CHAPTER 13
EARTH’S HISTORY
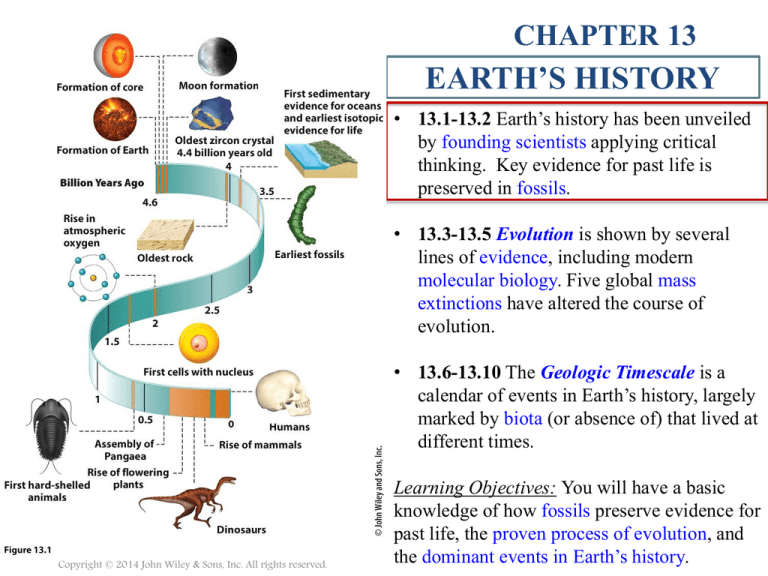
• 13.1-13.2 Earth’s history has been unveiled
by founding scientists applying critical
thinking. Key evidence for past life is
preserved in fossils.
• 13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several
lines of evidence, including modern
molecular biology. Five global mass
extinctions have altered the course of
evolution.
• 13.6-13.10 The Geologic Timescale is a
calendar of events in Earth’s history, largely
marked by biota (or absence of) that lived at
different times.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives: You will have a basic
knowledge of how fossils preserve evidence for
past life, the proven process of evolution, and
the dominant events in Earth’s history.
13-1 Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the
tools of critical thinking.
James Hutton (1726-1797)
• Proposed that geologic time was
indefinitely long
• Believed the Earth was self-renewing
(basis of rock cycle). “...no vestige
of a beginning--no prospect of an
end”
• Formulated the concept of
uniformitarianism.
“The present is key to the past”
-Sir Archibald Geikie (1835-1924)
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
“come on Jimbo,
lighten up would ya”
13-1 Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the
tools of critical thinking.
Nicholas Steno (1638-1686)
• Father of geology and stratigraphy
right hand shaka)
(and the
• First to suggest that fossils had once been
living organisms
• Developed the stratigraphic principles of....
Exercise 1:
(B)
(A)
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
(C)
13-1 Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the
tools of critical thinking.
Charles Lyell (1797-1875)
•
Father of modern geology
•
Wrote Principles of Geology, an seminal
reference for every 19th century earth scientist
•
Popularized uniformitarianism
•
Developed the stratigraphic principals of...
Exercise 1 (continued):
(D)
(E)
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
“Uhgg.. I hope my
sideburns aren’t
showing yet”
13-1 Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the
tools of critical thinking.
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
• Naturalist aboard HMS Beagle
• Studied Principles of Geology (by Charles Lyell)
• Wrote On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural
Selection
• Credited with the theory of evolution
No Charles. For the
4th time, its an
IGUANA, there are
no geckos here yet!
Darwin observed that all living things reproduce rapidly,
and yet no one group of organisms had been able to
overwhelm Earth’s surface. This led Darwin to conclude
that not all individuals in a generation will survive.
But, which survive and which do not?
Nature must select those with the most
favorable variations. Darwin proposed
that evolution occurred by natural
selection.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13-1 Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the
tools of critical thinking.
Photos of undergraduate Geology &
Geophysics majors on various field trips.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13-2 Fossils preserve a record of past life.
Fossils are the
remains of animals
and plants, or traces
of their presence,
that have been
preserved in the
crust.
Fossils preserve a
record of past life.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13-2 Fossils preserve a record of past life.
• Fossilization is the
process that turns a onceliving thing into rock.
• Preservation is typically
by replacement, formation
of mold, or cast.
• Fossil record is biased:
• Rapid burial required
• Usually only hard
tissue (shell, teeth,
bone) is preserved
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13-2 Fossils preserve a record of past life.
In rare cases, soft-part preservation occurs. This is
dinosaur skin, preserved inside a fossilized egg.
Brachiopod (a
marine invertebrate) fossils are
preserved as molds
in dolomite.
