WH_Chpt4_Sect_2_3
advertisement

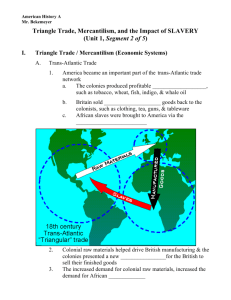
EUROPEAN NATIONS SETTLE NORTH AMERICA & THE ATLANTIC SLAVE TRADE Chapter 20.2 & 20.3 COMPETING CLAIMS IN NORTH AMERICA Colonies began with the goal of finding trade routes to Asia The French set up the colony of New France East coast of modern day Canada and the Northern United States Quebec would be the base of operations for French conquest of the Americas French would expand territory into Great Lakes region and Northern Mississippi Would claims all the lands of the Mississippi French colonists had little desire to build towns or raise families Very focused on bringing in money Most engaged in the fur trade New France - 1702 NEW FRANCE – 1750 THE ENGLISH ARRIVE English inspired by French and Spanish Jamestown – First settlement Very little organization More interested in adventures then establishing infrastructure At first 7-10 would die from conflict/starvation Eventually would thrive on Tobacco PURITAN NEW ENGLAND The second colony would be founded in Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay Both colonies founded by groups who faced religious persecution Faced dif ficulties but stabilized quickly due to large amount of families THE DUTCH AND NEW NETHERLAND Founded by Henry Hudson Areas around modern day Hudson River Established as a trading posts Dutch not quick to settle the area with towns Used primarily for financial reasons Would open its doors to many other cultures to promote settlement with some success The Dutch, English, and French would also establish colonies in the Caribbean. Lucrative agricultural centers Required large steady work force Primary cause for African slave trade THE STRUGGLE FOR NORTH AMERICA The English need Dutch lands to unite their colonies Seized the territory with a simple show of force, no shots required England and France go to war English desire for more territory brings them in contact with the French War breaks out in Ohio River area This war would include skirmishes all over Caribbean and Indian colonies A FEW ACRES OF SNOW NATIVE AMERICANS RESPOND French and Dutch settler develop a relatively peaceful relationship with Native Americans English relationships started good but ended very poorly English sought to populate colonies Required pushing Native Americans off their land Vast amount of land was needed for Tobacco production English settlers saw Native Americans as heathens or people without faith SETTLERS AND NATIVE AMERICANS BATTLE Conflict begans as early as Jamestown King Phillip’s War Metacom, or King Phillip, led Indian attacks on Massachusetts villages Hundreds of people would lose their lives Ultimately, the Native Americans would succumb to European diseases No immunity led to massive Smallpox outbreaks Easy expansion led to more land to farm, more land to farm led to a need for a bigger workforce, which will lead to adopting slavery THE CAUSES OF AFRICAN SLAVERY The American colonies are booming with growth but need more workforce to keep up production Slavery in Africa Slavery existed in Africa for centuries Increased when Muslim invaders took over regions of Africa In both African and Muslim societies slaves had some rights Also had some social mobility Portugal first reaches Africa in the 1400’s but primarily interested in gold AMERICAN DEMAND FOR AFRICANS Why Africans over Native Americans Africans had been exposed to European diseases and had immunities They had experience in farming Did not know the land so could not escape Skin color made them stand out Between 1500-1600 nearly 300,000 African slaves were transported to America 1 .3 Million by 1700 9.5 Million by 1870 SLAVERY SPREADS THROUGHOUT THE AMERICAS Spain began bringing slaves to the Caribbean Plantation, gold, silver mines Portugal was bringing slaves to Brazil Sugar plantations England would come to dominate slave trade Brought to Caribbean islands and the modern day United States AFRICAN COOPERATION AND RESISTANCE Many African rulers and merchants played willing roles in the slave trade European traders would meet merchants on the coast African rulers and merchants would capture and sell trade Several African rulers did oppose this practice Nonetheless, the slave trade continued to grow as merchants would work around African leaders not willing to participate TRIANGLE TRADE Along the way millions of Africans died Were part of Triangle Trade system Europeans traded manufactured goods to Africa for slaves Europeans sold slaves in the West Indies Brought back tobacco molasses and coffee back to Europe A FORCED JOURNEY Millions of Africans died on route to the colonies Brought along the Middle Passage Known as such because it was the middle leg of the Triangle Sickening cruelty characterized this journey Slaves were crammed into dark holds They endured beatings and whippings from merchants Many would jump overboard to avoid torture Others were overboard if determined to be sick or a threat SLAVE SHIPS SLAVE SHIPS SLAVERY IN THE AMERICAS Those who survived faced an equally dif ficult life Slaves were auctioned of f to the highest bidder They work in mines, fields, or as domestic servants Worked long days and suf fered beatings Living conditions were terrible Working for freedom very rare RESISTANCE AND REBELLION Slaves managed to keep oral storytelling and music alive They also found a way to resist Would lower productivity Break tools Uproot plants Thousands ran away Would occasionally break out in open revolt CONSEQUENCES OF THE SLAVE TRADE In Africa numerous cultures left generations of their strongest members African families were torn apart It also introduced guns to the continent which would plunge it into warfare Slavery did help the early colonies survive, many of which may not have without the labor African culture also impacted the growing American culture Africans were not the only cargo travelling across the Atlantic and around the world Next we will study the Columbian Exchange & Global Trade SECTION 2 – QUESTIONS Why were France’s North American holdings so sparsely populated? (Might want to look -up what sparsely means). How did Jamestown and the Massachusetts Bay colonies differ? How did the Dutch and French colonies differ from the English colonies in North America? Why were the French and Dutch able to coexist in peace with the Native Americans? Why did the issues of land and religion cause such problems between Native Americans and English Settlers? SECTION 3 - QUESTIONS What were some characteristics of Muslim and African slavery? What advantages did Europeans see in enslaving Africans? Why did many African ruler participate in the Atlantic Slave Trade? In what ways did enslaved Africans resist their bondage? What are some of the contributions that Africans have made to the Americas?