Marine Fishes - BIOL265MarineBiology
advertisement

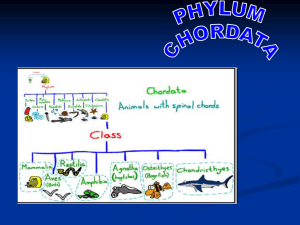
Marine Fishes BIOL265 Dave Werner Kingdom Animalia – Phylum Chordata Major Characteristics found in all chordates: 1. Notochord – a stiff but flexible rod along the length of the body 2. Dorsal hollow nerve chord – neural structure that develops into the brain and and central nervous system 3. Pharyngeal gill slits – openings or grooves found on the cavity behind the mouth (found in all chordates at least at some stage of their life cycle) 4. Post-anal tail Kingdom Animalia – Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata : Tunicates - ~1400 entirely marine species, including sea squirts. Sessile, filter feeders… Body may look like that of a sponge but they have a leathery outer protective layer called the tunic that feels very different from sponges… internally, they are quite complex… Kingdom Animalia – Phylum Chordata subphylum urochordata Although urochordates are sessile, they typically have motile larvae that truly exhibit all the chordate characteristics… In a few cases however (i.e. salps); the urochordates retain the larval form even as adults, remaining motile… Tunicates Also, tunicates may be solitary… … or colonial What would be the advantages or disadvantages of each of these lifestyles? Kingdom Animalia – Phylum Chordata Subphylum Cephalochordata : Lancelets - ~ 29 species of small “fish-like” organisms with all the typical “fish” characteristics, other than a backbone… They live on soft bottoms, and use gill slits to filter feed… Kingdom Animalia – Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata : The vertebrates represent a diverse group of animals… Simply put however, they are chordates with a backbone. Their backbone (or vertebral column, or spine) is made up of a dorsal row of hollow skeletal elements that protect the nerve cord (or spinal cord). Marine Fishes Class Agnatha – Jawless fishes … feed by suction and help from their round muscular mouth with rows of teeth… Include hagfish (or slime eels) that feed on dead or dying organisms… sometimes from the inside out!!! … include about 20 species. Other agnathans include lampreys which either feed on invertebrates, or attach to other fish and such their blood… include about 30 species. Jawless Fish Phylum: Chordata Sub-Phylum: Vertebrata Class: Agnatha • There are two primary marine types of the class Agnatha. They are Hagfish and Lampreys. • Most Primitive living fishes • Hagfish are of the order, Myxiniform. They are related to the slimefish. They have the peculiar habit of tying themselves into knots in order to shed their slime coat and make a new one. Hagfishes • • • • 20 known species Deep, cold waters 2.6 ft. Skin is used for leather goods Hagfish • • • feed on polychaete worms, shrimp, and dead or dying fish attach to fish, form a knot in the tail and pass it forward to rip off flesh. Image © BIODIDAC. usually enter coelomic cavity and feed on soft parts • many mucous glands present for antipredator defense Lampreys http://itech.pjc.edu/jwooters/zoology/virtual_review/lamprey.htm • Lampreys are of the order, Petromyzontiform. They are suckers and attach themselves to fish in order to parasitize off them. • Found in Freshwater • 30 species Sea Lamprey Life Cycle • A. Sea lampreys go through an extended larval phase before metamorphosing into the bloodsucking parasitic phase. Each summer and fall there is one group of parasitic sea lampreys actively feeding in the Great Lakes. B. The next spring, that group leaves the lake and migrates into tributary streams where they must build nests in clean gravel with flowing water. C. Each female spawns an average of 60 to 70 thousand eggs. D. After hatch, the larvae drift downstream to areas with slower currents and sand/silt bottoms. There, they establish permanent burrows and enter a larval stage varying in duration from 3 to 10-ormore years. E. Larvae lack eyes and the oral disc. Living concealed in their burrows, they are harmless and filter microscopic material from the water for food. When they reach lengths of 120 mm or more, some individuals begin metamorphosis in mid summer. F. During metamorphosis they develop eyes, the oral disc, and changes in their kidneys that (in their native range) would allow them to enter the salt water of the Atlantic Ocean. That fall or the following spring, they instead enter the Great Lakes to feed parasitically on fish that summer and fall, and mature and spawn the next spring—completing their life cycle. Sea lampreys only spawn once and then die after spawning.