Molds of Dinosaur feathers
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 13
EARTH’S HISTORY
• 13.1-13.2 Earth’s history has been unveiled
by founding scientists applying critical
thinking. Key evidence for past life is
preserved in fossils.
• 13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several
lines of evidence, including modern
molecular biology. Five global mass
extinctions have altered the course of
evolution.
• 13.6-13.10 The Geologic Timescale is a
calendar of events in Earth’s history, largely
marked by biota (or absence of) that lived at
different times.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives: You will have a basic
knowledge of how fossils preserve evidence for
past life, the proven process of evolution, and
the dominant events in Earth’s history.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Evolution occurs by
natural selection: “..the
process by which favorable traits
that are heritable (passed on to
offspring) become more common
in successive generations...”
Genetic Mutations
(random changes to
DNA)
• It is the incremental adaptation to
environmental or community
“pressures, whatever they may be.
• “Primitive” indicates prior and
different not inferior (or superior)
in general.
• “Evolved” indicates an adaptation
to more recent conditions, not
superior (or inferior) in general.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Genetic Variation
(differences in
inherited traits)
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
• Early proponents of Darwin’s theory had trouble convincing
colleagues that evolution was at work. Evolution can take
generations to reveal changes, making it difficult to observe as it
is occurring.
• Fossils provide clues to understanding this process:
(1) Phylogeny (forward progression of physical traits)
(2) Homologous (similar) structures
(3) Vestigial (remnant) structures
(4) Embryology (similarities among embryos)
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Fossils provide clues to understanding this process:
(1) Phylogeny (forward progression of physical traits)
(2) Homologous (similar) structures
(3) Vestigial (remnant) structures
(4) Embryology (similarities among embryos)
FIGURE 13.8 The phylogeny of the horse family shows consistent
changes in the lower leg area, the development of molars designed for chewing tough
grasses, and an increase in body size and strength.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Fossils provide clues to understanding this process:
(1) Phylogeny (forward progression of physical traits)
(2) Homologous (similar) structures
(3) Vestigial (remnant) structures
(4) Embryology (similarities among embryos)
FIGURE 13.9 The limbs of
various animals are modified
for different functions. Notice
that individual bones have
been modified in different
ways to accomplish specific
types of tasks (grasping,
walking, flying, and
paddling). All limbs possess
the same basic set of bones
in the same order.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Fossils provide clues to understanding this process:
(1) Phylogeny (forward progression of physical traits)
(2) Homologous (similar) structures
(3) Vestigial (remnant) structures
(4) Embryology (similarities among embryos)
FIGURE 13.10 (a) Whales possess a vestigial pelvis
& femur originally designed for walking. Proof that
modern whales have evolved from walking ancestors
was found in 1994 in the form of a fossil whale that
had flippers for front legs and long hind limbs with
elongate toes for webbed feet. (b) Boa constrictors
also have vestiges of legs.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Fossils provide clues to understanding this process:
(1) Phylogeny (forward progression of physical traits)
(2) Homologous (similar) structures
(3) Vestigial (remnant) structures
(4) Embryology (similarities among embryos)
FIGURE 13.11 Many animals
display remarkably similar
features during their
development as embryos.
Human embryos, for instance,
have a tail and primitive gill slits.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
(5) Molecular genetics provide evidence for evolution and allow us to define
evolutionary relationships among all life.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Anti-biotic resistant bacteria on the rise
HIV evolves new drug-resistant strains. It
hijacks a cell’s machinery to duplicate itself; the
new virus particles (yellow) then burst from cell
membrane (blue), killing it.
Flu viruses evolve very quickly:
that’s why a new flu vaccine is
introduced every year
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Exercise 2: What are the 5 forms of evidence for evolution?
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Mass extinctions: Large numbers of
species permanently die out within a
very short period of time.
Hypothesized causes include meteor
impacts and massive flood volcanism,
both of which would alter global
climate.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
251 Mya, most
catastrophic
440-450 Mya:
Shortly after
life immerged
onto land
200 Mya, may
have been caused
by massive
volcanism
360-375 Mya
65 Myr, killed the
dinosaurs,
possibly caused
by Chicxulub
impact
Mass extinctions influence the evolution of life.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
251 Mya, most
catastrophic
440-450 Mya:
Shortly after
life immerged
onto land
200 Mya, may
have been caused
by massive
volcanism
360-375 Mya
65 Myr, killed the
dinosaurs,
possibly caused
by Chicxulub
impact
??
Mass extinctions influence the evolution of life.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several lines of evidence, including modern molecular
biology. Five global mass extinctions have altered the course of evolution.
Exercise 3: How many major mass extinctions have their been? Which
one killed the dinosaurs?
CHAPTER 13
EARTH’S HISTORY
• 13.1-13.2 Earth’s history has been unveiled
by founding scientists applying critical
thinking. Key evidence for past life is
preserved in fossils.
