White Man's Burden - Spartanburg County School District 5
advertisement

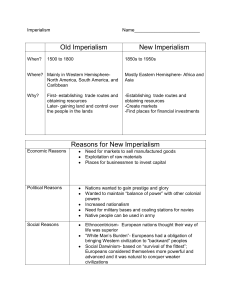
Bell Ringer What is Imperialism? Use Chapter 21 Section 1! #1 Not In Textbook Imperialism Old Imperialism vs. New Imperialism Old Imperialism New Imperialism Occurred between 16th EXTENSTION OF A and 18th centuries European powers built a series of trading stations Cooperated with local rulers in Africa, India, China, Japan, and Indonesia Traded for goods and slaves NATION’S POWER OVER OTHER LANDS Now European Countries wanted DIRECT control over their territories Motivations for Imperialism Economics Control trading markets and raw materials Rubber, oil, and tin Motivations for Imperialism Create Colonies Dominate Rivals Gain trading advantage National prestige Motivations for Imperialism Social Darwinism In the struggle between nations, the fit (most powerful( are victorious Europeans were believe to be superior to other races Racist ideologies Motivations for Imperialism Moral Responsibility “Civilize” the primitive people White Man’s Burden The White Man’s Burden Poem by Rudyard Kipling Written to urge the U.S. to help the British with the “burden” of colonization The ruling of other nations for their benefit The Brown Man’s Burden Poem by H.T. Johnson Written in response to Kipling’s poem Compared the treatment of the people in the Philippines to that of African Americans. Creating Your Own Burden You will create your own Student Burden, from evil imperialist teachers. Poems must have at least 8 lines. 2. Have describing adjectives of the student burden from your teacher like seen in question 2 on your worksheet about the white man’s burden. 3. Incorporate your knowledge of imperialism. 1. Do not mention any specific teachers’ names!!! Bell Ringer What is a protectorate? Use Chapter 21 Section 1! #2 Chapter 21 Section 1 Colonial Rule in Southeast Asia Great Britain in Southeast Asia 1819- Singapore Malay Peninsula Trade route Mid-1800s- Burma Modern Myanmar Protect possessions in India and land route to China France in Southeast Asia 1857- Vietnam Protectorate- a political unit that depends on another government for its protection Prevent British takeover of Vietnam 1880s- Cambodia, Annam, Tonkin, and Laos Union of French Indochina United States in Southeast Asia 1898- Philippines Gained after the Spanish American War Trade with China Prevent Japanese expansion “Civilize” Filipinos Indirect and Direct Rule Indirect Rule- Colonial government in which local rulers are allowed to maintain their positions of authority and status Gain access to natural resources Lower cost in government Less effect on local culture Indirect and Direct Rule Direct Rule- Colonial government in which local elites are removed from power and replaced by a new set of officials brought from the mother country Prevented rebellion Great Britain Burma France Northern Indochina Colonial Economies Modern Economic System Export Raw Materials Teak wood, Rubber, Tin, Spices, Tea, Coffee, Palm oil, and Sugar Natives were wage laborers on plantations Near poverty levels Increased profit Unhealthy living conditions 1,000s died High taxes Built infrastructure Roads, highways, bridges, etc Bell Ringer Identify annexed. Use Chapter 21 Section 2! #3 Chapter 21 Section 2 Empire Building in Africa West Africa 1808 Slave trade declared illegal (not slavery) Before 1880 No European Control After 1880 Great Britain, France, Germany, Belgium, Italy, Spain, and Portugal Late 1800s New trades Europe= Manufactured Goods Africa= Natural Resources 1874 G.B. annexed (took control of) the west coast Gold Coast North Africa 1805 Muhammad Ali took control of Egypt from the Ottoman Empire 1854-69 Suez Canal was designed by a Frenchman “Life line to India”- trade 1875- British took over the Suez Canal, Egypt, and Sudan 1879 French controlled Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco 1896 Italy tried to take over Ethiopia (lost) 1911 Italy invaded Turckish Tripoli (Libya) Central Africa Tropical Jungles 1841 David Livingstone (explorer) disappeared Lake Tanganyika Henry Stanley (journalist) found him Wanted G.B. to send settlers to Congo (No) Asked Belgium (King Leopold II) 1876 Settlers came from Belgium Eventually seized the Congo and all the surrounding area East Africa 1885 Great Britain and Germany Berlin Conference- staked out claims for European countries G.B. and Germany got most of East Africa Portugal- Mozambique No AFRICAN delegates were present South Africa 1865 200,000 white people Dutch settlers (Holland) Present in Cape Town since 17th c. Called Boers British pushed them north Transvaal and Orange