Introduction to Linux
advertisement

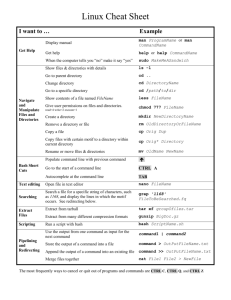
Julien Thibault Julien.thibault@utah.edu 1969 - Bells Labs develop a new operating system called “UNIX” Beginning of the 90’s Linus Torvalds PC becomes popular UNIX too slow for these machines and not free People switch to Windows 3.1 or MS-DOS 1991 – Linus Torvalds (University of Helsinki) starts working on the “Linux” project Written in C instead of assembly code Able to recycle code Improved compatibility between systems Free OS Compliant with the original UNIX Today – why do you care? De-facto OS for high-performance computing (clusters) More and more popular in federal agencies and large companies Pros Free and open source Large community Secure, almost no virus (compared to Windows) Scalable: from palm to cluster with more 100 nodes Cons Not as user-friendly as Windows or Mac but getting there Many distributions available: Ubuntu, RedHat, Fedora, SUSE, Mandriva, Debian… See: http://futurist.se/gldt/wp-content/uploads/11.04/gldt1104.png What a Linux distribution can look like today… Host: Login: Password: sanddunearch.chpc.utah.edu uNID uNID password Using PuTTY (Windows): Just enter the host name Using ssh (Mac or Linux): ssh [-Y] login@host The -Y option is used to enable GUIs (it can be slow!!) cd ls [-la] pwd mkdir mv cp [-r] change current directory list files show path to current directory create new directory move file/dir to new location copy file (use -r for directory) scp [-r] ssh secured copy over the network secured remote login man cmd cmd command manual Create the directory ~/workshops/linux/test in your home directory Copy the test directory to ~/workshops/linux/test2 Move test2 to your home directory and rename it testlinux Try out Emacs if you cant stand VI… http://www.cs.colostate.edu/helpdocs/emacs.html Insertion mode: Command mode: i ESC dd yy p u delete current line (and copy) copy current line paste before cursor undo /string or ?string n or N search string after or before cursor go to next or previous match :s/pattern/string/g replace pattern by new string :w :q :q! Save changes Exit Exit and ignore any changes More commands at: http://www.lagmonster.org/docs/vi.html Create a new text document, insert “Hello world” and save it as helloworld.txt Download Moby Dick from http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/2701.txt.utf8 and rename it mobydick.txt Delete everything that is before chapter 1 What is the title of chapter 107? What is the last line? Move the first paragraph (chapter 1) to be after the second one How many times does the word ‘France’ appear in the text? Permissions Root (super user) ▪ Can control machine configuration and programs for all the user ls -l will display the permissions for a file/dir Interactive shell configuration aliases (e.g. “ll” instead of “ls -l”) environment variables ▪ $PATH: path to the executables ▪ $HOME: point to your home directory bash / C shell ▪ 2 different scripting methods ▪ .bashrc , .bash_profile , .profile / .tcshrc Inside the configuration script: setenv / export alias Set environment variable Create alias C shell script example (CHPC) alias ll “ls -l” setenv EXEC “$HOME/programs” setenv PATH $EXEC/bin/:$PATH Bash script example alias ll=“ls -l” export EXEC=$HOME/programs export PATH=$PATH:$EXEC/bin/ source echo var apply changes to bash script for interactive shell display value of environment variable which ps [aux] top find grep cat tail [–n] returns the path to the command executable list of active processes list of top active processes (updated ) find a file or directory find a phrase in text display content of a file display the last lines of a file su chmod chown switch to superuser. Need root privileges change permissions on a file/dir change owner of a file/dir wget download file from URL Find the location of the Matlab install at CHPC Create an environment variable called $MATLAB_HOME that points to the install of Matlab version R2006 and add it to your PATH so it becomes the default version Create an alias to display the version of java Create a script called hello.sh that says “hello world” when you run it. Ctrl-C Ctrl-Z Cancel job Stop job cmd & bg fg jobs execute cmd in the background move job to background move job to foreground list current jobs $ sleep 100 — Start a dummy job in foreground. (sleep = waits a x amount of second) Press Ctrl+z to stop the current job. $ bg — Move the last stopped job to background. $ sleep 150 — Dummy job 1 Press Ctrl+z to stop the current job. $ sleep 140 — Dummy job 2 Press Ctrl+z to stop the current job. $ sleep 130 — Dummy job 3 Press Ctrl+z to stop the current job. $ jobs — List all active jobs. $ bg 2 — Move the 2nd active job to background.