Example of Data Guided Prevention planning using logic model
advertisement

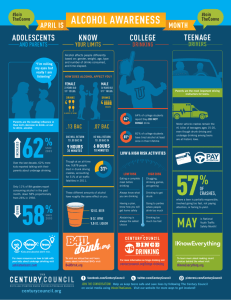
Evidence Based Environmental Strategies Reduce Underage Drinking and Accidental Death and Injury Among Youth Overall Objectives Participants will: Understand why it is important to take an environmental approach to underage drinking Get an overview of environmental strategies to reduce accidental death and injury among underage drinkers What research based approaches have met with success in communities Examine and discuss the relationship of policy and enforcement to alcohol prevention work Learn Available resources and tools to support this work Underage Drinking Enforcement and Training Center (UDETC) background Identify Promising Strategies Develop Curriculum Publish Supporting Documents Deliver Training Provide Technical Assistance Follow up ABOUT UDETC Why focus on Alcohol/Underage Drinking? ALCOHOL is the #1 drug problem in this country; and the #1 drug of choice for youth in the US and results in a host of physical, legal, economic, and social consequences for youth and the communities in which they live. FACT: The alcohol industry earns approximately $22 billion/year from underage drinkers? Underage Drinking Stats Alcohol Kills more than 5,000 Youth Each Year in the US, which equals 13 youth each day. Source: Why Do Adolescents Drink, What Are the Risks, and How Can Underage Drinking Be Prevented?, Number 67, January 2006, NIAAA Underage Drinking Stats Each day, more than 7,000 kids in the United States under age 16 take their first drink (IOM Report, 2004) Fact: 36% of eighth graders have consumed alcohol (Monitoring the Future, 2011) Underage Drinking Stats Most kids drink to get drunk consuming four to five drinks at one time. (NIAAA, 2006) Fact: In 2011, Monitoring The Future (MTF) data showed that 16% of 8th graders, and 54% percent of 12th graders report having been drunk at least once.. Underage drinking has many potential consequences • • • • • Accidental falls, burns, and drowning Alcohol dependence Alcohol poisoning Brain damage Cirrhosis of the liver • • • • • Death Impaired driving Pregnancy Poly drug use Poor school performance (including learning impairment) • • • • • • • Sexual assault STDs Traffic crashes Truancy Violence Vandalism Work productivity loss The HUMAN Costs of Underage Drinking (youth, ages 18-24) per year • • • • • • • • 1,700 college student deaths 599,000 youth who are unintentionally injured 696,000 youth who are assaulted 97,000 sexual assaults 400,000 incidents of unprotected sex 2.1 million drive under the influence 110,000 arrested for alcohol violations 31% of college youth meet the criteria for alcohol abuse Source: College Drinking: A Snapshot of Annual High-Risk College Drinking Consequences. www.collegedrinkingprevention.gov/facts/snapshot.aspx What’s Different About Youth Drinking Today? Before Today What’s Different About Youth Drinking Today? Before • • • • • • Pooled Money Meet in person or contact by “land line” Piled in 1 Car Modified Paper Licenses 6 Pack of beer shared by the group Drinking in Fields Today • • • • • • Everybody’s Got $$ Cell phone and text messaging Meet at the Beer Store Computerized Fake IDs Kegs/Large Quantities of Alcohol (Beer and liquor) Drink in Homes, Hotels, Limos, Remote locations The US Surgeon General issues a “Call to Action” to prevent underage drinking (March 6, 2007) Calls upon members of Society to recognize the severity of the problem of the underage drinking in the United States and reduce alcohol use by children and adolescents to protect them from the negative effects of underage drinking. Information can be found at: www.surgeongeneral.gov 2 Ways To Make Change 1. We can focus on what’s going on inside a person (i.e. feelings and individual choices). 2. We can focus on what’s going on around a person (i.e. conditions in the environment). 2 Types of Prevention Strategies Individual Strategies • • • • Focus on behavior, feelings, and skills School-based education programs Counseling services Incentives for healthy behavior Alternative activities for youth Environmental Strategies Focus on causes and conditions • Changing economic conditions • Cost & Availability • Changing social conditions • What people think & how they live • Changing media conditions • What people read, watch, hear & see • Changing political conditions • Who has power & influence None of us lives in a vacuum; we are all affected by the conditions in our environment. FAMILY COMMUNITY CHURCH WORK SCHOOL Individual TV MOVIES, MUSIC FRIENDS GOVERNMENT FINANCES What are Environmental Strategies? Strategies used to reduce problems associated with the use of alcohol through changes in the physical, social, legal, and economic environment Basic Concepts of Environmental Change Establishes or changes community standards • Policy-oriented • Addresses physical, social, legal, & economic factors • Involves citizen participation, including youth • Engages citizen action • Involves partnerships with law enforcement, the legal system, community groups, and community leaders • Environmental Strategies What’s So Great About Them? 1. 2. 3. 4. Effective and Efficient Immediate Results Long lasting effects Inherently Sustainable What questions should we be asking? • • • • • • • What alcohol laws/ordinances are in place or lacking? Are laws being consistently enforced? Do advertising laws exist? Is there comprehensive/collaborative enforcement of existing laws? Are there locations where youth can easily obtain or know they can easily obtain alcohol? What policies/programs exist in local schools? What are the attitudes of parents and other adults in the community? Limitations on Access Expressions of Community Norms Strategies Prevention of Impaired Driving Strategies Based in Schools Essential Elements of Effective Prevention of Alcohol Problems Policy Prevention Public Support Enforcement Environmental strategies integrate three key components into a comprehensive plan to address underage drinking within the community as a multi-pronged approach that occurs on an ongoing basis. Components of a Comprehensive Plan PIRE EXAMPLE OF DATA GUIDED PREVENTION PLANNING USING LOGIC MODEL Example: Logic Model for Reducing Underage SubstanceDrinking Substance Causal Strategies Related Consequences Use Alcohol-related crash fatalities Alcohol Poisoning Violence/Crime School Problems Teen Pregnancy Underage drinking Factors (Examples) Easy Retail Access to Alcohol for youth Educate retailers to check ID and enforce underage sales law Low enforcement of alcohol laws Enforce underage alcohol laws (compliance checks, sobriety checkpoints) Easy Social Access to Alcohol (parties, peers, family) Social Event Monitoring and Enforcement Social Norms accepting and/or encouraging youth drinking (peer, family, community) Media Advocacy to Increase Community Concern about Underage Drinking Promotion of alcohol use (advertising, movies, music) Restrictions on alcohol advertising in youth markets Low or discount pricing of alcohol Bans on alcohol price promotion/happy hours Outcome-Based Logic Models Represent complex systems of cause and effect Encourage planners and implementers to focus on the most important and strongest paths for creating change Can be constantly reviewed/revised to understand relationships, adapt to new circumstances, and accommodate success Bring data and evidence to selecting key strategies for prevention planning How can we use this outcomes based logic model for environmental strategies? UDETC recognizes four interlocking strategies to reduce underage drinking Limitations on Access Expressions of Community Norms Strategies Prevention of Impaired Driving STRATEGIES Strategies Based in Schools Limitations on access help reduce alcohol availability to minors. Limitations on Access ACCESS •Enforce minimum age purchase laws: -aimed at retailers - aimed at adults - aimed at youth •Strengthen minimum age purchase laws •Reduce social availability •Reduce overall community availability of alcohol Limitations on Access: Commercial Availability Limitations on Access Vigorous use of compliance checks Application of appropriate sanctions to violating merchants Education of merchants regarding techniques and responsibilities (RBS Training) Require alcohol sellers and servers to be at least 21 years old Prohibit those under 21 from entering alcohol establishments Limitations on Access Elected officials in the City of Knoxville and Knox County have stepped up their support and commitment to reducing underage drinking. As a result, the Knox County Commission and the Knoxville City Council have passed ordinances related to mandatory photo ID checks when purchasing alcohol and increased compliance check operations. A coordinated media campaign related to underage drinking prevention was created and was instrumental in maintaining high levels of public support for law enforcement efforts on underage drinking. Questions What obstacles do epidemiologists and prevention professionals face in proving the case for reducing alcohol density? How do scientists best make their case on issues that can be very political? What do you find is the best way to share data? Limitations on Access: Commercial Availability (continued) Limitations on Access Controls on hours of sale and drink specials Controls on outlet location/density Increase price through excise taxes Make the manufacture or purchase of false/fraudulent identification a crime Development of community support for enforcement operations Limitations on Access: Social Availability Limitations on Access Special enforcement campaigns to prevent parties where alcohol is served Keg registration laws Enforcement of laws against buying alcohol for minors (third-party transactions) Enforcement of social host laws Source Investigations Development of community support for enforcement operations Limitations on Access The community of Long Beach successfully adopted the first social host ordinance in the State of New York. Collaborations between law enforcement and key community leaders were instrumental in the passage of the policy change which has since been adopted as a model to be used by other communities throughout the State of New York to aide communities in more effectively addressing youth alcohol access issues in social settings. New York Tip: Use Comprehensive Community Interventions Involve multiple departments of city government and private citizens Use multiple program strategies – Community organizing and mobilization – Environmental policy change – Heightened enforcement – Media advocacy – Education Remember: Environmental (Not just educational!!!) Realistic Specific to the problem “Sellable” to the public Provides opportunities for wide involvement Be strategic Tell your success stories Never doubt that a small, committed group of people with a good idea can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. - Margaret Meade National Resources AIDA (American Indian Development Associates) AMA (American Medical Association) Center for Enforcing Underage Drinking Laws Program at PIRE (Funded by OJJDP) CADCA (Community Anti-Drug Coalitions of America) CAMY (Center on Alcohol Marketing and Youth) CDC (Centers for Disease Control) CSAP (Center for Substance Abuse Prevention) CSPI (Center for Science in the Public Interest) FACE: Truth and Clarity on Alcohol (Facing Alcohol Concerns through Education) National Resources Continued HEC (Higher Education Center) IACP (International Association of Chiefs of Police) Leadership to Keep Children Alcohol Free (Governor’s Spouses initiative) LCAT (Latino Council on Alcohol and Tobacco Prevention) MADD (Mothers Against Drunk Drivers) Marin Institute Municode.org NCPC (National Crime Prevention Council) NCJFCJ (National Council on Juvenile and Family Court Judges) National Resources Continued NJC (National Judicial College) NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) NIAAA (National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism) NLLEA (National Liquor Law Enforcement Association) OJJDP (Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention) ONDCP (Office of National Drug Control Policy) PERF (Police Executive Research Forum) National Resources Continued PIRE (Pacific Institute for Research and Evaluation) RWJ (Robert Wood Johnson Foundation) SAMHSA (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration) See our document, “Strategies to Reduce Underage Alcohol Use” for more information. •Visit our website to download free of charge: www.udetc.org STRATEGIES Other Services Provided by the UDETC Monthly Audioteleconferences Monthly Resource Alerts Success Story Features Research Information Toll-free Technical Assistance Hotline 1-877-335-1287 Internet Website www.udetc.org Web-based Alcohol Enforcement Databases Annual National Leadership Conference (August 10 to 12, Orlando, Florida)