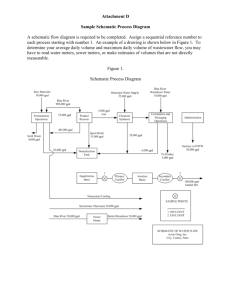
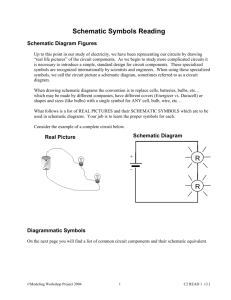
File - David Ricketts
advertisement

UNIT 2. ELECTRONICS PROJECT #1 In the table below, provide a definition as to the function of each of the listed electrical components, as well as an image of what each component looks like. In addition, include the schematic for the component, if available or appropriate. 1. RESISTANCE (Ohm) Definition: Image Schematic / Symbol Image Schematic Image Schematic A material's opposition to the flow of electric current; measured in ohms How can electrical resistance be useful? Electrical resistance impedes the flow of electrical current 2. CURRENT (Amperes) Definition: The time rate of flow of electric charge, in the direction that a positive moving charge would take and having magnitude equal to the quantity of charge per unit time measured in amperes. How can current be increased or decreased? When voltage remains constant and resistance increases the current in the circuit will reduce. Resistance is the degree of difficulty in moving charge from one place to another. If you increase that resistance, it is harder to move the charge. Current is rate of flow of that charge, hence current goes down. 3. VOLTAGE (Volts) Definition: The electrical force or pressure that causes current to flow in a circuit. Voltage is measured in volts How can voltage be increased or decreased? Usually when voltage increases current increases too, but when it happens that current decreases when voltage increase to minimize lose of power. What is the advantage of high voltage? Allows the use of conductors of practicable size. Economics (less volume of copper). Rreduce voltage drop along line. Reduce energy losses along line. 4. POWER (Watts) Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic Power is the rate (energy amount per time period) at which work is done or energy converted. Measured in watts. 5. SWITCH Definition: A device for making and breaking the connection in an electric circuit What are some different types of switches? Toggle switch, pushbutton switch, selector switch, joystick switch, lever actuator limit switch. 6. SPDT SWITCH Definition: In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit. What would you use a SPDT switch for? If you are using the SPDT knife switch, you have a "center off" position, which an ordinary wall switch would NOT have in which case you will need to add an SPST switch for shutting this circuit off. 7. DPDT SWITCH Definition: A six-terminal switch or relay contact arrangement that simultaneously connects one pair of terminals to either of two other pairs of terminals. Abbreviated dpdt switch. What would you use a DPDT switch for? Adding another pole to the SPDT creates a double-pole, double-throw (DPDT) switch. Basically two SPDT switches, which can control two separate circuits, but are always switched together by a single actuator. DPDTs should have six terminals. 8. INDUCTOR (COILS & RELAYS) Definition: A component in an electric or electronic circuit that possesses inductance. What can a coil be used for in a circuit? An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor (usually an insulated solid copper wire) is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. Image Schematic What can a relay be used for in a circuit? A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. 9. RESISTOR Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic A device having resistance to the passage of an electric current How does it change a current? In a true series circuit with known current, no, because Kirchoff's Current Law says that the current at each point in a series circuit is the same. 10. TRANSISTOR Definition: A semiconductor device with three connections, capable of amplification in addition to rectification. What does a transistor do in electrical circuit? A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. 11. CAPACITOR Definition: A device used to store an electric charge, consisting of one or more pairs of conductors separated by an insulator. What does a capacitor do in electrical circuit? A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy electrostatically in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric (insulator). 12. DIODE Definition: A semiconductor device with two terminals, typically allowing the flow of current in one direction only. What does a diode do in electrical circuit? They only allow current to flow in one direction. Image Schematic 13. LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED) Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source. What does a LED do in electrical circuit? In electronics, the basic LED circuit is an electric power circuit used to power a light-emitting diode or LED. There are many ways to power a LED. This is not straightforward, as a LED, being a semiconductor, has peculiar characteristics. 14. CONDUCTOR Definition: Any material that conducts heat or electricity (as opposed to an insulator, or nonconductor). 15. CIRCUIT Definition: A roughly circular line, route, or movement that starts and finishes at the same place. 16. STATIC ELECTRICITY Definition: A stationary electric charge, typically produced by friction that causes sparks or crackling or the attraction of dust or hair. Where would you find static electricity? A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). Why is static electricity a problem in electronics? It seems like during the winter months, every time I get out of my chair and walk away from my desk I seem to get shocked when I touch something metal. This is all too common, and truthfully it can be a disaster for electronic equipment that isn't grounded or if the circuits take a direct hit. In this hub, we will be exploring the understanding of what static electricity is and how it can make your computer electronics into paper weights. 17. CURRENT ELECTRICITY Definition: Image Dynamic electricity: a flow of electric charge. Schematic No schematic How is current electricity different than static? Static electricity is the BUILT UP STORE of electron charges [e-] between a pair of objects, while current electricity is the FLOW of electrons between these objects. Static electricity is a transfer of charge from one static body to another, resulting in an imbalance in positive and negative charges, while electric current is the flow of electrons, from one static body to another. List several ways that current electricity is used. ? 18. DIRECT CURRENT (DC) Definition: Image An electric current flowing in one direction only. Schematic No schematic In what equipment is DC current used? Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. What does DC Current look like? 19. AC CURRENT Definition: Image Schematic In alternating current (AC, also ac) the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In what equipment is AC current used? An electrical machine that functions as (1) a generator used to produce alternating current, or (2) a motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical work, or (3) a converter that changes the voltage or frequency of an electric current. AC machines are classified as synchronous or asynchronous. What does AC current look like? ? No schematic 20. THREE PHASE CURRENT (3-Phase) Definition: Image Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. Schematic No schematic In what equipment is 3-phase current used? Transformers. Why is it used? Three-phase electric power is a common method of electric power transmission. It is a type of polyphase system mainly used to power motors and many other devices. A three-phase system uses less conductor material to transmit electric power than equivalent single-phase, two-phase, or direct-current systems at the same voltage. 