Groundwater, Aquifers, and Flooding webquest
advertisement

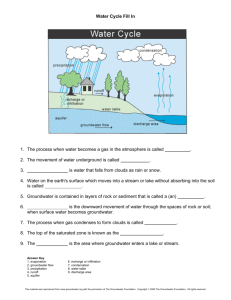
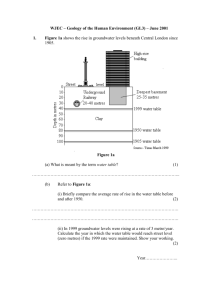
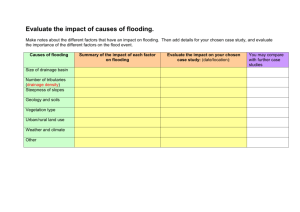
Groundwater, Aquifers, and Flooding Webquest Name ___________________________________ Use the links (also provided on Haiku) to answer the following questions: Basic Groundwater Hydrology http://www.issaquah.org/comorg/gwac/hydro.htm (Important terms on this site are in bold type; the Groundwater and Aquifers image section of the Groundwater and Flooding Haiku page will be helpful also!) 1. In terms of the hydrologic (water) cycle, what is infiltration? 2. Groundwater occurs in two different types of “zones.” What is the unsaturated zone? 3. What is the saturated zone? 4. The boundary between the unsaturated and saturated zones is known as the _______________. 5. What is an aquifer? 6. Describe the difference between an unconfined aquifer and a confined aquifer: 7. When the pressure in a confined aquifer is sufficient for a well to spout water several feet above ground, the well is referred to as a ______________________________. 8. In terms of groundwater, what is recharge? 9. What is discharge? 10. What features are found where the water table intersects the land surface? Water Movement in Aquifers http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/earthgwaquifer.html 11. Where can wells be drilled? 12. What is the source of water for refilling the aquifers? 13. If your well and your neighbor’s well draw from the same aquifer, what can happen if you pump your well too fast? Click on the image link Flooding from Groundwater https://surry.haikulearning.com/kyless/earthsciencefall12/cms_file/show/5364836.jpeg?t=1349094819 14. What are the most common sources of flooding? 15. When can flooding from groundwater happen? Look at the column on the right, key features of flooding from groundwater section. 16. What usually makes flooding from groundwater occur? 17. How long can this flooding from groundwater last? 18. Where is flooding from groundwater most common? Groundwater Flooding FAQ http://www.groundwateruk.org/faq_groundwater_flooding.aspx 19. How many people live in groundwater risk areas in England and Wales alone? 20. When does groundwater flooding tend to occur (look in the second paragraph)? 21. Why does groundwater flooding take longer to dissipate than surface water floods (look in the third paragraph)? Groundwater Flooding Research http://www.bgs.ac.uk/research/groundwater/flooding/groundwater_flooding.html (scroll towards the bottom of the page) 22. What are the three main settings where significant groundwater flooding occurs in the UK? 23. In which two of these settings does the majority of groundwater flooding in the UK occur? Click on the Unconfined major aquifers link. (http://www.bgs.ac.uk/research/groundwater/flooding/major.html) 24. What is clearwater flooding?