Supervising Module PowerPoint presentation
advertisement

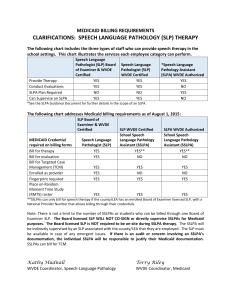
TRAINING MODULE Supervising Speech-Language Pathology Assistants (SLPAs) Roles and Responsibilities Resources West Virginia Department of Education Office of Special Programs Introducing this Module This module is designed to provide information and guidance for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) supervising speech assistants. The supervising SLP should view this module and document completion of the module on the supervision plan form. A module is also available for speech assistants which must be completed and documented on the supervision plan. Historical Perspective ASHA proposed guidelines for the use of support personnel as early as 1969. ASHA revised guidelines for speech-language pathology assistants (SLPAs) in 1988, 1995, & 2000. SLPAs have been utilized in school settings in many states since the 1970s. Increased use of SLPAs parallels use of assistants in OT, PT, & Education. Use of support personnel in recent years reflects the need to contain costs in health care and education. WVDE Guidelines WVDE developed Guidelines for the Use of Speech Assistants in West Virginia Public Schools • Provides guidance to WV school districts. • Outlines roles/responsibilities of SLPA and supervising SLP. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) resources were incorporated into guidelines. To access the document, click on the following link: http://wvde.state.wv.us/osp/guidelinesforspeechasst.pdf West Virginia Department of Education (WVDE) Definition: Speech Assistants • Speech Language Pathology Assistants (SLPA) individuals who may provide services to students with communication disorders under the guidance and direction of a certified SLP. • SLPAs may assist the supervising SLP with record keeping, generalization of learned skills to multiple settings, implementation of assistive technology devices/services, services for diverse and underserved populations, and other responsibilities. (WVDE, 2004) ASHA DEFINITION AND REFERENCES Support Personnel • Definition: Support personnel: people who, following academic and/or on-the-job training, perform tasks as prescribed, directed, and supervised by certified speechlanguage pathologists. There are different levels of support personnel based on training and scope of responsibilities. • ASHA References – Speech-Language Pathology Assistant Scope of Practice (2013) • http://www.asha.org/uploadedFiles/SP2013-00337.pdf – SLPA Frequently Asked Questions • http://www.asha.org/associates/SLPA-FAQs/ Criteria: Speech Assistant Hold a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in speech pathology or communication disorders from an accredited institution; Be employed by a local West Virginia board of education; Receive the recommendation of the district superintendent verifying that the applicant is the most qualified candidate for the position and that no fully certified speech-language pathologist has applied for the available position; and Complete Form 38 & Form 38A and submit them to the Office of Personnel Preparation , WVDE Speech Assistant Roles and Responsibilities Provide direct and indirect speech therapy services to students under the supervision of a certified SLP. Participate with the SLP in research projects, staff development and public relations programs, as deemed appropriate by the SLP. Assist with other clerical duties as assigned by the supervising SLP. Schedule activities, prepare charts, records, graphs, or otherwise display data. WVDE Application Forms • FORM 38 “Temporary Authorization for Speech Assistant” & Form 38A, “Supplement to Form 38” are contained in one document must be completed and submitted to the WVDE, Office of Personnel Preparation • http://wvde.state.wv.us/certification/forms/documents/Form38.pdf • Contact WVDE Office of Professional Preparation for questions : http://wvde.state.wv.us/certification/ • • Scottie Ford, smford@access.k12.wv.us Sherri Hudnall shudnall@access.k12.wv.us Supervision Requirements Speech Assistant • “It is the responsibility of the supervising SLP and the special education director to collaboratively design and implement a supervision system that maintains the highest possible standard of quality.” (WVDE Guidelines p. 8) • Supervision Plan MUST be completed and submitted annually for approval to: Kathy Knighton (kknighto@access.k12.wv.us) Office of Special Programs West Virginia Department of Education • WVDE, 2005 WVDE, 2005 The Supervision Plan The supervising SLP and special education director collaboratively design and implement a supervision system. The amount and type of supervision required should be based on the skills and experience of the speech assistant. The supervisory responsibilities should be mutually agreed on by the supervising SLP and special education director. (WVDE Guidelines p.11) Supervisor Requirements WVDE Guidelines specify SLP must hold a master’s degree SLP must be certified through WVDE SLP must have practiced speech-language pathology for at least two (2) years following certification. What are the Supervising SLP’s Responsibilities? The amount of supervision depends on the complexity of the case and the experience of the assistant. 