Slides with details research by the class
advertisement

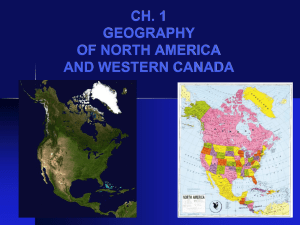
Physiographic Regions of Canada Physiographic Regions of Canada OBJECTIVES Section Objectives: Be familiar with the names, distributions and features of the physiographic regions of Canada (arctic, cordillera, interior plains, Canadian shield, St Lawrence lowlands, Appalachian) Compare the physiographic distribution with other forms of Regions (cultural, political, etc) Assess the impact of the land on historical and contemporary settlement (European and First Nations) Physiographic Regions of Canada REGIONS OVERVIEW Need to Know… Name Arctic, Appalachians… Characteristics (Place) Human, Physical Location Absolute, Relative, Major Provinces/Cities Jobs, Quality of Life, Safety, Access, Requirements Challenges/Opportunities (HEI) Patterns and Change Development, Population… Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Location: Eastern Canada Atlantic Canada Eastern US Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Characteristics: Low, rounded mountains (eroded from previous folded rock formations) Valleys and lowland areas (very fertile) Three broad highland areas (Southern Quebec, New Brunswick/Nova Scotia, Newfoundland) Maritime presence Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Characteristics: Natural Resources Coal** Iron Lead Zinc Timber/Lumber Fish- cod Oil- offshore Water- hydro Climate Cool, wet winters/most of the year Maritime influence- Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Characteristics: Population Approx 3-4 million Major centres and most people along the coastline Majority of British ethnic origin Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Challenges: - Low population- fewer stores, goods/services may be difficult to acquire. - Weather is a challenge - Many communities are isolated - Isolation from the rest of Canada (ROC) Opportunities: • High number of natural resources to be harvest—jobs • Low population- less competition for jobs, status, resources • Location- transport goods into Canada….US • Scenery…. Tourism, quality of life • Susatinability (food) Physiographic Regions of Canada APPALACHIAN REGION Relationship to Canada: - Not close…. Especially far West to far East… unfamiliarity… distant relatives - Isolated- cultural, language, beliefs, physical - Political differences- parties, laws - Labour/type of jobs/business- more blue collar than the ROC - Historically- dependent economically Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Location: Covers 46 000 km2 South Eastern Ontario South Western Quebec Toronto, Ottawa, Quebec City Lake Erie, Lake Superior, Lake Ontario, Lake Huron Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Characteristics: • St Lawrence River which opens to Atlantic Ocean • 5 Great Lakes (Canada/US border, 21% of world’s fresh water) • Altitude rangers from 0m to 150m (Grouse is 1200m) • Features a result of last ice age, river erosion and deposition, wind erosion • Clay base of soil Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Characteristics: Natural Resources Fresh water Agriculture (fertile soil) Minerals- iron, zinc, silver, copper, lead Climate Maritime effect/moderation 875mm precipitation/year 80cm of snow -30 degrees (January) +28 degrees Winds from Arctic/Mexico Pressure systems Source: http://www.nrcan.gc.ca/statistics-facts/home/887 Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Characteristics: Population Most densely populated area in Canada 14 million 50% of people who immigrate to Canada go to Ontario Traditionally Algonquian first nation territory Most of ethnic population (39%) is ‘other’ and 50% is British/British & other Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Challenges: Lifestyle: traffic/commute, big city problems Highest population density in Canada High levels of industry Opportunities: Centres of commerce (Toronto), government (Ottawa), culture (Montreal) Connections to US Economies of scale Physiographic Regions of Canada GREAT LAKES/ST LAWRENCE LOWLANDS REGION Relationship to Canada: Location of many “heartlands” Close proximity to many major historical events Sources: http://www.eclectecon.net/media/ Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Location: Covers almost half of Canada (8 million km2). Does not extend far into US. Borders the Arctic, Plains, St Lawrence Lowlands and Appalachian regions Thunder Bay & Sudbury(ON), Churchill (MB), Labrador, Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Nunavut, North West Territories Hudson Bay, Great Lakes Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Characteristics: • Geographical Features • Exposed precambrian rock “The region, as a whole, is composed of ancient crystalline rocks whose complex structure attests to a long history of uplift and depression, mountain building, and erosion. Some of the ancient mountain ranges can still be recognized as a ridge or belt of hills, but the present appearance of the physical landscape of the Canadian Shield is not so much a result of the folding and faulting and compression of the rocks millions of years ago as it is the work of ice in relatively recent geologic time. During the Pleistocene Epoch (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago), the vast continental glaciers that covered northern North America had this region as a centre. The ice, in moving to the south, scraped the land bare of its overlying mantle of weathered rock. Some of this material was deposited on the shield when the ice melted, but the bulk of it was carried southward to be deposited south and southwest of the Canadian Shield.” (Britannica Online) Source: http://www.maggiesale.ca Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Characteristics: Natural Resources Copper, zinc, gold, iron, silver, nickel, cobalt, tungsten. Climate Temperature: -39 degrees (January) to +32 (degrees) 250 days of sun Precipitation: 3001600mm of rain/snow Sudbury, ON 2005 Sudbury, ON 1888 Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Characteristics: Population Numbers: 3-4 million Where they live: southern part of region, scattered pockets (resource-towns) Demographic breakdown: German, Aboriginal, Dutch, Pilipino= 50%, Source: http://atlas.nrcan.gc.ca/auth/english/maps/archives/poster/population?maxwidth=1600&maxheight=1400&mode=navigator&upperleftx=0&upperlefty=0&l Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Challenges: - Isolation of cities (self-sustaining) - Huge range of climate (people, infrastructure) - Movement of people/goods between centres Opportunities: - Resources to be mined (jobs, economy) - Tight knit communities - Strong community leadership, arts, community support Physiographic Regions of Canada CANADIAN SHIELD Relationship to Canada: Source material for stereotypes? The most diverse region? A sense of cultural unity? Source: http://www/faculty.marianopolis.edu Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Location: Central Canada Prairies East of the Cordillera, West of the Shield Stretches into US Strong North/South stretch Alberta, Manitoba, Saskatchewan Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Characteristics: - Flat, rolling hills - Bordered by the Rocky Mountain range - Strong agricultural presence Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Characteristics: Natural Resources Agriculture Oil (AB, SK) Potash (SK) Coal, iron (minimal) Climate Temperatures: Harsh cold winters (30) “real hot” summers (+30) Precipitation: 200-400mm, most precipitation comes in the form of snow, dry summers Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Characteristics: Population Distribution wide, some pockets but otherwise thinly populated Approx 5 million in the region, mostly in cities 41-47% Majority is “other”…. European (German, Ukranian), Aboriginal Approx 1/3 are still British origin English dominant mother tongue Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Challenges: Environmental: flat (recreation, variety of landforms), climate Economic: isolation (variety of jobs, getting to/from, cost of living) Social: isolation (less interaction) Opportunities: Economic: farming (opportunity), building factories/industries Political: ease of election (less competition, face to face communication) Social: strength of communities, Physiographic Regions of Canada INTERIOR PLAINS Relationship to Canada: • Machine, a goods-producer • Hinterland relationship, colonial • Stereotype of Canada (hot summers, cold winters, farm, rural) • Boring…. Rural… one horse town • Marmish Aunt • Little bro/sister • Breadbasket of Canada Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Location: BC, Yukon (absolute) West Coast of Canada (relative) Between the pacific ocean and the interior plains (relative) Bordered by the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountain range Extends into the US (down into South America) Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Characteristics: Mountainous (jagged), heavily treed Variety in elevation and topography Elevation: -50m to 3954m (Mt. Robson), 4400m (Mt. Elbert), 5900m (Mt. Logan) Maritime/Coastal influence Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Characteristics: Natural Resources Fish Coal Lumber/forestry Gold Fresh water Other: wine, blueberries, cranberries Agriculture Climate Mild/wet/humid Varied between southern and northern reaches, mountain/non-mountain Maritime influence Temperatures 2-20 degrees (Vancouver) Precipitation 1113 mm annually (falls mostly as rain) Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Characteristics: Population 4.5 million (BC), 35 000 (YT) 4.7 people/km2 Pockets: Vancouver + , Victoria Setteled area: coast, interior (Kelowna, Kamloops) 33%- Other (high Asian percentage) 50% +- British/British+Other Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Challenges: • Environmental: earthquakes, natural disasters, natural elements • Social: big city problems (gangs, organised crime, drugs) Opportunities: • Economic: high quality job opportunities (resources: mining), service industry, trading with US and Asian Gateway • Social: more people (economies of scale), diversity in a way unique from other population centres Physiographic Regions of Canada WESTERN CORDILLERA Relationship to Canada: • Favourite child (beautiful, everyone wants to visit), some envy • Connected: Vancouver has important role in the import/export portion of the Canadian Economy • Separateness: on the coast, separated by a significant mountain range, outlook is more West (Asia) and South (US) than East (Toronto, etc), diverse culture, West Coast Lifestyle Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Location: North of the treeline North West Territories, Nunavut North of Canadian Shield, Interior Plains Connected to Russia, US, Finland, Denmark Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Characteristics: • Barren • Cold • Icy • Specific flora and fauna that are highly adapted to survive in the region Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Characteristics: Natural Resources Oil/Natural Gas Diamonds Nickel Animals: seals Climate Cold Temperatures: -50 to 10 degrees Precipitation: 20-50mm, mostly as snow Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Characteristics: Population Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Challenges: Opportunities: Physiographic Regions of Canada ARCTIC Relationship to Canada: Sources http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=A1ARTA00 07093 http://www.oneexchangecorp.com/facts.html