“Name of Model”
advertisement

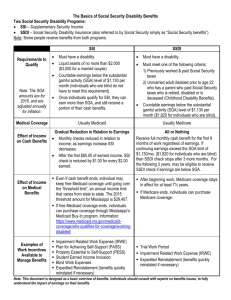
Work Incentives and Work Supports: The Ins And Outs Social Security, Medicaid Buy-In's And Other Community Supports JOE ENTWISLE NCHSD NTW AgrAbility Conference Grand Rapids, MI OUTLINE •SSI: Eligibility, Resources, Income, Work, Medical Assistance, PASS •SSDI: Eligibility, Work, Medicare •Self Employment •Work Incentive Planning and Assistance •Ticket to Work •Employed Individuals with Disabilities MBI Social Security’s Benefit Programs RSDI/SSDI Retirement, Survivors, Insurance) Medicare Concurrent Disability SSI- Supplemental Security Income Medicaid* • Social Security Disability Insurance(SSDI) provides benefits to disabled or blind people who are “insured” by workers’ contributions to the SSA trust fund. • Supplemental Security Income makes cash assistance payments to the aged, blind and disabled who have limited income and assets. Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI, Title II) Supplemental Security Income (SSI, Title XVI) KEY CONCEPTS “SGA” “COUNTABLE INCOME” Definition of Disability for both SSDI and SSI •“Assistance Program” •Must have low income & resources •“Countable Income” = Key Concept = $674 or less •Resources = less than $2,000 •Cash payment + Medical Assistance The maximum dollar amount a person can receive in federal SSI cash benefits on a monthly basis $674 month for eligible individual SSI pays the difference between the FBR and countable income General Income Exclusion of $20 Deducted first from unearned income Earned Income Exclusion $65 per month plus 1/2 of the rest o These are expenses that one must pay for out-of pocket in order to work. o They must be related to the primary disability or an established secondary disability. o The individual must have an IRWE approved by SSA first and must show receipts. o o o o o o medical appointment payments prescription co-payments prosthetic devices transportation costs for taxis costs of adaptive devices for automobiles special transportation used by persons who cannot drive an unmodified automobile. IRWE’s deducted from countable income before we divide by 2. Therefore, IRWE is not subtracted from countable income dollar for dollar (like it is with SSDI). Mary pays $100 per month for specialized transportation to and from work. She is paid $500 per month from her job. 500 Earned Income - 20 General Disregard - 65 Earned Income Disregard - 100 IRWE =315/2 =157.50 Countable Income : A person whose primary disability is a visual impairment can use BWE’s to deduct the cost of a large list of items. Unlike IRWES, BWEs are deducted AFTER we divide by 2. The entire BWE is deducted from income dollar for dollar. Because of this, BWEs can be used to deduct so much from countable income that often times the SSI check is not reduced at all! IRWEs State and Federal Taxes Union Dues Mandatory Pension Cost of Uniforms Reader Services, Driver Services, and Cost of Service Animal’s Care Childcare Transportation Meals Consumed at Work Adaptive Equipment Mary earns $500 per month. She has $100 in various BWEs (taxes, etc.) $500 Earned Income -20 General Disregard -65 Earned Income Disregard =415/2 =207.5 -100 BWE $107.5 Countable Income! Must be under the age of 22 and regularly attending school. Exclude up to $1550 of earned income per month when they figure the SSI monthly payment amount. The maximum yearly exclusion is $6,240. Mary earns $500 a month. But, she is also attending community college with enough hours to qualify for Student Earned Income Exclusion. $500 Earnings minus $500 SEIE (out of the possible $1550 max per month) NO SSI REDUCTION until she uses $6240! When work earnings reduce SSI payments to zero, MA will continue if yearly wages below “Threshold” amount Individual Thresholds can be higher based on an individual’s actual MA use SSDI DAC Entitlement programs Disability Medicare Coverage Paid from Social Security Disability Insurance Trust Funds Have worked in “covered” employment May be eligible on parents record if disability began before age 22 Gateway to Medicare 1. Gross average earnings minus any: - impairment-related work expenses;& - special conditions or subsidy 2. Consider the value of the work 3. Consider if work is an “unsuccessful work attempt” ( lasted 6 mo or less) TWP -Trial Work Period SGA - Substantial Gainful Activity EPE - Extended Period of Eligibility Expedited Reinstatement IRWE/Subsidy EPMC Medicare for people with disabilities who work 9 months of $700 or more (no limit) 80 hours of self-employment activity per month Don’t need to be consecutive Only one TWP per disability entitlement Review by SSA when completed Measure of ability to work $980 per month for 2009 $1,640 per month for the blind SGA If performing work that is “SGA” after the TWP cash SSDI benefits stop IRWE Subsidy Expenses that are necessary to work, related to the person’s disability and paid for by the worker May be considered to reduce countable income below SGA Value of additional support to perform a job, or difference between actual wages received and value of work performed May reduce income below SGA like IRWE EXAMPLES: more frequent breaks, more supervision/support, lower production requirements Consecutive 36 month period after TWP Cash benefits reinstated for months under SGA ($980) without