14 Specific responsibilities are listed in the WVDE Guidelines. These are listed on the next slide. SLPA Supervision Responsibilities 1. Inform families 2. Represent team 3. Determine caseload 4. Communicate with families 5. Diagnosis & evaluation 6. IEP review 7. Delegate tasks to assistant 8. Develop/ Review IEP WVDE, 2005 9. Interactions w/ other professionals 10. Review & sign progress notes 11. Coordinate assistant training 12. Provide & document supervision 13. Ensure practice is within scope of responsibility 14. Performance appraisal of assistant How Much Supervision? SLPAs: New Employees In the first 90 days • At least 30% supervision weekly • 20% must be direct supervision Returning SLPAs • Supervision may be adjusted depending on skills of SLPA based on previous evaluation data How Much Supervision? AFTER THE 90-DAY WORK PERIOD…… Additional supervision, beyond the minimum 30% may be necessary depending on the skills of the assistant. The amount of supervision may be adjusted depending on needs of individual served, and the nature of the assigned tasks. The minimum recommended is 20% supervision, with no less than 10% being direct. What Is Direct Supervision? • Direct supervision means on-site, in-view observation and guidance. What Is Indirect Supervision? Indirect supervision may include: • Demonstration • Record review • Review and evaluation of audio or videotaped sessions • Interactive television • Skype – Facetime • Supervisory conference conducted by telephone What Happens if the Supervisor is NOT Available? If for ANY reason the supervisor is no longer available to provide the level of supervision stipulated, the assistant may NOT perform tasks until an appropriately certified SLP has been designated as the assistant’s supervisor. How Many Assistants May an SLP Supervise? At no time may an SLP supervise more than three ( 3) speech assistants. SLPA FORMS These forms are to be used by the LEA and SLPA to document the services provided. There is no requirement to submit to the WVDE. • Session Documentation Form Use to document goals, materials, activities, evaluation and comments about sessions with students • SLPA Self-Evaluation Form Use to evaluate your clinical performance during direct therapy sessions with students • Supervising SLP Evaluation Form Use this to evaluate your supervisor and his/her clinical interactions with you Supervising SLP FORMS These forms are to be used by the LEA and supervising SLP to document the services provided. There is no requirement to submit to the WVDE. • WVDE Direct Observation Form • Use to record direct observation suggestions and follow-up • Supervision Log Direct / Indirect • Use to record direct and indirect supervision • WVDE Summary Observation Log • Document number of sessions provided and percentage of sessions supervised WVDE, 2005 Tips for Supervision • Effective Supervision is: an opportunity for teaching an opportunity to provide feedback in a way that facilitates learning an opportunity to develop professional relationship Components of Effective Supervision of SLPAs Defining & communicating the job activities and tasks that are within the scope of responsibilities of a speech-language pathology assistant. Counseling and coaching for improved performance. Providing job-related instruction including planning and organizing the work to be delegated to the SLPA. Components of Effective Supervision of SLPAs Evaluating the performance of the SLPA Providing formative feedback to the SLPA Providing consequences for less than acceptable performance Arranging the environment to support a positive performance……. from Moore, S.M. & Pearson, L. (2003) Competencies and strategies for speech-language pathology assistants. Delmar Learning: Clifton Park, NY. WVDE, 2005 Feedback Strategies Formal & informal notes Verbal feedback Documented observations Checklists Feedback from satisfaction surveys ( families, students, educators etc.) Feedback from other staff members Regularly scheduled conferences Videotape of session Electronic feedback Formal performance appraisal procedures accepted by the site Data related to client’s progress from Moore, S.M. & Pearson, L. (2003) Competencies and Strategies for SpeechLanguage Pathology Assistants. Delmar Learning: Clifton Park, NY WVDE, 2005 Resources Moore, S.M. & Pearson, L. , Competencies and Strategies for Speech-Language Pathology Assistants. Delmar Learning: Clifton Park, NY (2003) SLPA Questions and Answers (WVDE Website) Questions: Kathy Knighton, Office of Special Programs (kknighto@access.k12.wv.us) 304-558-2696 WVDE, 2005 THANK-YOU!!!!! 3/23/2016