File
advertisement

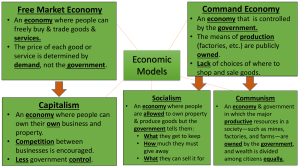
CHAPTER 18: SECTION 1 Amy De la Cruz Lizbeth Morales Luis Munoz Ruby Perez In the 1900’s, the world’s developed nations fell into 3 categories of economic systems-communism, socialism and capitalism. CAPITALISM • Capitalism: the means of production are privately owned • Ex: Germany, United States, India, & Japan Advantages Disadvantages Efficiency • Ignores production of public Freedom goods, produces private goods Highly decentralized and services Role of economy in government • Only produce for those who much smaller have demand • Consumer satisfaction • Ignores the poor, unemployed, • Flexibility to accommodate and less productive members of change society • • • • SOCIALISM • Socialism: an economic system in which government owns and runs some of the basic productive resources in order to distribute output in ways deemed to be in the best interest of society. • Ex: Finland, Canada, Ireland, & Belgium Advantages Disadvantages Those who are not fortunate or productive enough to earn a competitive income still share the benefits of society If workers receive government guarantees of jobs, more workers will be hired than are necessary, driving up the cost of production. Government provides broader ranges of services taxes are generally higher in socialist countries. COMMUNISM • Communism: a political and an economic framework where all property is collectively owned, labor is organized for the common advantage of the community, and everyone consumes according to their needs. • Ex: Cuba, North Korea, and the former Soviet Union Characteristics Disadvantages 1. Central planning authority 2. Movement of resources, particularly labor, is strictly controlled 3. The central planning authority makes all decisions 4. Individual risk-taking is strictly forbidden 1. Individual freedom is lost 2. Lacks effective incentives that encourage people to work hard 3. Fails to meet the needs and wants of consumers 4. Inefficiency of centralized planning