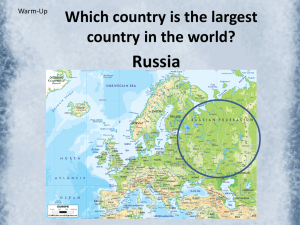
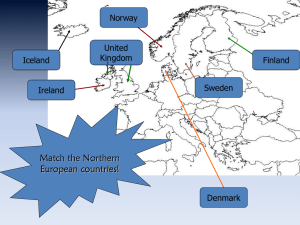
Physical Map of Europe
advertisement
Tuesday, August 30, 2011 Homeroom: •Use the restroom before class starts. You will not be able to go again until 2nd period. •SHARPEN PENCILS IF NEEDED! •RED time begins at 8:25 AM (no restroom after that) •Be ready… to write … RED TIME EQ: How can I use my reading skills to understand grade level text? Review the passage Assessment Write a 25 word summary of the passage. Choose your words wisely… Do Now… A natural resource is anything from the natural environment that people use to meet their needs. Some resources are renewable and others are nonrenewable. What are nonrenewable resources? A. resources such as forests and grasslands B. resources that were formed by nature over thousands of years C. resources such as plants and animals D. resources that can be replaced naturally and grown fairly quickly Physical Map of Western Europe What does everything look like? SS6G8 The student will be able to locate selected features of Europe. the Danube River, Rhine River, Volga River, English Channel, Mediterranean Sea, European Plain, the Alps, Pyrenees, Ural Mountains, Iberian Peninsula, and Scandinavian Peninsula, Strait of Gibraltar. How do I color in a physical map? Locate each Country Draw blue lines to represent rives and bodies of water. Make pointed shapes to represent mountains and mountain ranges DO NOT COLOR IN ANY OTHER LANDFORMS OTHER THAN THOSE LISTED Make sure you label each physical landform and body of water Physical Map of Europe Danube River Rhine River Volga River Ural Mountains Pyrenees Mountains Alps Mountains European Plain Where most of the crops are grown Iberian Peninsula Scandinavian Peninsula English Channel Separates the United Kingdom from Mainland Europe Mediterranean Sea The largest inland sea in the world. It takes 100 years for the water in this sea to circulate. Strait of Gibraltar 10. The use of natural resources affects the environment. Many human activities cause pollution. What is pollution? A. an agreement to restrict the number of resources being used B. the shipping of materials from country to country C. the use of renewable resources such as forests and grasslands D. putting impure substances into the land, water, and air