EnvironmentalHazards_Dinos
advertisement

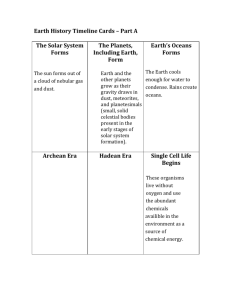
Environmental Hazards BRING: Video: Asteroids, Deadly Impact “Rock” samples – paper with parent and daughter percents Graph paper U238 parent daughter graph 2cmX8cm strips of paper DISCLAIMER: These notes do NOT cover everything you need to know. You may need to look up some item or concept online or in a text. Test questions are not exact copies of the OBJECTIVES but if you know the OBJECTIVES thoroughly, you should do well on the exams. Part 1 - Global Warming- rough notes Part 2 – What killed the dinosaurs? – rough notes Part 1 - Global Warming Rough Notes Covered in class and notes on “Comparative Environments” I will not ask you about this on Test 2. BUT be sure to do the assignment GLOBAL WARMING Points from this assignment COUNT TOWARD TEST 2. Part 2 – What killed the dinosaurs? – rough notes OBJECTIVES: Define and differentiate between the following: atom, element, molecule, ion, isotope. (Look up these on line or in your text.) What is meant by radioactivity? For what do astronomers use radioactivity? What is meant by parent and daughter in this context? Define half-life. If you start with 100 grams of radioactive material, how much is left after one half-life? After two half-lives? After three half-lives? Given a graph of a parent-daughter decay, and given a “sample” with a known parent percent, find the age of the “sample” What evidence suggests that a meteor strike killed the dinosaurs? When? CLASS: Death of dinosaurs ~65 million years ago Eras and mass extinctions from fossil records Permian (~251 million years ago) - ~ 90% of species on Earth wiped out Late Cretaceous (65 million years ago) – 70 % of species wiped out Others We will focus on the Late Cretaceous era. Some terminology regarding eras: Older sources define the era after the Cretaceous (symbol K) as the Tertiary (symbol T) era. Newer sources define the era after the Cretaceous as the Paleocene era. These notes use the older terminology. Something happened to wipe out the dinosaurs and 70% of the species on Earth Fossil record (Dinosaurs, ammonites) How do we know the ages? One way: Radioactive dating, half-life See http://www.agiweb.org/news/evolution/datingfossilrecord.html for example. Or http://www.astronomynotes.com/solfluf/s4.htm Or http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/radioactive-dating-game Done in class - Exercise on half-life and reading parent-daughter decay graphs to find the age of a sample. Sample parent-daughter graph (Currently unable to find the source for this graph.) Could volcanoes have wiped out the dinosaurs? Examples – Pinatubo, St Helens, Deccan Traps More likely a meteorite impact (Alvarez and company) Or a combination of the two Original Alvarez paper: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1980Sci...208.1095A Nice summary at: http://science.jrank.org/pages/2643/Extinction-asteroid-impact-theory.html Evidence for meteor impact 1. K-T layer or boundary Thin, dark layer, world-wide, 65 million years ago Dino fossils below, none above 70% of species on Earth died out 2. K-T layer is dark 3. Iridium in K-T layer 4. Shocked quartz in and near K-T boundary 5. Chixulub crater in Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/earth/features/chicxulub.cfm Has Earth been whacked before? Other craters http://liftoff.msfc.nasa.gov/academy/space/solarsystem/meteors/Craters.html Other impacts – Example Chelyabinsk Feb 2013 Other collisions in solar system: Jupiter impact (Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 in 1993) Chelyabinsk Feb 2013 Potential for future collisions http://liftoff.msfc.nasa.gov/academy/space/solarsystem/meteors/ImpactHazard.html See also video: “Asteroids: Deadly Impact” from National Geographic especially the part starting with Gene Shoemaker through Tunguska. Updates on what killed the dinosaurs 2012 Stronger argument for volcanoes as primary source http://www.livescience.com/25324-volcanoes-killed-dinosaurs.html 2015 Impact in Yucatan doubled volcanic activity in Deccan Traps https://www.theguardian.com/science/2015/oct/01/asteroid-that-killed-dinosaurs-also-intensifiedvolcanic-eruptions-study Revised 21 March 2016