level of measurment and statistics intro
advertisement

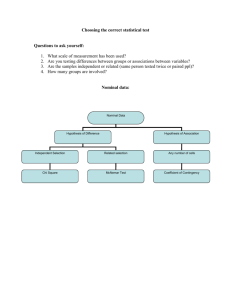
Statistics Data measurement, probability and statistical tests Learning Aims By the end of this session you are going to totally ‘get’ levels of significance and why we do statistical tests! Levels of measurement These are quantitative measures of data which are of extreme importance when conducting statistical tests There are 4 levels of measurement Also known as levels of data Nominal: Counting into categories, e.g. there are 4 men and 4 women in the room Ordinal: Results are put in order, they are ranked. E.g. we could rank the place that each horse came in a race Levels of measurement Interval: Data is defined as being a specific measure, this can be measured on an instrument, there are equal intervals between each piece of data. E.g. We can record the exact temperature using a thermometer. (can be minus) Ratio: This is like interval data except the scale has a meaningful value of zero. E.g. time and length. Why do we need to conduct statistical tests? Statistical tests tell us the significance of a set of findingsdid the IV really effect the DV or were the findings a fluke?! The more significant a finding is the more effect the IV had on the DV Probability: We need to use inferential statistics to tell us if the result that we have found is due to chance or not. To establish if our results are reliable we have to look at the probability of a result being due to chance or not. The minimum accepted level of probability commonly used in psychology is 5%, this is represented as 0.05. If the level of significance achieved from a test is equal to or less 0.05 than the results are said to be significant. This would mean that we are 95% sure that the IV caused the change in the DV Probability: Can be expressed as: A proportion: a 1 in 5 chance. As a percentage: 20% More commonly expressed as a decimal in psychology: 0.2. In psychology: 10%=0.10, 5%=0.05, 1%=0.01 and 0.1%=0.001 To go from % to decimal divide by 100, move decimal place 2 spaces to the left. Remember the more stringent (lower) the level of significance you set the more significant the results are Observed value: Every time you perform a statistical test you get an OBSERVED VALUE. This observed value tells you the extent to which your results are valid, you then have to compare this observed value to a table of CRITICAL VALUES to see of your results are significant or not. To be significant the observed value should be greater or less than the critical value depending on the type of test Note that there will be a different table of values for different statistical tests. Interpreting results: Usually in psychology if the results are significant it means that the probability of the result being due to chance is 5% or less P<0.05 means the results are significant- so we would accept the experimental hypothesis and reject the null hypothesis Interpreting results: P is used to represent “the probability that is due to chance” > =means greater than < =means less than ≥ means greater than or equal to. ≤ means less than or equal to. SO……………… P<0.05 means that the probability that the result is due to chance is less than 5%. Type 1 and type 2 errors: The 5% level of significance has been accepted as it represents a reasonable balance between the chances of making a type 1 or type 2 error These can occur because: Level of probability accepted is either too lenient (too high) or too stringent (too low) Type 1 and type 2 errors Type 1 error: Occurs when we conclude that there IS a significant difference when there is NOT This can happen if the accepted level of probability is set TOO LENIENT Significance level set at 20% Type 2 error: Occurs when we reject the experimental hypothesis and accept the null when there IS a difference This can happen if the probability level is TOO STRINGENT Significance level set at 1% Deciding on a statistical test You must decide the following: Are you trying to find out if your samples are related (correlate) or different? What design you have used- related, non related, matched pairs What level of measurement you have used. You can use the following table to help decide: What test to use? Design Nominal Ordinal, interval, ratio Correlation/ association Chi-square test of association Chi-squared test of independent samples Sign Test Spearmans Rank Independent measures Repeated Measures Mann Whitney U Wilcoxon T test Test your understanding! Using your newly found knowledge identify the test that would be suitable for the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. An experiment with nominal data and an independent groups design Ordinal data on both measures in a study to see if two measures are associated An experiment with and independent groups design in which the DV is measured on a ratio scale A study using a correlational technique in which one measure is ordinal and the other is ratio. A study testing an association using a nominal level of measurement An experiment in which all participants were tested with alcohol and without alcohol on a memory test An experiment in which reaction time was tested using an independent subject design ANSWERS 1. An experiment with nominal data and an independent groups design chi-squared test 2. Ordinal data on both measures in a study to see if two measures are associated Spearman’s rank correlation 3. An experiment with and independent groups design in which the DV is measured on a ratio scale Mann-Whitney U test 4. A study using a correlation technique in which one measure is ordinal and the other is ratio Spearman’s rank 5. A study testing an association using a nominal level of measurement = Chi-Square test of association 6. An experiment in which all participants were tested with alcohol and without alcohol on a memory test Wilcoxon’s T test 7. An experiment in which reaction time was tested using an independent subject design Mann-Whitney U test So…your data… GX For Spearmans Rho The observed / calculated value must be equal to or higher than the critical value for the result to be significant Observed / calculated = 0.685 Critical value = 0.456 (each test has a table of these – you do not need to know this for the exam…. You need to be able to conclude though so you need to be aware of what you need to do with these numbers) Is your data statistically significant? So, your results should say something like…. Observed value = 0.685 Critical value for one-tailed test p<0.05 = 0.456 From this, we can say that the results are statistically significant at p<0.01 meaning that there is less than a 1% possibility that the results obtained were due to chance As the results are significant ….link to hypothesis Also, link to your graph –positive correlation (not perfect…. Why??) So…. Your data…. DX For Spearmans Rho The observed / calculated value must be equal to or higher than the critical value for the result to be significant Observed / calculated = 0.378 Critical value = 0.4124 (each test has a table of these – you do not need to know this for the exam…. You need to be able to conclude though so you need to be aware of what you need to do with these numbers) So, your results should say something like…. Observed value = 0.378 Critical value for one-tailed test p<0.05 = 0.4124 From this, we can say that the results are not statistically significant at p<0.05 meaning that there is more than a 5% possibility that the results obtained were due to chance As the results are not significant ….link to hypothesis Also, link to your graph – zero correlation EX For Spearmans Rho The observed / calculated value must be equal to or higher than the critical value for the result to be significant Observed / calculated = 0.525 Critical value = 0.4265 (each test has a table of these – you do not need to know this for the exam…. You need to be able to conclude though so you need to be aware of what you need to do with these numbers) So, your results should say something like…. Observed value = 0.525 Critical value for one-tailed test p<0.05 = 0.4265 From this, we can say that the results are statistically significant at p<0.05 meaning that there is less than a 5% possibility that the results obtained were due to chance As the results are significant ….link to hypothesis Also, link to your graph –positive correlation Remember… The theory underpinning this report is??!!! Freud! The psychodynamic approach specifically the psychosexual stages of development If we become fixated in these stages it can impact our personality as an adult. Anal stage important focus ~ if a parent is too strict with toilet training, the child can become fixated and show personality characteristics such as being obsessively tidy (anal retentive). If a parent is too lenient with toilet training, the child could grow up showing personality characteristics such as being messy / untidy