Module The Study of Economics
advertisement

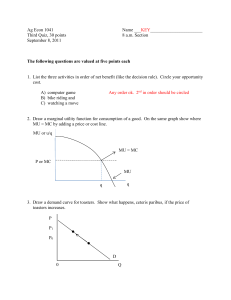
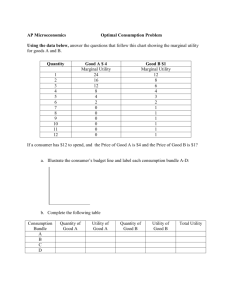
Module Micro: 15 Econ: 51 Utility Maximization KRUGMAN'S MICROECONOMICS for AP* Margaret Ray and David Anderson What you will learn in this Module: • How consumers make choices about the purchase of goods and services • Why a consumer’s goal is to maximizing utility • Why the principle of diminishing marginal utility applies to the consumption of most goods and services • How to use marginal analysis to find the optimal consumption bundle Maximizing utility In the Theory of Consumer Choice, consumers’ goal is to maximize their utility. Utility • Utility: a measure of the satisfaction the consumer derives from consumption of goods and services. • Utility and Consumption • The principle of diminishing marginal utility – Definition of 'Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility‘ A law of economics stating that as a person increases consumption of a product - while keeping consumption of other products constant there is a decline in the marginal utility that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product. Budgets • The budget line • The optimal consumption bundle The consumer’s challenge is two-fold: Good Y B C A 1. Find the bundles of goods that are affordable, given income and prices, and 2.Choose the bundle that provides the highest utility. Good X Spending the Marginal Dollar The “utility maximization rule” says that the consumer should spend all of his income on two goods such that: • Marginal utility • MU per dollar • Optimal consumption MU/P is equal for both (all) goods. As long as one good provides more utility per dollar than another, the consumer will buy more of the first good; as more of the first product is bought, its marginal utility diminishes until the amount of utility per dollar just equals that of the other product. Definition of 'Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility‘ Figure 51.1 Cassie’s Total Utility and Marginal Utility Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers A law of economics stating that as a person increases consumption of a product - while keeping consumption of other products constant - there is a decline in the marginal utility that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product. Figure 51.2 The Budget Line Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Table 51.1 Sammy’s Utility from Clam and Potato Consumption Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Table 51.2 Sammy’s Budget and Total Utility Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Figure 51.3 Optimal Consumption Bundle Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Table 51.3 Sammy’s Marginal Utility per Dollar Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Figure 51.4 Marginal Utility per Dollar Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers