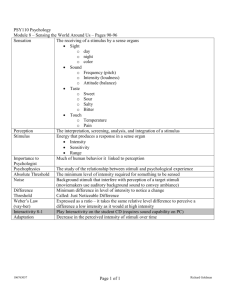
chapter
6
Customer Relationships
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Customer Relationships — Today’s
Objectives
Objectives will be to:
Develop a clear definition of relationship
Explore why firms want relationships with their customers
Discuss the relationship stages and interaction intensity
Examine the effects of the Internet and 2Is on customer relationships
Discuss some final points about customer relationships and the Web
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Relationship Type & Involvement
Continuums
Enduring Involvement
Exchange
Relationships
Communal
Relationships
Situational Involvement
Exhibit 6.2: A Continuum of
Relationship Involvement
High
Product type (cost,
level of symbolism,
risk)
Purchase situation
(visibility, social
acceptability)
Relationship
Involvement
Consumer type
(interests, values,
attitudes)
Low
Automobile
35-mm Camera
Expensive Watch
Stereo Component
Eyeglasses
Scotch Whiskey
Hair Coloring
Wine for Dinner Party
Washer/Dryer
Face Soap
Credit Card
Salad Oil
Deodorant Soap
Insecticide
Headache Remedy
Liquid Bleach
Insect Repellent
Disposable Razor
Potato Chips
Soft Drink
Paper Towels
Toilet Tissue
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
High
Low
Profitability
Exhibit 6.4: Length of Customer Tenure
and Profitability Relationship
Short
Long
Customer Lifetime
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Exhibit 6.6: Moving Through the
Relationship Stages
Awareness
Exploration/
Expansion
Commitment
Dissolution
Customers can advance through the stages in several different ways
Exhibit 6.7: Two Alternatives for
Customers at the Commitment Stage
Satisfied,
profitable customers
Stay
Committed
Commitment
Unsatisfied or
unprofitable customers
Dissolution
Customers can either stay committed or move to dissolution
Exhibit 6.10: Level of Interaction by
Stage of Customer Relationships
Four Key Stages of Customer Relationships
Awareness
Exploration /
Expansion
Commitment
Level of Intensity
Level of
Intensity
Intensity
Stages of Customer Relationships
Dissolution
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Are Interactivity and Individualization
Always Necessary?
Low Individualization,
Low Interactivity
Example: news service
Low Individualization,
High Interactivity
Example: library
High Individualization,
Low Interactivity
Example: bank statement
High Individualization,
High Interactivity
Exhibit 6.12: Online Privacy Attitudes
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Exhibit 6.13: Integrative Framework:
Building Relationships on the Web
Four Key Stages of Customer Relationships
Awareness
Exploration/
Expansion
Price
Marketing
Levers
Product
Promotion
Distribution
Brand
Commitment
Dissolution
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
EBay Case Study
Conclusion
Building Relationships at EBay
Four Key Stages of Customer Relationships
Awareness
No. 1 general
auction service
on the Internet
Exploration/
Expansion
EBay
encourages
browsing
before
registration for
the purpose of
exploration
Commitment
EBay offers (1)
community, (2)
individualization,
and (3) interaction
Dissolution
Users can stop
buying or selling
at any time
Chapter 6: Customer Relationships
Defining Relationship
Why Firms Want Relationships With Their Customers
The Relationship Stages and Interaction Intensity
The Effects of the Internet and the 2Is on Customer Relationships
Some Final Points About Customer Relationships and the Web
eBay Case Study
Conclusion
Customer Relationships —
Conclusion
The customer relationship stages are:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Awareness — The customer recognizes that the firm is a possible
exchange partner, but has not initiated any communication with the firm or
purchased its products
Exploration — The customer considers the possibility of exchange,
gathers information and perhaps initiates trial purchases
Commitment — The parties in a relationship feel a sense of obligation or
responsibility toward each other
Dissolution — This stage signals the separation of buyer and seller — the
loss of connection
The Internet allows firms to interact and to individualize in powerful
ways. As a result, firm-customer relationships can be formed and can
progress very quickly
Firms don’t always want a relationship with all customers . . . and vice
versa