Mastering Bylaws - Federation of Calgary Communities

Bylaw Basics
November 12, 2009
City of Calgary
Contents
Governance
Incorporation of Societies
Bylaws - the fundamental governing rules
Needed components of bylaws
Membership
Meetings
Government
Management & finances
Changes to bylaws
Resources & Links
Checklist & examples
Discussion & questions?
Expectation
If you are a society in Alberta, the expectation is that you will
GOVERN the organization in a democratic, efficient and effective way, according to your
BYLAWS AND POLICIES on behalf of the
PEOPLE YOU SERVE.
Governance
Governance is all about relationships and how we organize ourselves to do work
Each of the 3 areas are needed for strong
& effective governance
Fiduciary – define problems & reviews performance – oversight & authority
Strategic – solves problems & shapes strategies
Generative –frames problems & engages in sense-making – gives fresh perspective
Governance
Good governance can be in 3 concepts;
Strategic
(logical)
Governance as Leadership
Generative
(expressive)
Fiduciary
(productive)
Options for Incorporation
FOR NOT-FOR PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
Societies Act
Alberta Companies Act
The Canada Corporations Act
Other Special Statutes
Cooperative Associations Act
FCSS / Children’s Services Act
Agricultural Societies Act
Religious Societies Land Act
Etc.
Private Act of Legislature
Incorporation
Most not-for-profits in Alberta incorporate under the Societies Act
However Section 3 states:
“Five or more persons may become incorporated…or other useful purpose, but not for the purpose of carrying on a trade or business.”
Need application for incorporation and the
Bylaws for the society
Application includes: Name of the Society
Objects of the Society
Incorporators of the Society
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Under which Act is your organization incorporated?
What is your status under this Act?
Are you current with respect to any necessary filings?
Does your organization answer to any other governing bodies?
Are there any formal partnership agreements?
Does your organization have to meet licensing requirements?
Are you a chapter organization which answers to another governing body on a regional, provincial or national level? What are those levels and accountabilities?
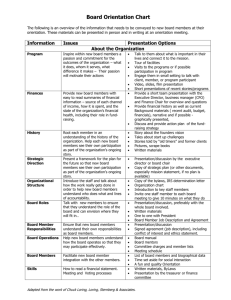
Bylaws
Bylaws are the fundamental governing rules and regulations of any society.
State how the society is to be governed and how the powers of the society are to be exercised.
Ground rules that the board uses to develop its structure, clarify roles, responsibilities and functions, and establish meeting and voting procedures.
May be called the Constitution, Charter, or Rules and Regulations or a combination of these terms.
Specific Techniques for Drafting Bylaws
Definitions – glossary with terms and acronyms
Draft carefully & use consistently
Plain Language – short sentences with 1 idea and short paragraphs
Numbering – Number each separate paragraph for reference
Content of Bylaws
1. Name of the Society*
2. Bylaws*
3. Definitions
4. Membership in the Society
Terms of Admission*
Rights of Obligation*
Conditions of Withdrawal*
Expulsion*
5. How to Draft Your Bylaws
Mode and time of calling general and special meetings*
Quorum*
Rights of Voting*
6. Governance Structure of the Society
The board of directors*
The executive
The committee
Appointment and Removal*
Duties and Powers*
Remuneration*
7. Management and Financial Matters
Registered office
Seal of the Society*
Financial records and books*
Minute books and other records*
Borrowing powers*
Audit*
Indemnities
8. Amendments*
9. Dissolution*
*These are the minimum requirements of the Societies Act.
Introductory Articles
Preamble – short paragraphs including the name & this document is the bylaws
Name must have: one of the required words, a descriptive element, a distinctive element
Definitions – a glossary defining terms and acronyms
Objects of the society –drafted clearly and precisely as they define what the society has the power to do
Drafting Bylaws: Membership
Membership Who the members are & how
What their rights and duties are as members
Categories of members
Examples often used: Voting Members, Honorary Members,
Affiliated Members, Junior Members, Life Members, Active
Members, Non-Voting Members, Associate Members, Senior
Members, Young Members, Full Members
Admission of members How does a person become a member?
