Growth and Expansion Booklet

Growth and Expansion
Booklet
Growth and Expansionism
Booklet
Section 1: Nationalism and Sectionalism
Vocabulary
Review Questions
Notes
Section 2: Religion and Reform
Vocabulary
Review Questions
Notes
Section 3: Manifest Destiny
Vocabulary
Review Questions
Notes
Section 1: Nationalism and Sectionalism
I. Vocabulary
Industrial Revolution
Francis Cabot Lowell
Lowell Girl
Interchangeable parts
Eli Whitney
Tariff of 1816
Cotton Gin
Nationalism
Henry Clay
American System
Adams-Onis Treaty
Monroe Doctrine
Missouri Compromise
Jacksonian Democracy
Spoils System
Indian Removal Act
Trail of Tears
Tariff of Abominations
John Calhoun
Nullification
Sectionalism and Nationalism Notes
Industry and Transportation
Technology transform manufacturing Industrial Revolution
Shift from agriculture to industry- New England flourishes
Textile factories, Lowell Mills, interchangeable parts, mass production
North vs. South Economy o North: smaller farms, growing cities, little need for slavery o South: Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin- increases need for slavery cash crop
An Era of Nationalism
Worried about sectionalism, Henry Clay proposes the American System- unite country o Transportation system o Protective tariff (make citizens buy
US goods) o Re-establish a national bank
Tariff of 1816- tax on imports from
Euro helps NE industry, hurts S. farmers
Several Supreme Courts cases boosted gov’t power o Gibbons vs. Ogden (1824)-
Steamboat operators arguing over territory; gov’t says US controls interstate commerce o McCulloch vs. Maryland (1819)-
Maryland tries to tax the Fed.
Bank US says no
Hudson River School- landscape painters form a school
Foreign policy based on nationalism nat’l interest above regional concerns
1819- US gains FL from Spain Adams-Onis Treaty
The Monroe Doctrine (1823)- Pres. Monroe says the western hemisphere is “closed”- no new colonies from outside powers
US promised not to interfere with Euro issues
Nationalism did not help growing slavery crisis:
The Missouri Compromise
Missouri and Maine apply for statehood
10 free states, 10 slave states
Miss. wants to be slave upset balance and starts arguments
Henry Clay proposes compromise- Miss. will be slave, Maine will be free 36◦30’ parallel was dividing line
Age of Jackson
“Corrupt Bargain” Election 1824 o Jackson wins pop. Vote, but tied electoral votes o House of Reps to decide winner, Henry Clay disliked Jackson, convinces HR to vote for John Adams o Jackson wins in 1828
Jackson practices spoils system- appointing friends to gov’t jobs
Native American issues- displace or convert?
Indian Removal Act of 1830- Remove NA to lands further west
Cherokee fight back- Worcester vs. Georgia o Gov’t allows Cherokee to stay on land, but Jackson refused o Trail of Tears- 800 mile journey; ¼ died
States’ Rights and a National Bank
Gov’t keeps increasing taxes on imports (N. likes, S. hates)
Tariff of Abominations was final straw- extremely high protective tariff
S. very mad The South Carolina Exposition- VP Calhoun writes nullification doc
1832- SC threatens to secede if tax isn’t stopped, tariff is reduced
Economic Problems
Jackson hates idea of BUS- corrupt idea
Jackson suggests “Pet Banks”-put gov’t funds in local banks devoted to Dem. Party
Whig Party is created in opposition to Jackson
Martin Van Buren (1836-1840)
Allows economy to fall into tail spin- Panic of 1837
Whig Party vs. Dems William Henry Harrison elected, died one month later
Section 1: Nationalism and Sectionalism
Review Questions
1. How did transportation developments and industrialization affect the nation’s economy?
2. How did the North and South differ during the first half of the 1800s?
3. How did domestic and foreign policies reflect the nationalism of the times?
4. What changes did Andrew Jackson represent in American political life?
5. What major political issues emerged during the 1830s?
6. Categorize and explain the factors that led to less industrial growth in the South than in the North.
Section 2: Religion and Reform
I. Vocabulary
Second Great Awakening
Evangelical
Joseph Smith
Mormon
Unitarian
Utopian Community
Transcendentalist
Public School Movement
Horace Mann
Dorothea Dix
Temperance Movement
Freedman
Nat Turner
Abolition Movement
William Lloyd Garrison
Frederick Douglass
Sojourner Truth
Women’s Movement
Seneca Falls Convention
Suffrage
Section 2: Religion and Reform
II. Review Questions
1.What were the main features of the public school, penitentiary, and temperance reform movements?
