CrossElasticity and Income Elasticity
advertisement

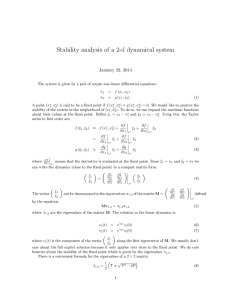
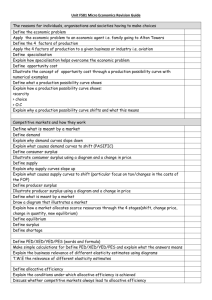
Cross Elasticity of Demand Definition • Measures how much the demand for the product changes when there is a change in the P of another product. • % change in QD of product X • % change in P of product Y Pizza and Burgers • Competitors Burger P drops from $2 to $1.80 • Because of this the QD of your Pizza’s drops from 400 to 380. • Burgers -20 = -10% -5 = 0.5 200 -10 • Pizza -20 = -5% 400 What this means • XED Explains the relationship between products. • Result can be + or – • This is important as unlike PED it matters. • If it is + then the 2 goods are substitutes for each other. The higher the Value, the closer the substitute. • Margarine example XED • When XED is – then the 2 goods are said to be complements. • Those that have very low values are said to be close complements. • Computer gaming example. • Some products such as Matchsticks and houses are not related at all so an increase in P in one would have no effect on the other. Questions • In each Q explain the relationship between the products, explaining whether they are substitutes or complements to one another and why you feel that way. • 2 products • McDonalds and Burgerking • P of Bmac falls from $3 to $2.50 • QD of Whopper falls from 400 to 350 • Calculate XED Questions • • • • Xbox Console Xbox games P increase from $200 to $220 for Console QD of games decreases from 300 to 250 games • Calculate XED and explain their relationship. Income Elasticity of Demand • Measures how much demand changes for a product when there is a change in the consumers income. • Income rises from $60,000 to $66,000, a change of 10% • Holiday spending increases from $2,500 to $3,000, a change of 20% • 20 = +2 • 10 Results • Like XED + or – is important as it tells us if it is a normal or an inferior good. • Normal? • Inferior? • Engel Curve. Questions on YED • Income of Mr. McKeown increases from $40,000 to $44,000 (he’s only a teacher!). • His spending on computers increases from $1,000 to $2,000 per annum. • Calculate the YED and explain its significance in relation to Mr. McKeown . Question • Income of Mr. Snowball decreases from $100,000 to $80,000 per annum. • His spending in Aeon falls from $10,000 to $8,000 per annum. • Calculate YED and its significance in relation to Mr. Snowball and his shopping.