human reproduction
advertisement

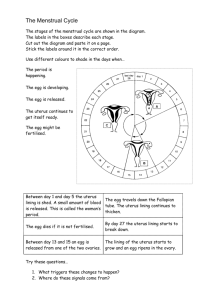
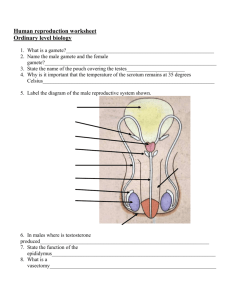
Human Reproductive System Living Environemnt Puberty – when a person becomes sexually mature and is capable of reproduction. Male Reproductive System: - Gonads = Testes - Gametes = Sperm Cells Sperm Cells made in the testes Testes - also act as an endocrine gland secreting testosterone, which is responsible for secondary sex characteristics. Body Hair, muscle development, deeper voice… Each testis consists of small coiled tubes called the Seminiferous Tubules. Immature sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules. After being produced sperm move to the epididymis where they are stored. Lave the epididymis through the vas deferens. The two vas deferens meet at the urethra. Glands secrete fluids into the sperm. The mixture or fluids and sperm = semen. The semen passes through the urethra by the process of ejaculation. Urine is blocked shortly before and after ejaculation. Female Reproductive System: - Gonads = Ovaries - Gametes = Eggs Ovaries make Eggs Ovaries – also secret female hormones including estrogen, which is responsible forsecondary sex characteristics. Breast Development, Broadened Pelvis… 2 ovaries that contain about 200,000 tiny egg sacs called follicles. Each Follicle contains 1 immature egg. These immature eggs are present at the time of birth. When one of the follicles ruptures the egg is released at the surface of the ovary = ovulation. First occurs at puberty. Oviduct or Fallopian Tube = tube with funnel like opening. Ciliated cells draw the egg into the oviduct. Passes through the oviduct into the uterus. Uterus = thick walled muscular pear shaped organ. Once the egg is in the uterus it can be fertilized by a sperm cell. Cervix connects uterus to the Vagina. During Pregnancy the child will pass through the cervix and leave the mother through the Vagina. Menstrual Cycle Mature egg is developed and released from one of the ovaries approximately every 28 days. The walls of the uterus have been building up preparing to accept the egg. If the egg is not fertilized the wall of the uterus breaks down. Material from the wall and the unfertilized egg and eliminate from the body. The cycle begins again with the maturing of another egg. This process is called the menstrual cycle. Begins during puberty age 12-15.Controled by hormones. Stages of the Menstrual Cycle: Follicle Stage = FSH (Follicle) Stimulating Hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland. FSH causes several follicles to begin to develop. Usually only one matures. As the follicle develops it secretes estrogen. Estrogen causes the uterine lining to become thicker.Usually lasts about 10 days Ovulation = High level of estrogen in the blood causes the pituitary gland to decrease the secretion of FSH and begin the secretion of LH (Luteinizing Hormone).When LH levels reach a certain point ovulation occurs. Follicle ruptures. Usually Takes place in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Corpus Luteum Stage = After ovulation LH causes the ruptured follicle to fill with cells forming a yellow body called the corpus luteum. Corpus Luteum begins to excrete the hormone progesterone, which continues the growth of the uterine lining. Lasts about 14 days. Menstruation = No fertilization occurs Menstruation = No fertilization occurs LH levels drop off Corpus Luteum breaks down Progesterone levels drop off Thick lining of uterus can not be maintained so it breaks down The extra lining, unfertilized egg, and a small amount of blood pass out the body through the vagina. Lasts about 4 days Pituitary gland begins to produce FSH again New egg begins to develop and cycle starts all over again Menstrual Cycle will stops temporarily during pregnancy. Around middle age (45-50) will stop permanently = menopause. Fertilization and Development: Sex - Hundreds of millions of sperm are ejaculated into the vagina. Travel through the cervix, across the uterus, and into the oviducts. If an egg is passing through the oviducts fertilization may occur. Zygote is formed. Implantation – Zygote undergoes cleavage developing into a blastula. At the same time it is moving down the oviduct toward the uterus. 5-10 days after fertilization zygote enters the uterus. Outer cells of the zygote secrets enzymes that eat away the lining of the uterus. Zygote attaches to that spot. Three germ layers develop. From this point on the developing human is called an Embryo. After 8 weeks the developing human is called a fetus. Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 During pregnancy the menstrual cycle is stopped. A hormone is secreted that prevents the break down of the corpus luteum, which continues to secrete progesterone, which maintains the thick lining of the uterus. In Vitro fertilization – fertilization occurs outside the body in a lab then zygote is placed back in the female’s uterus to develop. Between fertilization and implantation embryo survives off of food stored in the egg. After implantation embryo receives food and oxygen from the mother through the placenta. Outer layer of blastula forms chronin. Chronin = membrane that surrounds the embryo. Chronin villi project into the uterine lining and form the placenta. Placenta – has fetal side (fetus’s blood) and maternal side (mothers blood). Mother’s blood and Fetus’s blood never mix. Fetus is connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord. Carries nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, waste out of and away from the fetus. Placenta protects the fetus from harmful agents in the mother’s blood. Some things can still pass through the placenta = some viruses, alcohol, nicotine, most drugs. Extraembryonic Membranes – same as birds and reptiles, different purposes. Chronin = implantation. Amnion = filled with amniotic fluid, which surrounds and protects the fetus. Allantois and yolk sac = develops into the umbilical cord. Birth: Gestation period = length of pregnancy. In humans it is about nine months. When the fetus is ready to be born the uterus begin slow rhythmic contractions = labor. Same time cervix begins to enlarge. It must expand from 1 to 2cm to 11 or 12cm for birth to occur. When the cervix is completely expanded the amniotic membrane bursts lubricating the birth canal. Contractions force the fetus, head first, from the uterus into the vagina and out of the mother’s body. Once outside the mother’s body the umbilical cord is still attached. It is tied and cut leaving a scar = naval or belly button. Contractions continue after birth which expel the placenta and amnion = afterbirth. Fraternal Twins – two eggs become fertilized, imbed separately and develop separately. Identical twins – a fertilized egg divides into two embryos at an early stage of development. Each embryo then forms separately. Pregnancy drugs. Postnatal Development: Birth Growth Puberty Adult Aging Death