The Pineal Gland Regulation of Hormonal Receptor Sites, 55 Intracellular Mechanisms of Hormonal Action, 56 COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 4 The Estrus Cycle, 63 Puberty, 63 Periods of Estrous Cycle, 65 Hormonal Control of the Estrous Cycle, 66 Mating Behavior, 70 Seasonal Breeding, 72 Week 5 Spermatogenesis and Maturation of Spermatozoa, 77 Puberty, 77 The Process of Spermatogenesis, 79 The Seminiferous Epithelial Cycle and Spermatogenic Wave, 83 Capacitation of Spermatozoa, 85 COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 6 Ovigenesis and Fertilization, 89 Ovigenesis, 89 Ovulation, 91 Gamete Transport, 93 Fertilization, 95 Polyspermy, 98 Aging of Gametes, 98 Week 7 Male Mating Behavior, 141 Regulation of Mating Behavior, 143 Erection and Ejaculation, 145 Maintaining Libido, 146 First Exam COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 8 Semen and its Components, 149 Spermatozoa, 150 Seminal Plasma, 153 Energy Metabolism by Spermatozoa, 154 Factors Affecting Rate of Metabolism Week 9 Altering Reproductive Processes, 227 Synchronization of Estrus, 227 Superovulation and Embryo Transfer, 234 Week 10 Reproductive Management, 253 Measurements of Reproductive Efficiency, 253 Management Related to the Female 254 Week 11 Management Related to the Male, 272 COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 12 Pregnancy Diagnosis, 277 in cow, ewe, doe, mares, and sows Week 13 Environmental Management, 297 Environmental Stressors, Physiological Relationship of Environmental Stress to Reproduction Thermoregulation Modification of Summer Environments to reduce Stress Week 14 Nutritional Management, 307 Nutritive Components, Growing Animals Maintaining Reproductive Efficiency Second Exam COURSE OUTLINES THEORY Week 15 Anatomical and Inherited Causes of Reproductive Failure, 321 Freemartin, 321 Infantile Reproductive System, 323 Incomplete Structures, 324 Hermaphrodite, 325 Cryptorchid, 326 Injuries, 327 Prolapse of Vagina and Uterus, 329 Week 16 Phsiological and Psychological Causes of Reproductive Failure 331 Cystic Ovaries, 331 Retained Corpus Luteum, 334 Anestrus, 335 Irregular Estrous Cycles, 336 Quiet Ovulation, 338 Age, 339 Psychological Disturbances, 340 PRACTICAL Reading texts: Part 3 from the text book from chapter 13-17 Other Notes PRACTICAL Dissection a slaughterhouse material (genital organs) Inspection of external male and female genital organs in farm animals Introduction and History of Artificial Insemination, 161 Introduction, 161, History, 162 Advantages and disadvantages, 165 Facilities Needed for Semen Collection, 167 Methods of Semen Collection, 168 Semen Collection by Artificial Vagina from bull and ram Chemical characteristic of seminal plasma Ultra structure of sperm Semen Collection by Artificial Vagina from bull and ram Macroscopic evaluation of semen, Semen Evaluation, 181 Gross Examination, 182 Estimation the Mass Activity, Motility and Concentration of semen, Progressive Motility, 182, Concentration of Sperm Cells PRACTICAL Sperm Cell Morphology, 187 Differential Staining of Live and Dead Sperm, 189 Speed of Sperm, 190 Evaluating Frozen Semen, 190 Other Tests, 193 Semen Processing, Storage, Thawing, and Handling, 195 Importance and Properties of Semen Diluters, 195 Buffer Solutions Used in Semen Diluters, 196 Antimicrobial Agents for Semen Diluters, 197 Effective Semen Diluters for Bull Semen, 198 Processing Bull Semen, 199 Aim of dilution characters of extending media Dilution Technique Preservation of semen Semen processing for cooling PRACTICAL Dilution of semen with Egg yolk-Na citrate solution Storage and Handling of Bull Semen, 205 Processing Boar, Ram, Stallion and Buck Semen, 207 Insemination Techniques, 213 Insemination of the Cow, 213 Insemination of the Ewe and Doe, 221 Insemination of the Sow, 222 Insemination of the Mare, 222 Estimation of metabolic activity 1) Respiratory Activity 2) Methylene blue reduction test Fructolysis test Catalase Test Application of vaginal sponges in sheep