Osmolarity experiment
advertisement

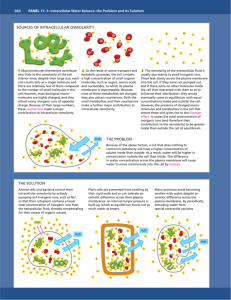
Osmolarity experiment Background information Osmosis is the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Solutes that are osmotically active include glucose, sodium ions, potassium ions and chloride ions. These ions are able to move because they are able to form bonds with water. There are many solutes within cells that are osmotically active. Osmolarity is the total concentration of osmotically active solutes in a solution; the units are osmoles or milliosmoles (mOsm). Human tissue is normally around 300 mOsm. Isotonic solution - the same osmolarity as a tissue. Hypertonic solution – a higher osmolarity. Hypotonic solution – a lower osmolarity. Experiment Complete an experiment to investigate the osmolarity of red onion cells. Research question How do hypertonic and hypotonic solutions affect the cells of a red onion? Method 1. Peel some epidermis from a red onion. 2. Cut a sample approx.. 5 x 5mm in size. 3. Mount the sample on a microscope slide with one drop of distilled water and a cover slip. 4. Observe the cells using a microscope. Record your observations in an appropriate table. 5. Mount a second sample of red onion epidermis, this time use one drop of sodium chloride solution. 6. Observe the cells using a microscope and record your observations in the table. You should be able to observe the process of plasmolysis (when plant cell membranes pull away from the cell wall). This technique could be used to investigate osmolarity. Online simulation lsvr12.kanti-frauenfeld.ch/KOJ/Java/Osmosis_fast.html Conclusion Write a conclusion to describe the your observations from this experiment. Further study Next week, we will study the structure and function of membranes. Do you have any questions relating to this experiment that you would like answered in the future? List them there.