Corporate PPT Template
advertisement

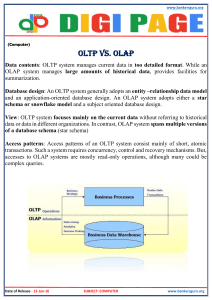
Carey Probst Technical Director Technology Business Unit - OLAP Oracle Corporation 3 Days: Raw Data to OLAP Session: 40206 A Practical Approach for Rapidly Delivering Successful OLAP Solutions Challenge Deliver fully-functional OLAP solution in 3 days Keys to Success: – – – – Existing, populated data source Well-defined scope of data destined for OLAP A little knowledge of Oracle Warehouse Builder A preference for a reporting interface How Is This Possible? Key points: Oracle moved the OLAP engine into the database – – No need to extract & reload data Leverage existing designs for OLAP Automation of complex OLAP design tasks with Oracle Warehouse Builder – Build, Deploy, Load & Query data Provide several methods of access – – – SQL access to OLAP Allowing mix-and-match of OLAP and Relational Support for multiple access tools & technologies OLAP Architecture & Terminology Oracle Database OLAP API Oracle Call Interface JDBC Relational Technology Object Technology OLAP Technology SQL Engine Table Functions Multidimensional Engine Relational Cubes Multidimensional Cubes Step 1: Populated Data Store Constructing OLAP solutions from warehouses is simple if – – – – – – Dimensions have been identified Hierarchies have been identified Measures are known Mapping to star schema is simplified Mapping to OLAP structures streamlined Many traditionally difficult queries can be easily solved by OLAP Step 2: Defined Scope of Data Know what data should logically be summarized for queries Know types of queries users will want to ask Known level of aggregation Known data transformations required Step 3: Oracle Warehouse Builder Oracle Warehouse Builder streamlines many complex tasks of building OLAP solution – Design & Metadata population – Deployment of OLAP Cubes – Loading of Data OLAP Design OLAP Design – Best Practices Best Practice Guidelines Long and Short Descriptions Dimension Attributes: – Level Attribute mapped to column with name suffixed by ‘_LONG_NAME’ or ‘_SHORT_NAME’ Time Dimension Descriptors: – – – – Table name suffixed with ‘_TIME’ Level Attribute with column suffix ‘_END_DATE’ Level Attribute with column suffix ‘_TIME_SPAN’ Level names suffixed with _DAY, _MONTH etc.. OLAP Design - Dimensions Metadata Design - Cubes OLAP Deployment OLAP Deployment Deploy scripts using the Deployment Manager Deploy OLAP metadata via OLAP bridge: – – – – Creates all skeleton objects (empty) Registered the objects in the OLAP catalog Binds the OLAP objects to the relational objects BI Beans enabled environment Creates a ROLAP environment OLAP Deployment OWB Generate Oracle Database Scripts OLAP metadata Bridge OLAP catalog metadata Register Register PL/SQL DDL Deploy Relational Views Publish Tables, Dimensions, PLSQL etc.. Analytic Workspace Create OLAP Deployment - Bridge OLAP Data Loading OLAP Data Loading Load relational objects via a normal mapping Load the OLAP Analytic Workspace – Methods: Mapping – post mapping process Process Flow activity – – Refresh or Insert into Dimensions Refresh or Insert into Cubes Using an OWB wrapper procedure on top of the RDBMS PL/SQL OLAP Data Loading Oracle Database OLAP catalog metadata Registered Relational Views Sources Insert/Update Cubes, Dimensions, Tables Publish Analytic Workspace Load/Refresh Step 4: Reporting Choices Currently OLAP access is provided through: BI Beans – – The Java query components to enable OLAP Enables custom application development with several deployment options Discoverer – – The Ad-Hoc query tool now utilizing OLAP OWB capable of generating Business Areas for Discoverer SQL – Analytic Workspaces can be queried through SQL OLAP Worksheet in OWB – Provides visualization during design & build iterations Ongoing – Maintenance Add new measures Add new dimensions or hierarchies Modify existing hierarchies Add self calculating measures (formulas) Add new stored measures Use Analytic Workspace Manager to define the stored measure Run add_stored_measure utility to add to an existing Standard Format (SF) cube Modify SQL views if using SQL queries Re-run AW enablement for BI Beans if using CWM2 metadata Add new dimensions or hierarchies Create new hierarchy Add descriptions of hierarcy Populate parent relationship. Run groupingid to set new hierarchy details Run hierheight to set new level details Re-run AW enablement for BI Beans if using CWM2 metadata Modify existing hierarchies Make changes to parents, levels, etc. as required. Run groupingid to set new hierarchy details Run hierheight to set new level details Re-run AW enablement for BI Beans if using CWM2 metadata Add self calculating measures (formulas) Use Analytic Workspace Manager to define the formula Run add_cube utility to add to create a new Standard Format (SF) cube Run set_measure_formula_properties utility to add to the new cube Modify SQL views if using SQL queries Re-run AW enablement for BI Beans if using CWM2 metadata Viewing Data - Samples BI Beans - Crosstab Drill to Relational Detail (adhoc jtable) Ad Hoc query tool Beanie – Drill to Relational coming Excel Discoverer SQL views – any query tool (olap_table) BI Beans - Crosstab Relational Table - jtable Ad Hoc query tool Beanie – Oracle Consulting Excel Summary Existing Star schema not required but knowledge of data is Basic understanding of OWB necessary OLAP design understanding is critical Knowledge of OLAP structures and functionality mandatory Can use Oracle Workflow to automate updates Next Steps…. Interested in leveraging Oracle OLAP – Joseph Rayman – joseph.rayman@oracle.com 443-253-2440 – Carey Probst – carey.probst@oracle.com 518-584-4388 – Larry Anderson – larry.anderson@oracle.com 973-895-6113 QUESTIONS ANSWERS Reminder – please complete the OracleWorld online session survey Thank you.