Risk assessment - Disability Safe
advertisement

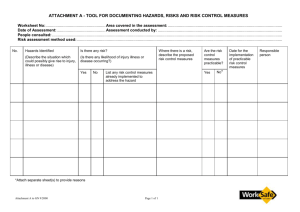
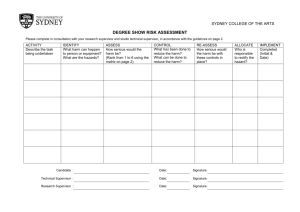
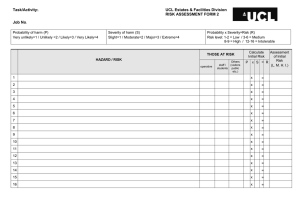
TOOL BOX TALKS OHS Risk Management Definitions • Hazard – anything with the potential to cause harm to a person or damage to property • Risk – the actual harm which can result • Think of a shark in a pool – shark is the hazard, risk relates to level of hunger, presence of people, swimming ability etc. How to identify hazards • Informally through observations or complaints • Formally through inspection checklists for your own workplace, clients home, community venues, host employer workplaces, client assessments, intake information, incident reports, MSDS or equipment audits, equipment instruction manuals, safety audits Organisations Hazard Identification Strategies • Discuss what you use, when it is used, who uses it and the consultation undertaken How to assess the level of risk • Refer to available information to determine the likelihood of harm occurring and the consequences of the harm i.e. severity of injury • Consider contributing factors such as work environment, capacity and experience of worker, training provided, knowledge of client mobility/behaviour • Consider workplace knowledge e.g. past history, work organisation, level of exposure etc • Rate the risk according to the following matrix Risk Assessment Exercise • Give some practical examples depending on services provided e.g. 1. providing home support and large dog present 2. Community access with client who is unsteady on feet 3. Client in a disability enterprise who tends to swear at other clients – upsetting them HAZPAK – Risk Assessment Model 1 How severely could it hurt someone, or how ill could it make someone? Kill or cause permanent disability or ill health ! Long term illness or serious injury !! Medical attention or several days off work !!! First aid needed 2 How likely is it to be that bad? __ VERY LIKELY LIKELY UNLIKELY VERY UNLIKELY Could happen any time Could happen sometime Could happen, but very unlikely Could happen, but probably never will 1 1 2 3 1 2 3 2 3 4 3 4 5 4 5 6 The numbers show you how important it is to do something: 1 Top priority: do something immediately 6 Low priority: do something when possible Risk Controls • Eliminate hazard if possible e.g. cease activity completely • Minimise risk from hazard by implementing suitable controls. • Develop in accordance with Hierarchy of Controls using one or more to achieve highest level of control possible. HIERARCHY OF CONTROLS In relation to discomfort whilst using oven cleaner 1. Eliminate the hazard e.g. Cease performing cleaning task If this is not practicable 2. Substitute the hazard with something of e.g. replace cleaning product with a low lesser risk toxic product If this is not practicable 3. Use engineering controls e.g. redesign, ventilation, isolation e.g Mechanise the process through a pump system, If this is not practicable 4. Use administrative controls e.g. write a safe work procedure covering cleaning tasks and provide training If this is not practicable 5. Use Personal Protective Equipment e.g. Issue gloves, mask and overalls 3/23/2016 Risk Control Exercise • Using previous examples developed develop some risk controls for the situations e.g. 1. Dog required to be confined to back yard during service (not including hanging out washing) 2. Utilise wheelchair when taking client out 3. Identify cause of swearing and address, separate client from others, reward client for not swearing by giving responsible task and include in behaviour support plan