2.How did reformers try to help enslaved people?
3.What steps did American women take to advance their rights in the mid- 1800s?
4.Why did the Second Great Awakening begin? What were some of the ways that it changed American Society?
5.How successful were slave revolts in helping enslaved African
Americans resist slavery?
6.What similar ideas did abolitionists and women’s rights reformers hold?
Religion and Reform Notes
Religion Sparks Reform
Religious revival sweeps America- Second Great Awakening ( focus on individual salvation)
Gathered large groups for days long sessions- revivals
Some reformers wanted an alternative culture o Transcendentalism-
Living simply and truth in nature
Literary movement follows- Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry David Thoreau (Walden)
Utilitarianism- emphasize reason to path to perfection
School and prison reform important- Dorothea Dix- focus on mentally ill and prisoners
1800s- no uniform school policy Horace Mann, implement 1 st BOE
Slavery and Abolition
Abolition was fueled by reform movement
White abolitionist William Lloyd Garrison- newspaper The Liberator called for immediate emancipation
Garrison begins working with ex-slave Frederick Douglass The North Star
Women and Reform
Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Lucretia Mott- Abolitionist and Women’s Reformer
Women restricted to home and family- Cult of Domesticity
Grimke Sisters argued for abolition, hoping it would eventually lead to women reform
Fight for temperance- prohibit drinking and sale of alcohol- downfall of society
Seneca Falls Convention: Held NY, Stanton and Mott create a women’s Declaration of
Independence
Section 3: Manifest Destiny
I. Vocabulary
Manifest Destiny
Santa Fe Trail
Mountain Men
Oregon Trail
Brigham Young
Treaty of Fort Laramie
Stephen Austin
Santa Anna
Autonomy
Lone Star Republic
Alamo
Sam Houston
James K. Polk
Zachary Taylor
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Gadsden Purchase
Wilmot Proviso
Forty-Niners
Placer mining
Section 3: Manifest Destiny
II. Review Questions
1. What long term effects did the introduction of horses and firearms have on Native Americans in the west?
2. Who might have agreed with the idea of Manifest
Destiny? Who would have disagreed?
3. Why do you think so few women or families made their way west?
4. In what way was the fighting in Texas the responsibility of both the Anglo- Texans and the Mexican government?
5. Identify three effects of the California Gold Rush. Which effect do you think was most important in the long term?
6. What other groups of people, besides farmers, made their way west in the 1800s? Why?
Manifest Destiny Notes
The Market Revolution
Shift from self sufficiency to specialization- raising cash crops to sell
Leads to market revolution- ppl buy and sell goods rather than making them for their own use
Inventions make life easier- farmers and industrial businessmen o Telegraph o Railroads
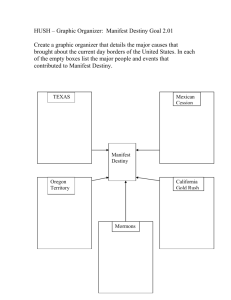
Manifest Destiny
Expansion fever grips nation- US destiny is to expand to Pacific Ocean mandated by God
NA unsettled by Manifest Destiny Treaty of Fort Laramie gives NA control of central plains territory promising in exchange not to attack new settlers
Santa Fe Trail- Missouri to New Mexico
Brigham Young leads group of Mormons to Utah-escape religious persecution
1844-James Polk calls for annexation of Oregon, British forts still there
“Fifty Four Forty or Fight” becomes rallying cry (Northern limit for boundary)
Expansion in Texas
More Americans in Texas than
Mexicans
Tensions build b/t Mexicans and
Americans- Mexico places restrictions on Texas growth
Texas declares a war for
Independence Remember the
Alamo o Texas militia faces Mexican
Army at the Alamo, an abandoned fort-Santa Anna destroys the small army- kills all involved
Sam Houston later beat Santa Anna
& declared a Republic of Texas
1845- Texas becomes a US state (
Fight over slavery)
War with Mexico
James K Polk urges war with M. to gain lands farther westquestion over Texas border and slavery
Requests to buy Cali and New Mexico refused Polk sees this as war
Zach Taylor led troops to Rio Grande & built forts Mexico attacks
War lasts for about a year- sign Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo o Agree to Rio Grande border o Gains Mexican Cession- CA, NV, NM, UT, AR, CO, WY o Concludes lower 48
Movement to forbid slavery in new territory Wilmot Proviso