Withdrawal of membership
Voluntary
Expulsion or suspension
Membership Fees – who decides, when are they due, etc.
not the amount
Rights & Obligations – of each category of members
Meetings
Annual General Meeting - AGM
Section 25 of the Societies Act states:
“25 A society shall hold an annual general meeting in
Alberta and shall present at that meeting a financial statement setting out its income, disbursements, assets and liabilities, audited and is signed by the society’s auditor.”
There is no right or wrong time to hold the AGM.
What is the best time for your particular society?
The bylaws should allow the AGM to take place as long as four months after the end of the fiscal year. It can take that much time to prepare financial statements.
Meetings- Annual General Meeting
Who calls the AGM? You must state who calls the AGM and who chooses its actual time and place.
board of directors usually calls the meeting or the executive or the president
Bylaws must specify the length of time required for notice.
Be careful that the time is not too short.
You must give your members a minimum of 21 days’ notice for a special resolution.
You may notify members of the meeting using:
A notice in a society newsletter
A notice published in newspapers
A notice may be circulated by e-mail
Posters placed in a location where most members gather
What is the AGM Agenda? - decide the business of the AGM
Bylaws should include:
A standard agenda for the AGM
Other agenda topics added by the board of directors
Other specific motions that any member has given notice of before the meeting is called
General Meetings : Include all prior info.
Other Regular General Meetings
Special General Meeting
Who can force the board to call a special general meeting?
What business can occur at this meeting?
What notice do members require?
What are the Procedural Rules for General meetings?
What is the quorum for meetings?
Are the meetings open to the public?
Who chairs the meeting –usually the President
How does the meeting adjourn?
How does voting occur? Special structure? By proxy?
What majority is needed?
Does the President or chair vote?
What happens if a member dose not get notice of a meeting?
Meetings: specify the basic rules
When to hold meetings
Who call the meetings (& how)
Who votes
How the votes occur
Governance Structure
Body/bodies that govern between general meetings
Basic Structure –what type of board?
Policy governing board
Administrative governing board
Board -"9(4)(d) The bylaws that accompany the application shall contain provisions for all of the following matters:
(d) the appointment and removal of directors and officers and their duties, powers and remuneration.”
Board of Directors
Board is required – may be called;
Executive, council, board of governors, board of administrators etc.
The powers & duties of the board
The Societies Act requires a meeting of all members to address certain important business. The matters are:
Amending the bylaws (s. 15)
Amending the objects (s. 16)
Issuing debentures (s. 18)
Surrender of Certificate of Incorporation (s. 34)
Winding up (s. 35(1))
Board of directors can legally deal with all other matters, unless restricted in the bylaws
Board of Directors
What size is the board?
Who are the directors?
How do are they elected?
Can a director be re-elected?
What are the terms for board members?
Other requirements for electing directors?
Can a director resign? Be removed?
How is a board vacancy filled?
How often does the board meet?
What rules govern the board meetings?
Executive Committee
May not need executive
If large society, no paid administrator, then board may be policy-making body and executive is management body
Consider;
Is an executive committee needed?
What is the relationship between board & executive (& administrator)?
Define roles & responsibilities of executive an administrator
Executive Committee
Bylaw to allow the board to delegate powers to the executive committee
How large is the executive?
Who is on the executive?
What rules govern the meetings of the executive committee?
Officers
Must have some officers
Minimum usually a president & secretary
What are the responsibilities and duties of each position?
How do we select the officers?
Can an officer resign? Be removed from office?
How do we fill a vacancy?
Other Committees
Bylaws should state that the board has the power to set up committees
Can give the board power to assign functions, responsibilities, and powers
What are the permanent or standing committees?
Executive
Nominating
Membership
Finance or fundraising
Personnel etc.
Other Committees
What are the relationships between committees & board or executive?
What are the duties of each committee
How do we form the committee?
How do we fill vacancies on committees?
What rules govern the meeting of the committees?
Management & Finances
Bylaws must describe important administrative, financial & management matters
Registered Office – choose the city/town only (not address)
Seal of the Society –shows authority
Adopting a seal
Who controls it
How & when to use the seal
Who countersigns the seal
Management & Finances
Fiscal Year of the Society – any consecutive period of 365 days
When is the AGM? Have a date reasonably close to AGM
What are the fiscal years of major sponsors?
