Introduction to media studies
advertisement

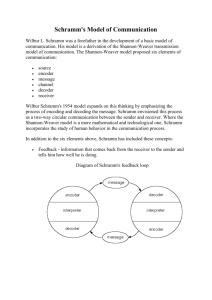
Introduction to media studies Early foci • Mass communication – Journalism – Print – Radio/TV/Film – Propaganda/political communication – Information campaigns More recent foci • • • • • Ideology/Framing Popular culture/cultural change Advertising/consumerism Identity/Disadvantaged groups Meaning making McQuail’s list of themes and issues • • • • • • • • • Time Place Power Social reality Meaning Causation and determinism Mediation Identity Cultural difference Let’s apply them to a few concerns of media studies • Political communication – The Healthcare debate – The death of Ted Kennedy • Gender communication – Pornography/Erotica – Treatment of female athletes on television • Online video – Hulu – YouTube McQuail’s ‘kinds of theory’ • • • • • Social scientific theory Cultural theory Normative theory Operational theory Everyday or common-sense theory Alternative traditions • Structural • Behavioural • Cultural “Elements that produce distinctive configurations of application and significance in the wider life of society” • Certain communicative purposes, needs, or uses; • Technologies for communicating to many at a distance; • Forms of social organization that provide the skills and frameworks for production and distribution; • Organized forms of governance in the ‘public interest’ Media features • • • • • • Senses engaged Industry structure Audience characteristics Uses and gratifications Economics Regulation Terms of media debate • Power of the new media • Social integration or disintegration they might cause • Public enlightenment Mass society • Disintegration of social bonds as a result of industrialization – Working conditions • Factory structure – Urbanization – Immigration • Move from bonds of personal affiliation to bonds of legal responsibility Mass society • Alienation – End of ties to work, production of entire article – Rootlessness – Anomie (normlessness) ‘Mass communication’ Mass communication process Mass audience Large-scale distribution and reception Large numbers One-directional flow Widely dispersed Asymmetrical relation Non-interactive and anonymous Impersonal and autonomous Heterogeneous Calculative or market relationship Not organized or self-acting Standardized content An object of management or manipulation Lasswell’s outline Schramm’s basic communication model Schramm’s conversation Schramm’s model of mass communication Schramm’s conditions of success What position is privileged in Schramm’s analysis? Hall’s Encoding/decoding model