v. Clouds
advertisement
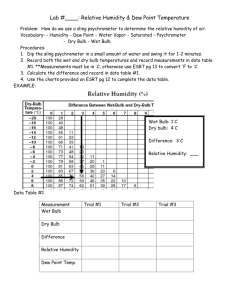
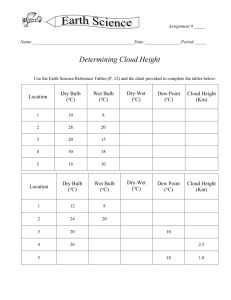
HUMIDITY AND DEW POINT DEW POINT The dewpoint is the temperature of air which is needed for condensation or dew (at that particular temperature). If you take a glass of ice water and it develops condensation on the glass surface, the air on the glass has condensed to its dewpoint and created dew. Dewpoint actually measures how much water vapor is in the air. RELATIVE HUMIDITY Relative humidity is a measure of how much water vapor the air actually could "hold" at a certain temperature. The relative humidity represents how close the air is to saturation. Saturated air will have an RH of 100 %. You need the RH of 100% to have rain form in clouds. How do we measure Humidity?????? To measure relative humidity use a sling psychrometer (hygrometer) Dry bulb thermometer and a wet bulb thermometer mounted together Dry bulb tells actual temperature Wet bulb shows how much water can be evaporated – temperature lowers as water is evaporated The difference in temperature on the 2 thermometers is an indication of the amount of water vapor in the air. Wet bulb. Dry Bulb How relative humidity (RH) is measured? Wet- and Dry Bulb Psychrometer Wet- and Dry Bulb Psychrometer Psychrometric Chart. If the difference between wet and dry bulb is 6º F and the temperature is 72º F (dry bulb), then the RH is 54%. Dry air: the water will evaporate quickly and cause a large drop in the wet-bulb temperature. This makes the difference in readings on the 2 thermometers greater. Moist air: little water will evaporate from the wet-bulb and the temperature decrease will be small. The difference between the wet bulb and dry bulb will be small. When the Wet bulb temperature = the dry bulb temperature……… 100% HUMIDITY!!! The "wetter or damper" you feel,, the higher is the relative humidity. If you feel the air is dry around you, the relative humidity is low. Glass of water demo Assignment •Blk text pg 505 6-9 CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATIONS V. Clouds & Precipitation A. Cloud Formation (condensation) 1. All clouds require 3 things: a. water vapor b. condensation nuclei- something for water to bond with c. cooling- air must be cooled below dew point . Expansion, or when air rises. When air in the atmosphere sinks it compresses causing heating. Cloud families •High altitude •Middle altitude •Low altitude •Vertical development C. Cloud Types 1. Cirrus- wispy, feathery high altitude clouds. a. Made of ice crystals 2. Stratus- flat, spread out layers. Low to middle altitude. a. form through horizontal air movement 3. Cumulus- fluffy, rounded, medium altitude clouds. a. form through vertical air movement b. cumulus- “piled” 4. Cumulonimbus- large rain/storm cloud a. nimbo – “rain” b. cumulo- “column like” Cirrus Cumulunimbus stratus cumulus G. Forms of Condensation 1. Frost- when the temp of the air is below 0°C, then the water vapor condenses as a solid. 2. Fog- cloud formation near Earth’s surface. a. Ground/radiation fog- during nighttime with sky clears, the ground loses heat rapidly by radiation. 1.) breeze mixes air at ground level 2.) air is cooled below the dew point and fog forms. b. advection fog- when warm, moist air blows over a cool surface. Topic Questions 511 blk text • Complete the following questions. • 10, 11, 12a, 14a,b, 15a. • Read pg 512-514 topics 16-17. then draw diagram 27.12 in your notes and describe in your own words how rain drops forms and the types of precipitation.