Is there a natural season?
What about finances & society’s books?
Must keep books properly
Who signs the checks?
Who keeps the books
Who audits the books –Audit must be presented at AGM
What about contracts of the Society?
Management & Finances
What are the borrowing powers of the Society?
May not borrow without bylaws
This includes overdraft - so include some authority for the board to borrow small sums
Will board members be paid honorariums?
Be careful about paying members for additional services
What about indemnity & protection for directors & officers?
Not absolute protection
Should have adequate insurance protection too
CHANGES TO YOUR BYLAWS
May need to make fundamental changes to its structure or bylaws occasionally
The Societies Act has special requirements on bylaw changes:
Amending the bylaws
Changing the objects
Issuing debentures
Surrendering the Certificate of Incorporation
CHANGES TO YOUR BYLAWS
These changes must have the approval of the members
Must be a special resolution at a Special
General Meeting called for that purpose or an
Annual General Meeting.
Must be at least 21 days’ notice to all members.
At least 75% of the members who vote at the meeting must approve the change.
Your bylaws must state the procedure for amending the bylaws or the objects of the society.
WHAT IS INVOLVED?
Re-drafting bylaws can be a simple or timeconsuming procedure;
has it been done on a regular basis?
are there are issues that cause conflict or contention among members?
What is the availability of the writing team?
Changes require ratification by a majority vote of members, according to the quorum numbers identified in your filed bylaws
And provided that notice of any proposed changes was forwarded to each member with the notice of meeting as specified in the filed bylaws.
HOW LONG WILL THIS TAKE?
Once drafted, the change procedure will take twenty-one days or more. Additional fees may be required.
Bylaws must be dated and signed by the same 5 people who signed the application (if they are the original version), or by the people who are listed on the records as the duly elected directors.
Signatures must be witnessed (signature and address).
Bylaws, including amendments, do not come into effect until the Registrar has received them, reviewed them, approved them and stamped them “filed” and returned the stamped copy to the organization. This can take up to six weeks.
Resources on Bylaws
City of Calgary – Recreation Coordinators
Alberta Culture & Community Spirit,
Community Development, kim.rowe@gov.ab.ca
Board Development Program, http://culture.alberta.ca/bdp/default.aspx
Drafting & Revising Bylaws – PDF workbook http://culture.alberta.ca/bdp/workbooks/
Drafting_%20Revising09.pdf
Resources on Governance
City of Calgary – Recreation Coordinators
Alberta Culture & Community Spirit,
Community Development http://culture.alberta.ca/communitydevelopment/default.aspx
CentrePoint for Non-Profit Management http://www.thecentrepoint.ca/today/index.html
Other Resources
How to Incorporate a Not-For-Profit Society (Alberta)
How to Register a Charitable Organization (Alberta) http://www.servicealberta.ca/900.cfm
http://www.servicealberta.ca/661.cfm
How to Register a Charity (Government of Canada - Canada Revenue Agency) http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/tx/chrts/menu-eng.html
Registering A Charity for Income Tax Purposes (Handbook) 1-800-267-2384 for toll-free calls (English); http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/E/pub/tg/t4063/t4063-e.html
Societies Act http://www.qp.gov.ab.ca/documents/acts/S14.CFM
Societies Regulation http://www.qp.gov.ab.ca/documents/regs/2000_122.cfm
Keeping Records (Canada Revenue Agency) http://www.cra-arc.gc.ca/E/pub/tg/rc4409/rc4409-e.html
Board Development Information Bulletins http://culture.alberta.ca/bdp/bulletins.aspx
Voluntary Sector Publications (Insurance etc.) http://www.culture.alberta.ca/voluntarysector/publications.aspx
Service Alberta – Corporate Registries http://www.servicealberta.ca/Corporate_Registries.cfm
Corporate Link is Corporate Registry's automated telephone information service. The link provides information via Corporate Link Codes on Alberta and extra-provincially registered corporations, trade names, partnerships, limited partnerships, and non-profit organizations. Telephone number:
780-427-2311 Edmonton, Alberta, Canada (AB RITE line 310-0000)
Resource Centre for Voluntary Organizations http://www.rcvo.org/