a new application If at SGA at end of EPE, no more SSDI payments When someone’s Social Security or SSI disability benefits have ended due to earnings from work, he/she is able to request reinstatement without filing a new application Within 5 years of last benefits received Beneficiaries must be unable to work due to their medical condition They may receive temporary benefits (as well as Medicare/ Medicaid) for up to 6 months while SSA evaluates their medical condition Federal health insurance program 24-month waiting period after SSDI benefits start $96.40/month Part-B premium (2009); Part A is free Continued Medicare coverage even if no longer eligible to receive SSDI payment because of work At least 93 months of coverage after TWP ends Billed quarterly for months an SSDI payment isn’t received After EPMC, Medicare can continue if beneficiary pays the monthly premiums Must continue to have disabling condition State may pay Medicare premium through the Medicare Buy-In program, if income guidelines are met Programs designed to allow workers with disabilities to buy into Medicaid at higher income and asset levels ◦ First and only Medicaid work incentive ◦ Operating in 40 states Program features: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Vary from state to state Required to pay premiums Eligible from 16-64 and above Most offer ability to increase assets 35 ◦ Must have a disability to participate ◦ Must be working to participate ◦ Provides wrap around coverage for private insurance More than 100,000 participants nationwide Many offer participants the ability to retire while maintaining eligibility Utilize net income for eligibility on selfemployment 36 o o o 7.8% of the general population is self employed 12.2% of people with disabilities are self employed 90% of businesses started by people with disabilities are successful due to planning and pre-determined supports o Provide greater flexibility and freedom to the owner o Allow independence and autonomy o Provide greater income potential o Allow for building of assets o Accommodate some disabilities more readily than wage employment Determine if it is self employment. Determine Net Earnings from Self Employment (NESE). For SSDI, determine TWP Determine countable earnings for SSDI and SSI (NESE minus any applicable deductions). Adjust checks accordingly. Is the beneficiary showing good faith intention of making a profit or producing income? AND Is the beneficiary engaged in the activity on a regular basis? AND Is the beneficiary presenting him/herself to others as ‘a business’? SSA will calculate the Net Earnings from Self Employment (SSI and SSDI) Utilize SSA deductions (IRWE, Unpaid help etc..) Establish countable income Determine impact on benefit o Plan for Achieving Self Support o Individual Development Accounts o Vocational Rehabilitation Services SSI recipients submit their business plan to SSA for approval as a PASS. Expenses within the business plan may be approvable for a PASS. A SSI recipient must have NESE or assets in order to fund the PASS! May use SSDI as funds for PASS, making SSI eligible Under the Rehab Act, VR agencies are allowed to support self-employment as a goal and can help to fund a business. Rules vary from state to state and some states have strict requirements. VR agencies can work with other workforce systems, such as the Small Business Development Centers, to support individuals. o o o A matched savings account in cooperation with a local bank; goal can be small business. Individual Development Accounts may be used on their own, or in conjunction with a PASS or Family Self-Sufficiency Plan, to fund a business. Federal IDA programs are exempt from most public benefit programs like SSI. This means that what the individual deposits, matching deposits and interest earned will not count as a resource. Pizza Restaurant Owner: o Developed PASS to fund rent for restaurant ($35,000). o State VR funded a Business Enterprise Program grant ($50,000). o Individual Development Account containing wages from previous employment ($15,000) $100,000 for the Business!! www.start-up-usa.biz http://www.worksupport.com/resources/listCont ent.cfm/5/2/0 http://digitalcommons.ilr.cornell.edu/edicollect/ 53/ www.griffinhammis.com Self Employment For People with Disabilities http://www.brookespublishing.com/store/books /griffin-6520/index.htm Work Incentive Planning and Assistance ◦ Information and Referral ◦ Benefit Problem Solving and Advocacy ◦ Benefits Analysis and Advisement ◦ Benefit Support Planning ◦ Benefit Management SSA’s Website https://secure.ssa.gov/apps10/ oesp/providers.nsf/bystate Provides beneficiaries with more choices for receiving employment services Provides greater incentives for entities providing employment services • – – – Employment Network (EN) Any qualified State, local, or private entity Assumes responsibility for coordination and delivery of employment services, vocational rehabilitation services, or other support services under the Ticket to Work program see www.yourtickettowork.com for list in our area 1-866-968- 7842(yourticket) TDD 1-866-833-2967 INFORMATION WWW.SSA.GOV Red Book on Work Incentives SSA Employment Support Programs WWW.SSA.GOV/WORK www.yourtickettowork.com 1-800-772-1213 Joe Entwisle 312.401.3909 www.nchsd.org jentwisle@hdadvocates.org 55