21. POLARITY Definition: Image The relative orientation of poles; the direction of a magnetic or electric field. Schematic No schematic What happens when you reverse polarity? ???? 22. ANALOG SIGNAL Definition: An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature (variable) of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity Where are analog signals used? An analog signal can be used to measure changes in some physical phenomena such as light, sound, pressure, or temperature. Image Schematic No schematic 23. DIGITAL SIGNAL Definition: The term digital signal is used, to refer to more than one concept. Where are digital signals used? ? Image Schematic No schematic 24. INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (IC) Definition: Image An integrated circuit, or IC, is small chip that Schematic No schematic can function as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, microprocessor, or even computer memory. Where might an IC be used? Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a condition that results in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. What does it do? ? 25. PHOTO-DIODE Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic A semiconductor diode that, when exposed to light, generates a potential difference or changes its electrical resistance. Where a photo-diode might be used? A photodiode is a type of photo detector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation. The common, traditional solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode. What does it do? Photodiodes are similar to regular semiconductor diodes except that they may be either exposed (to detect vacuum UV or X-rays) or packaged with a window or optical fiber connection to allow light to reach the sensitive part of the device. Many diodes designed for use specifically as a photodiode use a PIN junction rather than a p-n junction, to increase the speed of response. 26. PHOTOCELL Definition: a transducer used to detect and measure light and other radiations. Where is a photo-cell used? Well let’s see how many things work off of photocell technology. Street lights, hand held calculators, low voltage landscape lighting, automatic car head lights, battery charges, automatic rest room controls. That's just the easy stuff there is a whole array of power producing photocells that provide backup power, or in some cases supply all the power for an entire home. The cheaper these cells get the more they will be used, they are the future, clean, renewable energy. What does it do? 27. THERMISTOR Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic An electrical resistor whose resistance is greatly reduced by heating, used for measurement and control. How does it work? A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a portmanteau of thermal and resistor. Thermistors are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, self-resetting over current protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. 28. THERMOCOUPLE Definition: A thermoelectric device used to measure temperatures accurately, especially one consisting of two dissimilar metals joined so that a potential difference generated between the points of contact is a measure of the temperature difference between the points. How does it work? A thermocouple is a temperature-measuring device consisting of two dissimilar conductors that contact each other at one or more spots. It produces a voltage when the temperature of one of the spots differs from the reference temperature at other parts of the circuit. Thermocouples are a widely used type of temperature sensor for measurement and control and can also convert a temperature gradient into electricity. 30. ELECTRONIC SPEED CONTROLLER (ESC) Definition: An electronic speed control or ESC is an electronic circuit with the purpose to vary an electric motor's speed, its direction and possibly also to act as a dynamic brake. How does it work? An ESC can be a stand-alone unit which plugs into the receiver's throttle control channel or incorporated into the receiver itself, as is the case in most toy-grade R/C vehicles. 31. SERVO CONTROLLER Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Servo control from a radio control receiver to the servos is done by sending each servo a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal, a series of repeating pulses of variable width. How could you use a servo controller? (2 ways) Small radio control servos are connected through a standard three-wire connection: two wires for a DC power supply and one for control, carrying the pulses. 33. SERIAL SIGNAL Definition: Serial means one event at a time. It is usually contrasted with parallel, meaning more than one event happening at a time. No schematic What does a serial signal look like? How does it differ from a Parallel signal? ? 34. USB SIGNAL Definition: Image Schematic No schematic How is it different from serial and parallel? 35. DC MOTOR Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic A DC motor is an electric motor that runs on direct current (DC) electricity. What could you use a DC motor for? The introduction of DC motors to run machinery eliminated the need for local steam or internal combustion engines, and line shaft drive systems. DC motors can operate directly from rechargeable batteries, providing the motive power for the first electric vehicles. Today DC motors are still found in applications as small as toys and disk drives, or in large sizes to operate steel rolling mills and paper machines. How does a DC Motor work (think stator) 36. SERVO MOTOR Definition: Where would you use a servo motor? (3 uses) 37. STEPPER MOTOR Definition: What is the advantage of a stepper motor? 39. TV VIDEO SIGNAL – COAX CABLE Definition: Image Schematic Image Schematic Image Schematic What does a video signal look like? How many wires do you need to carry it? How do the two formats differ (NTSC and PAL)? 40. DIGITAL VIDEO (DV) SIGNAL Definition: How is this different than an analog video signal? What are the advantages / disadvantages? 41. HIGH DEFINITION (HD) VIDEO SIGNAL Definition: How is this different than a standard video signal? What is the advantage, if any? 41. PROGRESSIVE vs. INTERLACED VIDEO DISPLAY (TVs) Definition: Progressive display Definition: Interlaced Display What is the advantage, if any, of these two different display methods on a TV? Image Schematic UNIT 2. ELECTRONICS PROJECT 1.2 Identify the components? Using the information contained in your completed table, above, identify and describe each of the electrical components contained in the display. Each one is identified with a letter. Place the name of the component in the correct space number. Component E.g. Resistor A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z Specification of the component 15 KΩ (15 kilo-Ohms)