Conics
advertisement

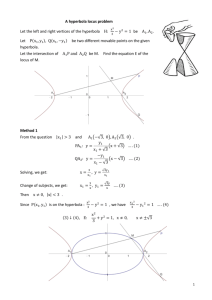
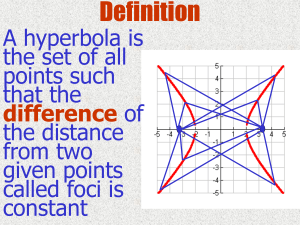
Conics Hyperbola Conics Hyperbola Cross Section Hyperbola A hyperbola is the set of all points in a plane whose distances from two fixed points in the plane have a constant difference. The fixed points are the foci of the hyperbola. The line through the foci is the focal (major) axis. The point on the focal axis midway between the foci is the center. The points where the hyperbola intersects its focal axis are the vertices of the hyperbola. Horizontal Vertical Axis The chord lying on the focal axis connecting the vertices is the transverse axis. Semi transverse axis—the distance from the center to the vertex—(a) Hyperbola with center (0,0) Horizontal Vertical STD Focal Axis Foci Vertices Semi-Tran Axis Semi-Conjugate Axis Pythagorean Rel. Asymptotes x-axis (±c,0) (±a,0) a b c²=a²+b² y=±(b/a)x y-axis (0, ±c) (0, ±a) a b c²=a²+b² y=±(a/b)x E1 • 1) Plot x² - y² = 1 E1 a2 = 1, so a = 1 b2 = 1, so b = 1 This equation is for a hyperbola whose center is at the origin. So sketch in the green square. Draw the green lines through the diagonals of the square, these are the asymptotes. The vertices occur at y=0, substituting into the equation we get: x2 - 0 = 1. x = ± 1 Plot the vertices (red dots) and sketch the branches without crossing the asymptotes. E2 Plot (x²/9) – (y²/16) = 1 E2 • Here a2 = 9, so a = 3 • and b2 = 16, so b = 4 • when y = 0, x2 = 9 so the vertices are • at x = ± 3 • Plot the green rectangle, sketch in the asymptotes, and mark the vertices. Now sketch in the hyperbola without crossing the asymptotes. Hyperbola with Center (h,k) E3 Plot (y²/49) – (x²/4) = 1 E3 • • • • • • Notice that the signs have interchanged, the minus is in front of x2 and the plus sign is in front of y2. This is a hyperbola the opens along the Y axis. We have b2 = 49, so b = 7 and a2 = 4, so a = 2. The vertices are at x=0, substituting in we get y2 / 49 - 0 =1 which is y2 = 49 so y = ±7 Plot the green rectangle, the asymptotes through its diagonals and the vertices then sketch in the hyperbola without crossing the asymptotes.