Native Texans
advertisement

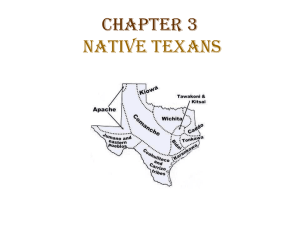
Native Texans Main Idea for Studying Native Texas Tribes • Native Texans developed their own distinct cultures. • Each group’s lifestyle and practices were uniquely suited to its environment and specific needs. Learning Target: • I can compare cultures of American Indians in Texas prior to European colonization. • I can identify cultural traits and methods of adaptation/interaction based on the geographic location of each tribe. • • • • • • Nomadic Sedentary Agriculture Artifact Forage Dwelling Definitions • Nomadic – no fixed home and moves from place to place in search of food, water, and/or grazing land. • Sedentary – to remain in one place • Agriculture - The science, art, and business of cultivating soil, producing crops, and raising livestock; farming. • Artifact - an object made by a human being, typically an item of cultural or historical interest. • Forage - search widely for food or provisions • Dwelling – a place to live in “Which Tribes, and Where Did They Live?” Plains Cultures KIOWAS COMANCHES WICHITA CADDO TIGUA APACHE Pueblo Cultures JUMANOS TONKAWA KARANKAWAS COAHUILTECANS Southeastern and Gulf Cultures The Caddo The Caddo • A very civilized tribe that lived in organized villages. The most numerous and most productive of all Texas tribes • Primarily farmers - farming was the best way to get food. Their region had plentiful rainfall, rivers, creeks, springs, and an ideal climate for farming. There were no big herds of buffalo or other animals…just the occasional buffalo or deer. (sedentary) • They built dome-shaped permanent dwellings from timber, mud, straw • They made beautiful pottery to store grains, food, seeds. (typical of a farming culture) • They lived in the Piney Woods and created several tools to work with wood. (stone axe) The Caddo…continued • Caddo often engaged in warfare. • Formed their own government that consisted of two leaders – women could also be leaders. • From 1520-1690, population shrank from around 200,000 to only 12,000 b/c of European disease. • The Caddo formed confederations to protect and defend themselves from other tribes with their large numbers. • They also traded goods all over Texas, the Mississippi river valley and the southeastern United States. Caddo Timeline http://www.texasbeyondhistory.net/tejas/fundamentals/timeline.html The Karankawa The Karankawa • Coastal dwellers who used the resources in the Gulf and bays. • Semi-sedentary. In the fall and winter, they would live by the sea or bays when shellfish are safe to eat. Lots of food coming into the bays means they could stay in one place without moving and without farming. For the spring and summer, they would later move inland as hunter gatherers for the rest of the year to harvest berries and hunt deer. • Made Canoes from trunks of trees (prized possession), Made nets and wickiup houses similar to the Caddo, but not as permanent. • Very little information about the Karankawa exists, but they seemed to have been friendly. They shared the inland areas they roamed in with other tribes and they traded with many other tribes. • When North American settlers moved to the Coastal Plains in the 1820’s fighting broke out. By the mid 1800’s almost all Karankawa had been displaced or killed. The Coahuiltecans The Coahuiltecans • “Coahuiltecan” is the term used to categorize all the indigenous peoples (hundreds of hunter-gatherer groups)of the south Texas plains and northeastern Mexico. • All members enjoyed equal status. Everyone had to work…men hunted, women took care of the camp • Rarely stayed in one place more than a few weeks…constantly on the move to find food. • Used bows and arrows to hunt deer, bison, and javelina. When game was scarce, they would gather cacti, mesquite, and other plants or would eat worms, lizards, and plants The Plains Cultures (Comanche, Kiowa, Apache, Tonkawa) The Native Texans that lived on the plains based their lives and their culture on the buffalo. Large parts of North, Central, and West Texas were a sea of grass that provided a plentiful food supply for millions of buffalo. Plains Indians • Lived in North, West, and Central Texas • These tribes based lives and cultures around buffalo …for food and shelter – – – – Dried buffalo meat for jerky Pounded dried meat and mixed it with nuts/berries to form Pemmican Used bones for tools Used hide for clothes, tepees, shoes, blankets • Nomadic people —followed the buffalo • Used dogs to drag things from place to place • First cultures to fully incorporate horses into culture • Willing to aggressively claim territory & resources • Also gathered plants for food • Family was basis of society • Groups of families banded together under one chief • Groups were very self-sufficient and brave The Apache • Occupied Northern Great Plains region • Originally semi-sedentary – Apache farmed and after harvest, they hunted buffalo on foot (before the Spanish brought horses) – Apache would run/scare buffalo off of a cliff • After horses, hunting was much easier. The Apache gave up farming and became nomadic hunters. • Continued to migrate south until they ran into Comanche around central Texas. Comanche forced Apache to split into two groups…one went south (Lipan). The other group (Mescalero’s) went west to where the Jumano and Tigua tribes once lived. The Kiowa Allies to the Comanche Nomadic, lived in tepees Similar to Comanche lifestyle, adaptations. Kept histories of their travels and painted pictures on buffalo hides to record important events in their lives. • All males were members of a warrior society. Men also hunted while women gathered. • Kiowa famous for long-distance raids. Some raids all the way down to Mexico from the Panhandle and some raids went all the way up to Canada. • Forced onto reservations in the 1860’s. • • • • The Comanche The Comanche • Comanche migrated from Canada in the 1700’s. • Comanche life centered on two activities – hunting and war • Buffalo hunts were important events that involved the whole group – hunters on horses surrounded the buffalo and forced the herd to move in a circle. Then the hunters would use bows, arrows, and spears to make kills when the buffalo passed by. The Comanche would eat some of the meat, but always dried and saved the remainder for another time. • Captured horses, taken from Comanche enemies were prized possessions. The Comanche became so skilled at riding, that the Spanish referred to them as “lords of the plains” • The Comanche continued to keep their land and fight until 1875. The destruction of the buffalo herds and loss of their horses forced them to accept reservation life in Indian Territory (present day Oklahoma) • Comanche viewed their children as their most precious gift. Children were rarely punished. The Tonkawa • The Tonkawa lived in central Texas near modern Austin • Tonkawa means, "the people of the Wolf". The Tonkawa claimed they were all descended from a mythical wolf. For this reason the Tonkawa would never kill a wolf. • They refused to farm because they said they were wolves and wolves hunted for food and did not farm. So they got their food by hunting and gathering • The Tonkawa lived in both huts, wickiups and tee-pees. • The Tonkawa tattooed their bodies and faces. They would have black tattooed lines all over their bodies Pueblo Cultures • Jumanos Jumano • Lived in the arid west Texas Mountains and Basins region near present day El Paso. • Built individual homes from adobe and formed villages in low river valleys of the Rio Grande. Homes were large, stayed cool in the winter, warm in the summer, and in the dry climate, lasted a very long time. • Sedentary – farmers – used irrigation methods with the Rio Grande as their water source. They grew a variety of crops and some scholars believe they grew cotton as well. • When crops failed, they would forage and hunt to meet their food needs. • The Jumano decorated themselves with tattoos 1. Far West Texas Indians Jumanos a. b. c. d. e. 2. Lived in farming villages of one-room houses along the Rio Grande from El Paso to Big Bend Houses were made of Adobe (cool in summer and warm in winter) Houses were brightly painted inside Planted crops along rivers Sometimes hunted and traded Tiguas a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Came to Texas in late 1600s with Spanish settlers avoiding Pueblo uprising in New Mexico Settled along Rio Grande near El Paso Lived in adobe houses Cooked food in round adobe ovens Hunted, fished, and grew corn, tomatoes, squash, beans, and grapes Made beautiful pottery cooking and storing food Grew cotton and wove it into cloth Ysleta del Sur…oldest continuous settlement in Texas Jornada a. b. c. d. Far West Texas Indians Sedentary Originally “pit” housing…partially underground Transition to Pueblo style adobe housing GONE BY 1400…?