Free State Indigenous (native) people were put on reservations Zulu (African tribe) waged constant war with Europeans 1880sSouth Africa British policy supported diamond and gold industry Rhodesia- new name of Transvaal 1889-1902 Boer War British and Boers (former Holland settlers) Guerrilla warfare (Boers) British burned crops Detention Camps 120,000 Boer women and children 20,000 deaths- lack of food British won 1910 Union of South Africa Cape Colony and Boer territory Colonial Rule in Africa 1914 GB, France, Germany, Belgium, Italy, Spain, and Portugal divided up Africa Liberia and Ethiopia Only independent African nations GB used indirect rule Led to tribal tensions Others used direct rule Assimilate African subjects into European culture Bell Ringer What was the purpose of the Suez Canal? Use Chapter 21 Section 2! #4 Bell Ringer #5 Which European nation had a monopoly on the colonization of India? Use Chapter 21 Section 3! Chapter 21 Section 3 British Rule in India Colonial Rule in India British government used direct rule in India Viceroy- a governor who ruled as a representative of a monarch Staff of 3,500 ruled over 300 million people Benefits for India Brought order and stability India had previously been divided by civil war Honest and efficient government New school system Train Indian children to serve in the government and army Elite, upper-class citizens 90% of population was illiterate Improved infrastructure Railroads, telegraph, postal service Negative Impact for India British entrepreneurs and a few Indian businessmen gained wealth British manufacturing destroyed local industries Textile Corrupt tax collectors Peasants lost most of their land More cotton/indigo production than food Shortage of food 1800-1900 30 mil. died from starvation Negative Impact for India Indians were seen as inferior to Britons Best housing was reserved for British citizens British disrespected India’s cultural heritage Taj Mahal (sacred tomb) became a venue for weddings and parties Pieces were chipped off as souvenirs Led to an Indian nationalism movement Indian Nationalist Movement Upper-class, well educated, and from urban areas Mumbai (Bombay) Slow pace of reform led to revolution Indian National Congress- 1885, called for Indians to participate in the government Split due to differences between the Hindu and Muslim members Indian Nationalist Movement Gandhi- Indian Hindu Educated in London Lawyer 1893- Helped Indians living in South Africa 1915- Returned to India and called for independence from GB Non-violent resistance Improve the life of the poor Led to Indian independence Bell Ringer What was the purpose of the Monroe Doctrine? Use Chapter 21 Section 4! #6 Chapter 21 Section 4 & Not In Textbook Nation Building in Latin America & United States Expansion and Imperialism Continental United States By 1853, the US controlled all of the modern continental part of the nation 1867- Alaska 1898- Hawaii Soon aimed to control other territories Motives for Expansion and Imperialism Manifest DestinyGod’s will for US to expand from sea to sea 1. Desire for military strength 2. Thirst for new markets 3. Belief in cultural superiority 1. Desire for Military Strength Land = Money = Power Build up the US Navy Steel-hulled cruisers Industrial Revolution fueled growth in military 2. Thirst for New Markets Industrial Revolution fueled US production Made too many goods Americans couldn’t buy it all (overproduction) Needed more raw materials Lumber, tin, coal, gold Created jobs Trade, mining, etc 3. Belief in Cultural Superiority Social Darwinism Spread Christianity Took land from Native Americans Not considered US citizens “White Man’s Burden” Monroe Doctrine 1823 President James Monroe Monroe Doctrine- guaranteed the independence of Latin American nations and warned against European intervention in the Americas Protected US interests in Latin America Mexico Texas Revolution Americans in Texas (Mexico) revolt against Mexican government US gained Texas, New Mexico, and parts of Oklahoma, Colorado, and Utah Mexican American War Fought over Texas’ southern border US gained Arizona, California, Nevada, and parts of Utah, Wyoming, and Colorado Spain Spanish America War US fought Spain in the Caribbean and the Pacific Human Rights violations US gained Puerto Rico, Cuba, the Philippines, and Guam Panama US aided Panama in a revolt against Colombian control Panama gains independence and lets US build a canal Panama Canal Shortcut from Atlantic to Pacific NYC to San Francisco 12,600 miles to 4,900 miles Present Day Territories District of Columbia Guam Northern Marianas Islands Puerto Rico US Virgin Islands