IE130 - SharePoint - Erie Community College
advertisement

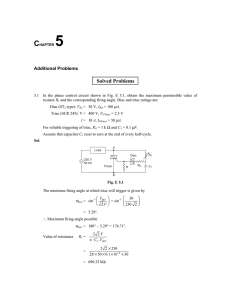
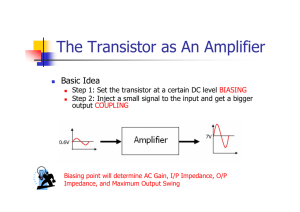
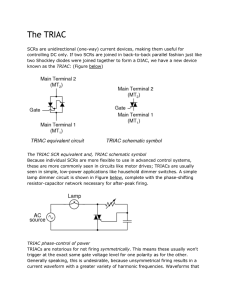
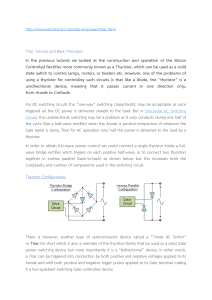
ERIE COMMUNITY COLLEGE – NORTH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: IE130 Industrial Electronics CURRICULUM: Industrial Technology CATALOG DESCRIPTION: IE130 (2-2-3) Topics include: review of AC voltage and current phase relationship and computations of reactance and power; transformers and transformer applications; introduction to generators and motors; single-phase motors; three-phase alternators and motors; DC motors and generators and AC and DC motor control fundamentals. Experiments include: AC phasor computations, single-phase transformers, three-phase wye and delta connected transformers, single-phase AC motor characteristics, three-phase alternators, three-phase motors, DC motor and generator characteristics, simple motor starter and control circuits. Prerequisites: IE 100 and IE101. (N) DURATION OF INSTRUCTIONAL PERIOD: 50 minute lecture two times per week for 15 weeks; Lab: Once per week for 100 min. ACADEMIC CREDIT HOURS: CONTACT HOURS: LECTURE, LAB, CREDIT HOURS: Three (3.0) Credit Hours Four (4.0) Contact Hours (2-2-3) SUGGESTED TEXT/ COURSE MATERIAL: Electronics: Principles & Applications By Charles. A. Schuler COURSE OUTCOMES: Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of silicon and germanium diodes. 2. Identify the operating conditions of diodes and their functions in simple DC circuits. 3. Explain the functional blocks of a basic power supply having: half-wave or bridge rectifier, simple capacitor filtering and a Zener regulator and define the terms - % ripple and voltage regulation. 4. Identify and describe transistor amplifier configuration. 5. Explain the DC load line and Q point that describes the various biasing arrangements that are used with the three transistor configurations. 6. Apply the knowledge of AC equivalent circuits and explain the operation of small signal amplifiers. 7. Identify the function and operating conditions of Field Effect Transistors. 8. Identify the types of amplifier circuits common to Field Effect Transistors. 9. Identify various operational amplifiers. 10. Explain the operation of large signal amplifiers 11. Evaluate the operation of SCRs, DIAC and TRIAC. 12. Understand and use an oscilloscope to observe and measure electronic voltages and signals. 13. Use test equipment to verify the operation of electronic components. 14. Identify various electronic devices in a circuit and determine their operational function in the circuit. 15. Explain the operation of rectifiers, regulators and filters in a power supply. 16. Breadboard an amplifier, measure and determine the circuit operating point, voltage gain and phase angle for transistors, FETs and operational amplifier. 17. Write a well-organized and comprehensive report of the experimental results. PROGRAM COMPETENCIES: N/A SUNY GENERAL EDUCATION TEN KNOWLEDGE AREAS: N/A ECC GRADUATE LEARNING OUTCOMES: 1. Communicate effectively. 2. Read and think critically. 3. Apply appropriate mathematical procedures and quantitative methods. 10. Demonstrate competence with computers and technology. ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING: Three (3) hourly exams (60 min.) @ 100 pts. One (1) Final Exam (2-3 hours) Homework and Quizzes 11 Labs ) ) ) 60% 40% 100% Total score averaged and presented as a letter grade: A = 90% B = 80% C = 70% D = 60% F = 50% RELATED LIBRARY PROJECTS: None required LECTURE TOPICAL OUTLINE: WEEKS I. Introduction 1. Course overview, syllabus 2. Review of DC/AC principles; superposition 2/3 II. Solid state physics 1. Semi-Conductor Materials; intrinsic material, germanium/silicon 2. Temperature effects; extrinsic, N-/P- sloping 2/3 III. Diodes 1. Characteristics of diode curve; forward/reverse bias 2. Diode symbol, nomenclature, ratings, specifications 2/3 IV. Diode Applications 1. Clippers/Clamps 2. Power Supply; 1/2 wave/bridge rectifier, cap. filters, surge current, PIV, ripple voltage, loading effect 3. Zener characteristics , symbol, nomenclature, ratings 4. Zener regulation; voltage regulation 4/3 HOURLY I 1/3 V. Transistors 1. NPN/PNP, symbol, nomenclature, specifications 2. Characteristic curves, temperature effects; load line, Q point 3. KCL device, A, B; Switch mode operation 3/3 VI. Small signal Amplifier 1. Gain, CE configuration, DC biasing techniques 2. Q point, cutoff, saturation, thermal effect of Q point 3. CC, CB configuration, emitter follower 4/3 VII. FET Theory 1. FET characteristic curves, symbols, nomenclature, specifications 2. Q point, DC biasing techniques, load line 3. Amplifier circuits; advantage FET vis transistor 3/3 HOURLY II 1/3 VIII. Operational Amplifiers 1. Op Amp characteristic curve, symbol nomenclature, specifications 2. Open loop gain, frequency effects, impedance 3. Application; Inverting/Non-Inverting, 4. Adder/subtractor, filtering theory, filter circuits 5. Multistage, special circuit use 5/3 IX. Troubleshooting technique 1. Preliminary checks, "divide 'n conquer" 2. Distortion, noise, intermittent 2/3 X. Oscillators 1. Oscillator fundamentals, feedback effects, resonance 2. Types of oscillator; RC phase shaft, LC Hartley/Colpitts 3. Wein bridge, crystal; square wave oscillator, spurious oscillators 3/3 HOURLY III 1/3 XI. LIC 1. 555 timer, square wave generator 2. Specialty ICs 2/3 XII. SCR, TRIAC, DIAC 4/3 1. SCR operation, characteristic curves, symbol, nomenclature, specifications 2. SCR application 3. TRIAC/DIAC operation, characteristic curves, symbols, nomenclature, specifications 4. TRIAC/DIAC applications XIII. Review 1/3 COMPREHENSIVE FINAL LABS I. INTRODUCTION 1. Overview of course, syllabus, report format 2. Lecture: oscilloscope theory of operation 3. Video: 1 II. SCOPE LAB 1 - DC/AC Amplitude Measurements 1 III. SCOPE LAB 2 - Measurement of Frequency 1 IV. SCOPE LAB 3 - Phase Measurement 1 V. Diode/Zener Characteristic Curve 1 VI. POWER SUPPLY 2 1. 1/2 and full wave rectification, w/cap filtering, variable loads 2. Zener regulation, effect on ripple VII. TRANSISTOR AS A SWITCH 1 VIII. TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIER BIASING 2 1. Base bias, emitter, biasing, cap. bypass 2. Voltage divider biasing IX. JFET AMPLIFIER OPERATION 1 X. OP AMP CIRCUITS 2 1. Inverting, Non-Inverting, adder 2. Comparator, integrator/differentiation XI. SCR CONTROL CIRCUIT 1 XII. TRIAC/DIAC CURRENT CONTROL 1 PREPARED BY: AL Ashman, June, 2000 REVISED BY: Anthony Dalessio, June 2009 APPROVED BY: EET Curriculum Committee, June 2009