• 13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several
lines of evidence, including modern
molecular biology. Five global mass
extinctions have altered the course of
evolution.
• 13.6-13.10 The Geologic Timescale is a
calendar of events in Earth’s history, largely
marked by biota (or absence of) that lived at
different times.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives: You will have a basic
knowledge of how fossils preserve evidence for
past life, the proven process of evolution, and
the dominant events in Earth’s history.
13.6-13.10 The Geologic Timescale is a
calendar of events in Earth’s history,
largely marked by biota (or absence of)
that lived at different times.
Like a calendar divided into days,
weeks, months & years
The Geologic calendar is divided
into epochs, periods, eras, and
eons
Geologic
Column Drag
and Drop
Animation
But these divisions are defined
stratigraphically, largely by biota,
and are not fixed intervals in time
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Hadeon Eon (4.6-3.8 Bya)
•
•
•
•
•
•
Extraterrestrial barrage
Formation of the moon
Loss of first atmosphere (H2, He) and
formation of new noxious atmosphere (rich
in water vapor, CO2, NH3-ammonia, CH4methane, but no O2)
Iron catastrophe
Magma “ocean”
Earliest crust and H2O oceans
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Archian Eon (3.8-2.5 Bya)
Continental Cratons Form
• Noxious 2nd atmosphere (methane,
ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water vapor)
from extraterrestrial bombardment &
volcanic outgassing.
• Continental cratons formed.
• Life first appeared as bacteria
(stromatolites) in oceans.
• Photosynthesis was triggered, producing O2
in atmosphere.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Proterozoic Eon (2.5 Bya – 542 Mya)
• Continents developed. First supercontinent
(Rodinia) in the southern hemisphere.
• Mountains were built.
• Noxious gases were displaced by oxygen-rich
atmosphere.
• Eukaryotes and multicellular life flourished with
much biologic diversification. Soft-bodied
animals first appeared.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Paleozoic Era (542-251 Mya)
Complex life flourished, the first land animals
emerged and the continents reorganized
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cambrian explosion
burst of a highly
diverse, multi-celled
animal assemblage is
recorded in the
Burgess Shale (BCCanada).
Paleozoic Era (542-251 Mya)
Complex life flourished, the first land animals
emerged and the continents reorganized
Cambrian explosion:
burst of a highly
diverse, multi-celled
animal assemblage is
recorded in the
Burgess Shale.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Paleozoic Era (542-251 Mya)
Complex life flourished, the first land animals
emerged and the continents reorganized
First land
animals
Cambrian explosion:
burst of a highly
diverse, multi-celled
animal assemblage is
recorded in the
Burgess Shale.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Paleozoic Era (542-251 Mya)
Complex life flourished, the first land animals
emerged and the continents reorganized
Massive coal deposits,
store sun’s energy from
the Pennsylvanian
and sequester A LOT of
CO2
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mesozoic Era (251-65 Mya)
Laurasia
Pangea breaking
into
Tethys Ocean
Gondwanaland
Early Jurassic, ~190 Mya
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mesozoic Era (251-65 Mya)
Tethys Ocean
Cretaceous, ~90 Mya. Warm
climate & high sealevel. Oldest
Hawaiian volcanoes are active.
Laurasia
Pangea breaking
into
Tethys Ocean
Gondwanaland
Early Jurassic, ~190 Mya
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cenozoic Era (65 Mya-present)
Dinosaurs are extinct. Mammals
flourish.
Collision of India hypothesized to
enhance weathering, drawing
down atmospheric CO2, cooling
of atmosphere, and lowering sea
level
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cenozoic Era (65 Mya-present)
Quaternary Epoch is noted for its
glacial (ice age) and interglacial
cycles, about every 100,000 yrs
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cenozoic Era (65 Mya-present)
Humans arose starting in the late
Piocene
Sahelanthropus tchadensis,
“Toumai”, 6-7 Mya
Australopithecus
afarensis:
3.9-3.0 Myr
Homo Sapiens:
200,000 yrs to present
Homo Erectus:
1.8-0.3 Myr
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 13
EARTH’S HISTORY
• 13.1-13.2 Earth’s history has been unveiled
by founding scientists applying critical
thinking. Key evidence for past life is
preserved in fossils.
• 13.3-13.5 Evolution is shown by several
lines of evidence, including modern
molecular biology. Five global mass
extinctions have altered the course of
evolution.
• 13.6-13.10 The Geologic Timescale is a
calendar of events in Earth’s history, largely
marked by biota (or absence of) that lived at
different times.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives: You will have a basic
knowledge of how fossils preserve evidence for
past life, the proven process of evolution, and
the dominant events in Earth’s history.





